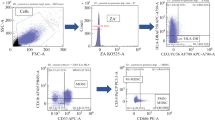
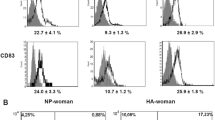
Abstract
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is analyzed here as an endogenous ligand for type 4 Toll-like proteins (TLR4). It is demonstrated that hCG actively binds to TLR4 molecules on monocyte surfaces. Using flow cytometry it was revealed that in the presence of high hCG concentrations (100 and 1000 IU/mL) the level of CD14+TLR4+-positive cells was reliably lowered in the gate of monocytes on 1, 5, and 10 min of experiment. Inhibition assay was used to study the role of TLR4 molecules in realization of hCG effects on monocyte functional activity. Monoclonal antibodies against TLR4 and/or resveratrol that blocks TRIF/TRAF6 intracellular proteins involved in signal transduction to IRF3 and NF-κB, respectively were applied to block TLR4-dependent signal transduction. In addition, protein kinase A (PKA) engaged in signal transduction from LH-receptor was suppressed. It was revealed that the inhibitory effect of hCG on monocyte phagocytic activity was TLR4-dependent, whereas its effects on myeloperoxidase (MPOex) secretion and spontaneous oxidative monocyte activity were PKA-dependent. It was found that hormone effects on stimulated oxidative activity of monocytes and their production of interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-8 depended both on TLR4 availability and PKA activity. Thus, a novel mechanism of hormone-monocyte interactions has been revealed that is mediated by TLR4 molecules that serve as non-canonical hormone receptors in monocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo H.F. 2002. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the hormone of life and death: A review. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2(3), 133–145.
Shirshev S.V., Zamorina S.A. 2006. Effect of chorionic gonadotropin on the activity of monocytes in relation to the phases of a menstrual cycle. Problemy endocrinol. (Rus.). 5, 31–34.
Kosaka K., Fujiwara H., Tatsumi K., Yoshioka S., Sato Y., Egawa H., Higuchi T., Nakayama T., Ueda M., Maeda M., Fujii S. 2002. Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) activates monocytes to produce interleukin-8 via a different pathway from luteinizing hormone/HCG receptor system. J. Clin. Endocrin. Metab. 1(87), 5199–5208.
Shirshev S.V. 2002. Mekhanizmy immunnorndokrinogo kontrolya protsessov reproduktsii (The mechanisms of immune and endocrine control of reproduction). Yekaterinburg, Ural. Otd. Ross. Acad. Nauk. Vol. 2.
Shirshev S.V., Zamorina S.A. 2006. Role of Toll-like proteins in the realization of effects of chorionic gonadotropin on the functional activity of monocytes. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 409, 241–243.
Rosemblit N., Ascoli M., Segaloff D.L. 1988. Characterization of an antiserum to the rat luteal luteinizing hormone/chorionic gonadotropin receptor. Endocrinology. 123(5), 2284–2290.
Tsan M.F., Gao B. 2004. Endogenous ligand of Tolllike receptor. Leukocyte Biology. 76(3), 514–519.
Lukić I.K., Jelusić-Drazić M., Kovacić N., Grcević D. 2009. Damage-associated molecular patterns — emerging targets for biologic therapy of childhood arthritides. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Target. 8(2), 139–145.
Kozlov I.G. 2011. Signal receptors of congenital immunity: A new molecular target for diagnostics and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk (Rus.). 1, 42–50.
Van den Berg J.W., Dik W.A, van der Zee M., Bonthuis F., van Holten-Neelen C., Dingjan G.M., Benner R., Ijzermans J.N., Khan N.A., de Bruin R.W. 2011. The β-human chorionic gonadotropin-related peptide LQGV reduces mortality and inflammation in a murine polymicrobial sepsis model. Crit. Care Med. 1(39), 126–134.
Dorfling P., Wischner S. 1987. Isolation of macrophages from splenocyte suspension. Immunologicheskie metody (Immunological methods). Ed. G. Frimel. Moscow, Medicine. p. 373–378.
Cole L.A. 2012. HCG, the wonder of today’s science. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 10(24)o. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-10-24.
Youn H.S., Lee J.Y., Fitzgerald K.A., Young H.A., Akira S., Hwang D.H. 2005. Specific inhibition of MyD88-independent signaling pathways of TLR3 and TLR4 by resveratrol: Molecular targets are TBK1 and RIP1 in TRIF complex. J. Immunol. 175(5), 3339–3346.
Jakus P.B., Kalman N., Antus C., Radnai B., Tucsek Z., Gallyas F. Jr., Sumegi B., Veres B. 2012. TRAF6 is functional in inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB activation by resveratrol. J. Nutr. Biochem. dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.04.017.
Parvathenani L.K., Buescher E.S., Chacon-Cruz E., Beebe S.J. 1998. Type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase delays apoptosis in human neutrophils at a site upstream of caspase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 273(12), 6736–6743.
Shirshev S.V., Kuklina E.M., Zamorina S.A., Nikitina N.M., Nekrasova I.V. 2007. Method for determining phagocytic activity of human peripheral blood neutrophils from bioluminescence extinction degree data. RF Patent 2292553, 27.01.2007.
Dahigren C. 1984. Myeloperoxidase modulates the phagocytic activity of polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes. Studies with cells from a myeloperoxidase deficient patient. J. Clin. Invest. 73, 366–373.
Kondratieva I.A., Yarilin A.A., Egorova S.G., Freze K.B., Vorobjeva N.V., Burakova O.V., Maluchenko N.V., Moisenovich M.M., Novikov K.N., Simonova A.V., Pinegin B.V., Kitashova A.A., Kitashov A.V., Zayakin N.A. 2004. Determination of myeloperoxidase activity in phagocytizing cells of human peripheral blood. In: Praktikum po immunologii (Immunology manual). 2nd Edition. Moscow, Academia. p. 193–195.
Shirshev S.V., Zamorina S.A. 2004. Role of CD14-associated molecules in immunomodulating activity of human chorionic gonadotropin. Dokl. RAN (Rus.). 395(2), 277–279.
Zamorina S., Shirshev S. 2009. Chorionic gonadotropin as endogenous ligand for Toll-like proteins. Eur. J. Immunol. 39(S1), 62.
McGettrick A.F., O’Neil L.A. 2010. Localisation and trafficking of Toll-like receptors: An important mode of regulation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 22(1), 20–27.
Simpson D.Z., Hitchen P.G., Elmhirst E.L., Taylor M.E. 1999. Multiple interactions between pituitary hormones and the mannose receptor. Biochem. J. 343(2), 403–411.
Shumacher A., Brachwitz N., Sohr S., Engeland K., Langwisch S., Dolaptchieva M., Alexander T., Taran A., Malfertheiner S.F., Costa S.D., Zimmermann G., Nitschke C., Volk H.D., Alexander H., Gunzer M., Zenclussen A.C. 2009. Human chorionic gonadotropin attracts regulatory T cells into the fetalmaternal interface during early human pregnancy. J. Immunol. 78(9), 5488–5497.
Kane N., Kelly R., Saunders P., Critchley H. 2009. Proliferation of uterine natural killer cells is induced by hCG and mediated via the mannose receptor. Endocrinology. 150(6), 2882–2888.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.A. Zamorina, S.V. Shirshev, 2013, published in Biologicheskie Membrany, 2013, Vol. 30, No. 5–6, pp. 372–379.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamorina, S.A., Shirshev, S.V. Role of toll-like receptors in realization of human chorionic gonadotropin effects on monocyte functional activity. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 8, 37–43 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747813050243
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747813050243