Abstract
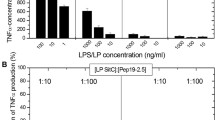
The outcome of pathological process during sepsis caused by Gram-negative bacteria depends on the reaction of human blood cells to bacterial structural components, lipopolysaccharides (LPS). A general inflammatory response develops due to the increased production of proinflammatory cytokines. One of the current methods of prevention of inflammatory response is the inhibition of LPS binding to cellular receptors. We have studied the efficacy of antagonistic properties of LPS from Rhodobacter capsulatus on the production of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β cytokines induced by toxic LPS from Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli in human whole blood. LPS from R. capsulatus in concentrations of 0.1 and 1 μg/mL did not induce synthesis of TNF-α, IL-6, or IL-1β. Measurements of cytokine levels showed that LPS from R. capsulatus exerted a clear protective effect against toxic LPS. In particular, LPS from R. capsulatus fullly inhibited the production of TNF-α and IL-1β and significantly decreased the IL-6 production induced by LPS from S. typhimurium. Additionally, LPS from R. capsulatus antagonized the effects of LPS from E. coli, fully inhibiting the TNF-α production and decreasing the IL-6 and IL-1β levels by 60% and 70%, respectively. Thus, LPS from R. capsulatus acts as a potent antagonist of cell activation induced by toxic LPS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prokhorenko I.P., Zolotushchenko E.V., Tarasevich N.V., Avkhacheva N.V., Safronova V.G., Grachev S.V. 2007. Respiratory burst activated by Escherichia coli in human neutrophils primed with different lipopolysaccharides. Biol. membrany (Rus.). 24 (6), 442–450.
Vinokurov M.G., Yurinskaya M.M., Prokhorenko I.P., Grachev S.V. 2006. Lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter capsulatus neutralizes endotoxin-induced responses of human peripheral blood neutrophils and monocytes. Molek. Meditsina (Rus.). 4, 56–62.
Prokhorenko I.P., Kustanova G.A., Grazhdankin E.B., Kabanov D.S., Murashev A.N., Prokhorenko S.V., Grachev S.V. 2005. Effects of lipopolysaccharides having different structures on cardiovascular system of Wistar rats. DAN (Rus.). 402 (6), 838–840.
Andra J., Gutsmann T., Muller M., Aschromm A.B. 2009. Interactions between lipid A and serum proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 667, 39–51.
Makhneva Z.K., Vishevetskaya T.A., Prokhorenko I.P. 1996. Effect of isolation procedures on the yield and composition of the lipopolysaccharides from photosynthetic bacteria. Prikladnaya biokhimia i mikrobiologia (Rus.). 32, 444–447.
Schromm A.B., Brandenburg K., Rietschell E.T. 2000. Biological activities of lipopolysaccharides are determined by the shape of their lipid A portion. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 2008–2013.
Beutler B., Jiang Z.F., Georgel P., Crozat K., Croker B., Rutschmann S., Du X., Hoebe K. 2006. Genetic analysis of host resistance: Toll-like receptor signalling and immunity at large. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 24, 353–389.
Saitoh S., Akashi S., Yamada T., Tanimura N., Kobayashi M., Konno K., Matsumoto F., Fukase K., Kusumoto S., Nagai Y., Kusumoto Y., Kosugi A., Miyake K. 2004. Lipid A antagonist, lipid IVa, is distinct from lipid A in interaction with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-MD-2 and ligand-induced TLR4 oligomerization. Int. Immunol. 16, 961–969.
Bradley J.R. 2008. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 214, 149–160.
Mark K.S., Trickler W.J., Miller D.W. 2001. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin release in brain microvessel endothelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 297 (3), 1051–1058.
Chia S., Qadan M., Newton R., Ludlam C.A., Fox K.A.A., Newby D.E. 2013. Intra-arterial tumor necrosis factoralpha impairs endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and stimulates local tissue plasminogen activator release in humans. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 695–701.
Ben-Sasson, S.Z., Hu-Li J., Quiea J., Cauchetaux S., Ratner M., Shapira I., Dinarello C.A., Paula W.E. 2009. IL-1 acts directly on CD4 T cells to enhance their antigen-driven expansion and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106 (17), 7119–7124.
Mera S., Tatulescu D., Cismaru C., Slavcovici A., Zanc V., Flonta M., Carstina D. 2009. Serum profile of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-12 and IFN-Γ in early sepsis. Therapeutics, Pharmacol. Clin. Toxicol. 13 (1), 81–85.
Rieckmann P., Tuscano J.M., Kehrl J.H. 1997. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in B-lymphocyte function. Methods. 11 (1), 128–132.
Kishimoto T. 2010. IL-6: From its discovery to clinical applications. Internat. Immunol. 22 (5), 347–352.
