Abstract
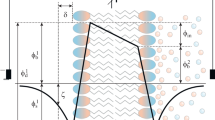
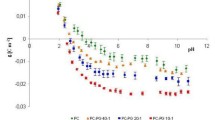
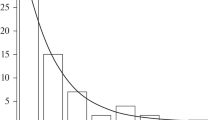
The kinetics of binding of proton with bilayer lipid membrane (BLM) upon their fast release on the surface of the membrane has been studied by measuring the changes of the capacitance and electrostatic potential of the membrane. The release of proton was a result of excitation of 2-methoxy-5-nitrosulphate (MNPS) molecules, adsorbed on the surface of the membrane, by UV light. The adsorption of anions of MNPS on BLM led to a change of the boundary potential measured either by the inner field compensation method or as a change of ζ-potential of liposomes determined by the dynamic light scattering method. The illumination of BLM with the adsorbed MNPS molecules led to changes of the membrane capacitance and a shift of the boundary potential to positive values. This shift of the boundary potential was due partially to the MNPS decomposition and partially to the binding of protons on the membrane surface. With an increase in the buffer capacity, both the potential jump and the change in capacitance were significantly reduced in magnitude. Restoration of the membrane capacitance and boundary potential after the light flash took about tens of seconds. The changes of the potential and capacitance were observed not only on BLM formed from phospholipids but also on BLM formed from glycerol monooleate. These results are explained assuming that the protons released from MNPS during the flash of light are bound on the surface of the membrane in a layer of oriented water molecules.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cherepanov D.A., Feniouk B.A., Junge W., Mulkidjanian A.Y. 2003. Low dielectric permittivity of water at the membrane interface: Effect on the energy coupling mechanism in biological membranes. Biophys. J. 85 (2), 1307–1316.
Georgievskii Yu., Medvedev E.S., Stuchebrukhov A.A. 2002. Proton transport via the membrane surface. Biophys. J. 82, 2833–2846.
Agmon N., Bakker H.J., Campen R.K., Henchman R.H., Pohl P., Roke S., Thamer M., Hassanali A. 2016. Protons and hydroxide ions in aqueous systems. Chem. Rev. 116 (13), 7642–7672.
Zhang C., Knyazev D.G., Vereshaga Y.A., Ippoliti E., Nguyen T.H., Carloni P., Pohl P. 2012. Water at hydrophobic interfaces delays proton surface-to-bulk transfer and provides a pathway for lateral proton diffusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109 (25), 9744–9749.
Ferguson S.J. 1985. Fully delocalised chemiosmotic or Iocalised proton flow pathways in energy coupling? A scrutiny of experimental evidence. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 811, 47–95.
Serowy S., Saparov S.M., Antonenko Y.N., Kozlovsky W., Hagen V., Pohl P. 2003. Structural proton diffusion along lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 84 (2 Pt 1), 1031–1037.
Springer A., Hagen V., Cherepanov D.A., Antonenko Y.N., Pohl P. 2011. Protons migrate along interfacial water without significant contributions from jumps between ionizable groups on the membrane surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 108 (35), 14461–14466.
Weichselbaum E., Osterbauer M., Knyazev D.G., Batishchev O.V., Akimov S.A., Hai N.T., Zhang C., Knor G., Agmon N., Carloni P., Pohl P. 2017. Origin of proton affinity to membrane/water interfaces. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 4553.
Kaplan J.H., Forbush I.B., Hoffman J.F. 1978. Rapid photolytic release of adenosine 5'-triphosphate from a protected analogue: Utilization by the Na : K pump of hunab red blood cell ghosts. Biochemistry. 17, 1929–1935.
Apell H.J., Sokolov V.S. 2015. Pumps, Channels and Transporters: Methods of Functional Analysis. Eds Clarke R.J., Khalid M.A.A. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley, p. 23–49.
Geissler D., Antonenko Y.N., Schmidt R., Keller S., Krylova O.O., Wiesner B., Bendig J., Pohl P., Hagen V. 2005. (Coumarin-4-yl)methyl esters as highly efficient, ultrafast phototriggers for protons and their application to acidifying membrane surfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 44 (8), 1195–1198.
Fibich A., Janko K., Apell H.J. 2007. Kinetics of proton binding to the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase in the E1 state. Biophys J. 93 (9), 3092–3104.
Vishnyakova V.E., Tashkin V.Yu., Terent’ev A.O., Apell H.J., Sokolov V.S. 2018. Binding of potassium ions in the access channel from the cytoplasmic side of Na+,K+-ATRase. Biol. Membrany (Rus.). 35 (5), 376–383
Tashkin V.S., Sherbakov A.A., Apell H.J., Sokolov V.S. 2013. Competitive transport of sodium ions and protons in the cytoplasmic channel of Na+,K+-ATPase. Biol. Membrany (Rus.). 30 (2), 105–114.
Taskin V.Yu., Gavrilchik A.N., Ilovaiskaya I.A., Apell H.J., Sokolov V.S. 2015. Electrogenic binding of ions from the cytoplasmic side of Na+,K+-ATPase. Biol. Membrany (Rus.). 32 (2), 110–118.
Sokolov V.S., Kuzmin V.G. 1980. Measurement of the difference between the surface potentials of bilayer membranes by the second harmonic of the capacitive current. Biofizika (Rus.). 25 (1), 170–172.
Ermakov Yu.A., Sokolov V.S. 2003. Planar lipid bilayers (BLMs) and their applications. Eds Tien H.T., Ottova-Leitmannova A. Amsterdam etc.: Elsevier, p. 109–141.
Sokolov V.S., Mirsky V.M. 2004. Ultrathin electrochemical chemo- and biosensors: Technology and performance. Ed. Mirsky V.M. Heidelberg: Springer–Verlag, p. 255–291.
Sokolov V.S., Gavrilchik A.N., Kulagina A.O., Meshkov I.N., Pohl P., Gorbunova Y.G. 2016. Voltage-sensitive styryl dyes as singlet oxygen targets on the surface of bilayer lipid membrane. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 161, 162–169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by E. Puchkov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tashkin, V.Y., Vishnyakova, V.E., Shcherbakov, A.A. et al. Changes of the Capacitance and Boundary Potential of a Bilayer Lipid Membrane Associated with a Fast Release of Protons on Its Surface. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 13, 155–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747819020077
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747819020077