Abstract
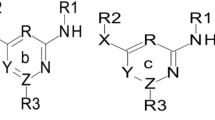
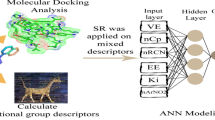
Multiple Linear Regression (MLR), artificial neural networks (ANN), simulated annealing algorithm (SA), genetic algorithm (GA) and imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) were employed to select the most appropriate descriptors. The obtained results from four combinations of modelling-optimization methods were compared. A high predictive ability was observed for the MLR–ICA model with the best number of empires/imperialists (nEmp = 30) with root-mean-sum-squared errors (RMSE) of 0.013941 in gas phase. In the Monte Carlo method, CORAL software was used and the correlation coefficient (R2), cross-validated correlation coefficient (Q2) and standard error of the model were calculated to be respectively 0.9827, 0.9761, 0.173 for the training set; and 0.9855, 0.9648 and 0.460 for the test set with an optimum threshold of 3. The best Doxazolidine derivative (according to –log IC50) was exposed to reaction with DNA at a 5'-NGC-3' using B3lyp/lanl2dz to investigate the stability of the formed complexes. It was concluded that the combination of different theoretical methods which was employed in this work, can be practically useful in designing new drugs by providing useful information on their physical and structural molecular properties, and understanding of the relation between physico-chemical, structural or theoretical molecular descriptors of drugs to their biological activities.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Di Marco, M. Gaetani, and B. Scarpinato, Cancer Chemother. Rep. 53, 33 (1969).
C. Young, R. F. Ozols, and C. E. Myers, N. Engl. J. Med. 305, 139 (1981).
G. C. Post, B. L. Barthel, D. J. Burkhart, J. R. Hagadorn, and T. H. Koch, J. Med. Chem. 48, 7648 (2005).
D. Fenick, D. J. Taatjes, and T. H. Koch, J. Med. Chem. 40, 2452 (1997).
P. Gramatica and E. Papa, Mol. Inform. 22, 374 (2003).
D. B. Horvath and B. Mao, QSAR Comb. Sci. 22, 498 (2003).
A. P. Toropova, A. A. Toropov, E. Benfenati, et al., J. Comput. Chem 32, 2727 (2011).
A. A. Toropov, A. P. Toropova, S. E. Martyanov, et al., Chemom. Intell. Lab. 109, 94 (2011).
E. Shokrollahpour, M. Zandieh, and B. Dorri, Int. J. Prod. Res. 49, 3087 (2011).
S. Hosseini and A. Al Khaled, Appl. Soft. Comput. 24, 1078 (2017).
S. J. MousaviRad, T. F. Akhlaghian, and K. Mollazade, Int. J. Comput. Appl. 40, 41 (2012).
E. Tanış, N. Çankaya, and S. Yalçın, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 13, 49 (2019).
K. Levenberg, Quart. Appl. Math. 2, 164 (1944).
S. H. Sadat Hayatshahi, P. Abdolmaleki, M. Ghiasi, and S. Safarian, FEBS Lett. 581, 506 (2007).
R. Sayyadi kord Abadi, A. Alizadehdakhel, and S. Dorani Shiraz, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 11, 307 (2017).
M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, M. Caricato, X. Li, H. P. Hratchian, A. F. Izmaylov, et al., Gaussian 09 (Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009). https://gaussian.com/glossary/g09/.
SPSS, Version 19. http://www.spssscience.com. Accessed 2010.
O. G. Maksimova and A. V. Maksimov, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 11, 15 (2017).
Yu. M. Sivergin, S. M. Kireeva, and S. M. Usmanov, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 9, 952 (2015).
S. Putta, J. Eksterowicz, C. Lemmen, and R. Stanton, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 43, 1623 (2003).
E. Atashpaz-Gargari and C. Lucas, in Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng., Singapore, 2007), p. 4661. https://homepages.ecs.vuw.ac.nz/~yimei/resources/ICA_Atashpaz.pdf.
E. A. Gargari, F. Hashemzadeh, R. Rajabioun, and C. Lucas, Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 1, 337 (2008).
J.-L. Lin, Yu-H. Tsai, C.-Y. Yu, and M.-S. Li, Algorithms 5, 433 (2012).
A. M. Veselinović, J. B. Milosavljević, A. A. Toropov, and G. M. Nikolić, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 48, 532 (2013).
J. Veselinović, A. Veselinović, A. Toropov, A. Toropova, I. Damnjanović, and G. Nikolić, Sci. J. Faculty Med. Niš 31, 95 (2014).
R. Todeschini and V. Consonni, Hand Book of Molecular Descriptors (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2008).
J. H. Schurz, P. Selzer, and J. Gasteiger, J. Chem. Inform. Comput. Sci. 36, 334 (1996).
R. Sayyadikord Abadi, A. Alizadehdakhel, and S. Tajadodi Paskiabei, J. Korean Chem. Soc. 60, 225 (2016).
R. Sayyadikord Abadi and A. Alizadehdakhel, Rev. Roum. Chim. 63, 171 (2018).
R. Sayyadikord Abadi, A. Alizadehdakhel, and S. Dorani Shiraz, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 11, 307 (2017).
A. Golbraikh and A. Tropsha, J. Mol. Graph. Model. 20, 269 (2002).
A. Kumar and S. Chauhan, SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 28, 179 (2017).
A.H.-J. Wang, Y. G. Gao, Y. C. Liaw, and Y. K. Li, Biochemistry 30, 3812 (1991).
H. Zhang, Y. G. Gao, G. A. van der Marel, J. H. van Boom, and A. H. Wang, J. Biol. Chem. 268, 10095 (1993).
B. T. Kalet, M. B. McBryde, J. M. Espinosa, and T. H. Koch, J. Med. Chem. 50, 4493 (2007).
5. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support provided by the Islamic Azad University of Rasht.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maria Nikkar, Robabeh SayyadikordAbadi, Alizadehdakhel, A. et al. Monte Carlo Method and a Novel Modelling-Optimization Approach on QSAR Study of Doxazolidine Drugs and DNA-Binding. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 15 (Suppl 1), S32–S41 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S199079312109013X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S199079312109013X