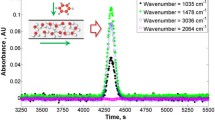
Abstract—The three most common methods for measuring chromatographic dead time in supercritical fluid chromatography are tested. It is shown that at low concentrations of a polar cosolvent in the mobile phase, the use of the simplest “system peak” method leads to highly inaccurate results. With an increase in the percentage of the cosolvent to 10–15%, this method can be used for a rough estimation of dead times, especially for nonpolar stationary phases. The use of nitrogen(I) oxide as a marker of the dead time of an unretained component, on the contrary, is well suited in the case of using pure carbon dioxide as a mobile phase. The static method, based on other principles, can theoretically yield very accurate values for dead time, but it requires knowledge of the velocity profile of the mobile phase along the path of the entire chromatography.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Lesellier and S. West, J. Chromatogr., A 1382, 2 (2015).
G. Guiochon and A. Tarafder, J. Chromatogr., A 1218, 1037 (2011).
A. Rajendran, J. Chromatogr., A 1250, 227 (2012).
T. L. Chester, J. Chromatogr., A 1037, 393 (2004).
T. L. Chester, in Supercritical Fluid Chromatography, Ed. by C. Poole (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2017).
S. H. Page, S. R. Sumtper, and M. L. Lee, J. Microcol. Sep. 4, 91 (1992).
M. Roth, J. Microcol. Sep. 3, 173 (1991).
M. Roth, J. Chromatogr., A 1037, 369 (2004).
K. D. Bartle, A. A. Clifford, S. A. Jafar, J. P. Kithinji, and G. F. Shilstone, J. Chromatogr. 517, 459 (1990).
C. A. Rimmer, C. R. Simmons, and J. G. Dorsey, J. Chromatogr., A 965, 219 (2002).
http://www.chromatographyonline.com/column-dead-time-diagnostic-tool.
P. Vajda and G. Guiochon, J. Chromatogr., A 1309, 96 (2013).
F. Gritti, Y. Kzakevich, and G. Guiochon, J. Chromatogr., A 1161, 157 (2007).
J. F. Parcher and M. I. Selim, Anal. Chem. 51, 2154 (1979).
T. Nakahara, P. S. Chappelear, and R. Kobayashi, Ind. Eng Chem. Fundam. 16, 220 (1977).
E. W. Lemmon, M. O. McLinden, and D. G. Friend, Thermophysical Properties of Fluid Systems, NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database No. 69, Ed. by P. J. Linstrom and W. G. Mallard (Natl. Inst. Standards Technol., Gaithersburg MD, USA, 2005).
H. G. Janssen, H. M. J. Snijders, J. A. Rijks, and C. A. Cramers, J. High Res. Chromatogr. 14, 438 (1991).
F. Gritti, M. Martin, and G. Guiochon, J. Chromatogr., A 1070, 13 (2005).
Funding
The study was carried out as part of the state assignment no. 0088-2014-0003 of the Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, subject no. 45.3 in the field of basic scientific research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by O. Zhukova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostenko, M.O., Pokrovskiy, O.I., Parenago, O.O. et al. Comparison of Methods for Determining Dead Times in Supercritical Fluid Chromatography. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 13, 1111–1116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990793119070145
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990793119070145