Caroff, M., Karibian D., Cavaillon J.-M., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. 2002. Structural and functional analyses of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Microb. Infect. 4 (9), 915–926.
Gangloff S.C., Hijiya N., Haziot A., Goyert S.M. 1999. Lipopolysccharide structure influences the macrophage response via CD14-independent and CD14-dependent pathways. Clin. Infect. Dis. 28, 491–496.
Oshiumi H., Sasai M., Shida K., Fujita T., Matsumoto M., Seya T. 2003. TIR-containing adapter molecule (TICAM)-2, a bringing adapter recruiting to Toll-like receptor 4 TICAM-1 that induces interferon-β. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 49751–49762.
Grachev S.V., Prokhorenko I.R., Zubova S.V., Kabanov D.S., Kosiakova N.I., Prokhorenko S.V., Mel’tser M. 2012. Molekuliarnye mekhanizmy vzaimodeistviya endotoksinov s kletkami-misheniami (Molecular mechanisms of interactions of endotoxins with target cells). M.: Med. Inform. Agenstvo.
Morrison D.C., Betz S.J., Jacobs D.M. 1976. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for LPS-initiated mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J. Exp. Med. 144, 840–846.
Manthey C.L., Vogel S.N. 1994. Elimination of trace endotoxin protein from rough chemotype LPS. J. Endotoxin. Res. 1, 84–91.
Tapping R.I., Akashi S., Miyake K., Godowski P.J., Tobias P.S. 2000. Toll-like receptor 4, but not toll-like receptor 2, is a signalling receptor for Escherichia and Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. J. Immunol. 165, 5780–5787.
Loppnow H., Libby P., Freudenberg M., Krauss J.H., Weckesser J., Mayer H. 1990. Cytokine induction by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) corresponds to lethal toxicity and is inhibited by nontoxic Rhodobacter capsulatus LPS. Infect. Immun. 58 (11), 3743–3750.
Seydel U., Oikawa M., Fukase K., Kusumoto S., Brandenburg K. 2000. Intrinsic conformation of lipid A is responsible for agonistic and antagonistic activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 3032–3039.
Golenbock D.T., Hampton R.Y., Qureshi N., Takayama K., Raetz C.R.H. 1991. Lipid A-like molecules that antagonize the effects of endotoxins on human monocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 266 (29), 19490–19498.
Brandenburg K., Lindner B., Schromm A.B., Koch M.H.J., Bauer J., Merkli A., Zbaeren C., Davies J.G., Seydel U. 2000. Physicochemical characteristics of triacyl lipid A partial structure OM-174 in relation to biological activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 3370–3377.
Kirkland T.N., Finley F., Leturcq D., Moriarty A., Lee J.D., Ulevitch R.J., Tobias P.S. 1993. Analysis of lipopolysaccharide binding by CD14. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 24818–24823.
Thomasa C.J., Kapoora M., Sharmaa S., Bausingerb H., Zyilanb U., Lipskerb D., Hanaub D., Suroliaa A. 2002. Evidence of a trimolecular complex involving LPS, LPS binding protein and soluble CD14 as an elector of LPS response. FEBS Lett. 531, 184–188.
Viriyakosol S., Mathison J.C., Tobias P.S., Kirkland T.N. 2000. Structure-function analysis of CD14 as a soluble receptor for lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3144–3149.
Thomas C.J., Kapoor M., Sharma S., Bausinger H., Zyilan U., Lipsker D., Hanau D., Surolia A. 2002. Evidence of a trimolecular complex involving LPS, LPS binding protein and soluble CD14 as an effector of LPS response. FEBS Lett. 531, 184–188.
Shin J.H., Lee H., Park J.D., Hyun H.C., Sohn H.O., Lee D.W., Kim Y.S. 2007. Kinetics of binding of LPS to recombinant CD14, TLR4, and MD-2 proteins. Mol. Cells. 24 (1), 119–124.
Viriyakosol S., Tobias P.S., Kitchens R.L., Kirkland T.N. 2001. MD-2 binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 38044–38051.
Shimazu R., Akashi, S., Ogata, H., Nagai, Y., Fukudome, K., Miyake, K., Kimoto, M. 1999. MD-2, a molecule that confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1777–1782.
Hajjar A.M., Ernst R.K., Tsai J.H., Wilson C.B., Miller S.I. 2002. Human Toll-like receptor 4 recognizes host-specific LPS modifications. Nat. Immunol. 3 (4), 354–359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.V. Voloshina, N.I. Kosiakova, I.R. Prokhorenko, 2013, published in Biologicheskie Membrany, 2013, Vol. 30, No. 5-6, pp. 357–363.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voloshina, E.V., Kosiakova, N.I. & Prokhorenko, I.R. Lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter capsulatus counteracts the effects of toxic lipopolysaccharides and inhibits the release of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in human whole blood. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 8, 23–29 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747813050231
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747813050231