Abstract
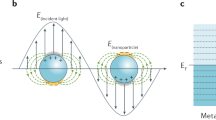
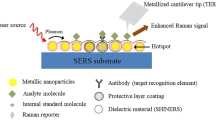
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (RS) spectroscopy is a sensitive analytical method that makes it possible to detect individual molecules. The substantial enhancement of the intensity of the signals in this method when compared to traditional Raman scattering is associated with two mechanisms, namely, electromagnetic and chemical. The first mechanism is associated with the enhancement of both the impinging and scattered radiation (electromagnetic enhancement), while the second mechanism is explained by the electron interaction between the molecule being analyzed and metal nanoparticles, namely, by the change in the polarizability of the adsorbed molecule, which results in the displacement and broadening of the electron levels of the adsorbed molecule or in the occurrence of new levels and promotes the enhancement of the signal in the Raman scattering spectrum. Graphene and material associated with it such as graphene oxide, graphite oxide, and reduced forms of graphene and graphite oxides are advanced materials for the creation of a significant chemical enhancement. Taking into account the different nature of the enhancement of the signal from the nanoparticles of noble metals and graphene and its derivatives, it is reasonable to study the effectiveness of hybrid structures on the basis of derivatives of graphene and noble metal nanoparticles in the Raman scattering spectroscopy of the analyte molecules with an aromatic structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Moskovits, “Persistent misconceptions regarding SERS,” Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., No. 15, 5301–5311 (2013).
X. Ling, L. M. Xie, Y. Fang, H. Xu, H. L. Zhang, J. Kong, M. S. Dresselhaus, J. Zhang, and Z. F. Liu, “Can graphene be used as a substrate for Raman enhancement?,” Nano Lett., No. 10, 553–561 (2010).
M. E. Kompan, F. M. Kompan, P. V. Gladkikh, E. I. Terukov, V. G. Rupyshev, and Yu. V. Chetaev, “Thermal conductivity of a composite medium with a disperse graphene filler,” Tech. Phys. 56(8), 1074 (2011).
Liang Zhou, Huaimin Gu, Can Wang, Juling Zhang, Meng Lv, and Ruoyu He, “Study on the synthesis and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy of grapheme-based nanocomposites decorated with noble metal nanoparticles,” Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, No. 430, 103–109 (2013).
W. S. Hummers and R. E. Offeman, “Preparation of graphitic oxide,” J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80(6), 1339–1339 (1958).
J. Turkevich, P. C. Stevenson, and J. Hillier, “The formation of colloidal gold,” J. Phys. Chem., No. 57, 670–673 (1953).
J. A. Peck, C. D. Tait, B. I. Swanson, and G. E. Brown, “Speciation of aqueous gold(III) chlorides from ultraviolet/visible absorption and Raman/resonance Raman spectroscopies,” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 55, 671–676 (1991).
F. Tuinstra and J. L. Koenig, “Raman spectrum in graphite,” J. Chem. Phys. 53, 1126–1130 (1970).
D. R. Dreyer, P. Sungjin, C. W. Bielawski, and R. S. Ruoff, “The chemistry of graphene oxide,” Chem. Soc. Rev., No. 39, 228–240 (2010).
Shengtong Sun and Peiyi Wu, “Competitive surfaceenhanced Raman scattering effects in noble metal nanoparticle-decorated graphene sheets,” Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 21116–21120 (2011).
A. N. Sidorov, G. W. Sławin’ski, A. H. Jayatissa, F. P. Zamborini, and G. U. Sumanasekera, “A surfaceenhanced Raman spectroscopy study of thin graphene sheets functionalized with gold and silver nanostructures by seed-mediated growth,” Carbon, No. 50, 699–705 (2012).
Xing Ma, Qiuyu Qu, Yun Zhao, Zhong Luo, Yang Zhao, Kee Woei Ng and Anli Zhao, “Graphene oxide wrapped gold nanoparticles for intracellular Raman imaging and drug delivery,” J. Mater. Chem. B, No. 1, 6495–6500 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.A. Eremina, E.E. Ondar, A.V. Sidorov, A.V. Grigor’eva, E.A. Gudilin, 2015, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2015, Vol. 10, Nos. 5–6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eremina, E.A., Ondar, E.E., Sidorov, A.V. et al. Reduced graphite oxide decorated with gold nanoparticles for Raman scattering spectroscopy. Nanotechnol Russia 10, 370–379 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078015030052
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078015030052