Abstract
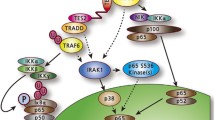
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) encoded by the LMP1 gene is a transmembrane protein, which can activate a number of cellular signal cascades and transcriptional factors leading to cell transformation. In the present study the sequencing of full-length LMP1 variants isolated from Russian patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL), non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHL) and infectious mononucleosis (IM) has been carried out. The phylogenetic analysis of the obtained sequences revealed dominance of the LMP1 variants belonging to proteins of the low-divergent group LMP1-B95.8b characterized by minimal set of mutations. Investigation of biological properties in the Russian representatives of this group revealed that expression of the studied LMP1 variants in embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells was accompanied by an insignificant increase in activation of the transcriptional factor NF-κB and had minor influence on activation of the transcriptional factor AP-1. It was also detected that all investigated low-divergent LMP1 variants expressed in Rat-1 cells caused activation of inducible NO-synthase (iNOS) and intracellular production of nitric oxide (NO). At the same time the level of NO accumulation was lower than that induced by the low-transforming prototype variant LMP1-B95.8. The data obtained indicate that the LMP1 variants, which are the most common among Russian patients with EBV-associated lymphoproliferative diseases, are characterized by minimum number of mutations and rather low ability to activate basic cellular signaling pathways regardless the nature of pathological process, benign (IM) or malignant (HL, NHL). It is suggested that in addition to the modest activation of NF-κB and iNOS induction by LMP1 other factors are involved in the cell transformation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTAR1:
-
C-terminal activating region 1
- CTAR2:
-
C-terminal activating region 2
- Dex:
-
dexamethasone
- EBV:
-
Epstein-Barr Virus
- HL:
-
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- IM:
-
infectious mononucleosis
- iNOS:
-
inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
- LMP1:
-
latent membrane protein 1
- NHL:
-
non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
References
Kaye, K.M., Izumi, K.M., and Kieff, E., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1993, vol. 90, pp. 9150–9154.
Moorthy, R.K. and Thorley-Lawson, D.A., J. Virol., 1993, vol. 67, pp. 1638–1646.
Kulwichitm, W., Edwards, R.H., Davenport, E.M., Baskar, J.F., Godfrey, V., and Raab-Traub, N., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, vol. 95, pp. 11963–11968.
Fennewald, S., van Santen, V., and Kieff, E., J. Virol., 1984, vol. 51, pp. 411–419.
Cahir-McFarland, E.D., Izumi, K.M., and Mosialos, G., Oncogene, 1999, vol. 18, pp. 6959–6964.
Wu, L., Nakano, H., and Wu, Z., J. Biol. Chem., 2006, vol. 281, pp. 2162–2169.
Eliopoulos, A.G. and Young, L.S., Oncogene, 1998, vol. 16, pp. 1731–1742.
Eliopoulos, A.G., Blake, S.M., Floettmann, J.E., Rowe, M., and Young, L.S., J. Virol., 1999, vol. 73, pp. 1023–1025.
Lam, N. and Sagden, B., Cell Signal., 2003, vol. 15, pp. 9–16.
Dawson, C.W., Tramountanis, G., Eliopoulos, A.G., and Young, L.S., J. Biol.Chem., 2003, vol. 278, pp. 3694–3704.
Coffin, W.F., Erickson, K.D., Hoedt-Miller, M., and Martin, J.M., Oncogene, 2001, vol. 20, pp. 5313–5330.
Walling, D.M., Shebib, N., Weaver, S.C., Nichols, C.M., Flaitz, C.M., and Webster-Cyriaque, J., J. Infect. Dis., 1999, vol. 179, pp. 763–764.
Hu, L.F., Zabarovsky, E.R., Chen, F., Cao, S.L., Emberg, I., Klein, G., and Winberg, G., J. Gen. Virol., 1991, vol. 72, pp. 2399–2409.
Edwards, R.H., Seiller-Moiseiwitsch, F., and Raab-Traub, N., Virology, 1999, vol. 261, pp. 79–95.
Nitta, T., Chiba, A., Yamamoto, N., and Yamaoka, S., Cell. Signal., 2004, vol. 16, pp. 1071–1081.
Pavlish, O.A., Diduk, S.V., Smirnova, K.V., Scherbak, L.N., Goncharova, E.V., Shalginskikh, N.A., Arkhipov, V.V., Kichigina, M.Yu., Stepina, V.N., Belousova, N.V., Osmanov, E.A., Yakovleva, L.S., and Gurtsevitch, V.E., Vopr. Virusol., 2008, vol. 53, pp. 10–16.
Sandvej, K., Peh, S.C., Andresen, B.S., and Pallesen, G., Blood, 1994, vol. 84, pp. 4053–4060.
Nathan, C., FASEB. J., 1992, vol. 6, pp. 3051–3064.
Moncada, S., Palmer, R.M., and Higgs, E.A., Pharmacol. Rev., 1991, vol. 43, pp. 109–142.
Yu, J.S., Tsai, H.S., Wu, C.C., Weng, L.P., Li, H.P., Chung, P.J., and Chang, Y.S., Oncogene, 2002, vol. 21, pp. 8047–8061.
Edwards, R.H., Seiller-Moiseiwitsch, F., and Raab-Traub, N., Virology, 1999, vol. 261, pp. 79–95.
Sandvej, K., Gratama, J.W., Munch, M., Zhou, X.G., Bolhuis, R.L., Andresen, B.S., Gredersen, N., and Hamilton-Dutoit, S., Blood, 1997, vol. 90, pp. 323–330.
Edwards, R.H., Sitki-Green, D., Moore, D.T., and Raab-Traub, N., J. Virol., 2004, vol. 78, pp. 868–881.
Thomson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G., Nucl. Acid. Res., 1997, vol. 24, pp. 4876–4882.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M., Mol. Biol. Evol., 1987, vol. 4, pp. 406–425.
Van de Peer, Y. and de Wachter, R., Comput. Applic. Biosci., 1994, vol. 10, pp. 569–570.
Felsenstein, J., Evolution, 1985, vol. 39, pp. 783–791.
Bradford, M.M., Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Tang, W., Pavlish, O.A., Spiegelman, V.S., Parkhitko, A.A., and Fuchs, S.Y., J. Biol. Chem., 2003, vol. 278, pp. 48942–48949.
Fielding, C.A., Sandvej, K., Mehl, A., Brennan, P., Jones, M., and Rowe, M., (2001) J. Virol., 2001, vol. 75, pp. 9129–9141.
Diduk, S.V., Smirnova, K.V., Pavlish, O.A., and Gurtsevitch, V.E., Biochemistry (Moscow), 2008, vol. 73, pp. 1414–1421.
Ma, N., Kawanishi, M., Hiraku, Y., Murata, M., Huang, G.W., Huang, Y., Luo, D.Z., Mo, W.G., Fukui, Y., and Kawanishi, S., Int. J. Cancer, 2008, vol. 122, pp. 2517–2525.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.V. Smirnova, S.V. Diduk, V.E. Gurtsevitch, 2010, published in Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smirnova, K.V., Diduk, S.V. & Gurtsevitch, V.E. The functional analysis of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane proteins (LMP1) in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. B 4, 386–394 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990750810040116
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990750810040116