Abstract
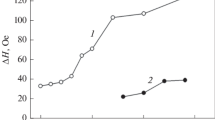
The magnetic behavior of Mo/Fe/Co three-component superlattices with varied thickness of Co layer was investigated. [Mo(12 Å)Fe(10 Å)Co(x Å)] × 100 (x = 4–25) magnetic superlattices have been obtained by cathode sputtering from two opposing cathodes in a high voltage (HV) discharge with oscillating electrons on substrates of mica (muscovite). The basic magnetic properties were measured along and across the planes of the samples. There are such oscillatory characteristics of the basic magnetic parameters as spontaneous magnetization, remanent magnetization, and coercivity field on the Co thickness with a period of ∼7 Å. This could be due to interference effects in electron waves leading to the formation of quantum wells in the interfaces. Some samples Mo/Fe/Co have drag and a stepped shape of hysteresis loops, which is related to the existence of the vortex-type magnetic structure and the dynamics of their behavior in magnetic field. This is evidenced by atomic force microscope studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. D. Antipov, G. E. Goryunov, A. P. Krasheninnikov, V. A. Senina, G. V. Smirnitskaya, and P. N. Stetsenko, “Specific Features of Magnetic Properties of Three-Component Magnetic Superlattices Based on Fe/Co/Mo,” Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci.: Phys. 71(11), 1613 (2007).
S. D. Antipov, G. E. Gorjunov, S. A. Granovsky, E. A. Konstantinova, G. V. Smirnitskaya, V. A. Senina, and P. N. Stetsenko, “Magnetic States of Fe Ions in Fe/Co/Mo Superlattices,” Solid State Phenom. 152–153, 265–268 (2009).
F. Aguilera-Granja, A. Vega, and L. J. Gallego, “A Density-Functional Study of the Structures, Binding Energies, and Magnetic Moments of the Clusters MoN (N = 2–13), Mo12Fe, Mo12Co, and Mo12Ni,” Nanotechnology 19, 145704 (2008).
J. Jorritsma and J. A. Mydosh, “Temperature-Dependent Magnetic Anisotropy in Ni Nanowires,” J. Appl. Phys. 84(2), 901 (1998).
K. Nakamura, T. Ito, and A. J. Freeman, “Curling Spin Density and Orbital Structures in a Magnetic Vortex Core of an Fe Quantum Dot,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 68, 180404(R) (2003).
A. Fernandez and C. J. Cerjan, “Nucleation and Annihilation of Magnetic Vortices in Submicron-Scale Co Dots,” J. Appl. Phys 87, 1396 (2000).
T. Pokhil, D. Song, and J. Novak, “Spin Vortex States and Hysteretic Properties of Submicron Size NiFe Elements,” J. Appl. Phys 87, 6319 (2000).
K. Yu. Guslienko, V. Novosad, Y. Otani, H. Shima, and K. Fukamichi, “Magnetization Reversal Due to Vortex Nucleation, Displacement, and Annihilation in Submicron Ferromagnetic Dot Arrays,” Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 65, 024414 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.D. Antipov, G.E. Goryunov, A.A. Ezhov, A.A. Kornilov, M.N. Pivkina, V.A. Senina, G.V. Smirnitskaya, P.N. Stetsenko, 2011, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2011, Vol. 6, Nos. 7–8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antipov, S.D., Goryunov, G.E., Ezhov, A.A. et al. Investigation of magnetic behavior in nanoscale superlattices Mo/Fe/Co. Nanotechnol Russia 6, 468 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078011040033
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078011040033