Abstract
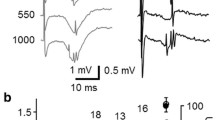
The mechanisms of activity-dependent modulation of burst discharges in rat hippocampal slices have been studied. The extracellular registration of field responses (population spike, PS, and field excitatory postsynaptic potential, fEPSP) induced by repetitive electrical stimulation (1–4 Hz) of Schaffer collaterals (with 30 pulses trains separated by 5-min resting intervals) was performed in cellular and dendritic layers of CA1 area. It has been established that repetitive orthodromic stimulation exerts biphasic modulation of burst discharges in Mg2+-free medium: use-dependent potentiation (UDP) and use-dependent inhibition (UDI). The former was manifested as an increase in the number of PS in the burst discharge associated with a corresponding lengthening of the fEPSP. During the UDI development the number of NMDA-dependent PS in the burst was diminished despite the continuing increase in the fEPSP duration. In some cases UDI was followed by spreading depression. Both UDP and UDI were reversible. The development of UDP and UDI could be effectively suppressed either by the NMDA antagonists or by the GABAergic inhibition enhancer, diazepam. The picrotoxin (PTX)-induced burst discharges did not undergo either UDP or UDI development. However, removal of Mg2+ from PTX-containing solution during continuing repetitive stimulation led to the appearance of NMDA-dependent UDI. Analysis of the data obtained indicates that: (1) UDP results from a progressive decrease in GABA-mediated inhibition in the course of low-frequency (1–4 Hz) repetitive stimulation (the so-called “fatigue of synaptic inhibition”); (2) UDI is caused by excessive Ca2+ influx into the neurons due to overactivation of NMDA receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PS:
-
population spike
- fEPSP:
-
field excitatory postsynaptic potential
- UDP:
-
use-dependent potentiation
- UDI:
-
use-dependent inhibition
- SD:
-
spreading depression
- PTX:
-
picrotoxin
- DZ:
-
diazepam
References
Anderson, W.W., Lewis, D.V., Schwartzwelder, H.S., and Wilson, W.A., Magnesium-Free Medium Activates Seizure-Like Events in the Rat Hippocampal Slice, Brain Res., 1986, vol. 398, pp. 215–219.
Mody, I., Lambert, J.D.C., and Heinemann, U., Low Extracellular Magnesium Induces Epileptiform Activity and Spreading Depression in Rat Hippocampal Slices, J. Neurophysiol., 1987, vol. 57, pp. 869–888.
Tancredi, V., Hwa, G.G., Zona, C., Brancati, A., and Avoli, M., Low Magnesium Epileptogenesis in the Rat Hippocampal Slice: Electrophysiological and Pharmacological Features, Brain Res., 1990, vol. 511, pp. 280–290.
Zhang, C.L., Dreier, J.P., and Heinemann, U., Paroxysmal Epileptiform Discharges in Temporal Lobe Slices after Prolonged Exposure to Low Magnesium are Resistant to Clinically Used Anticonvulsants, Epilepsy Res., 1995, vol. 20, pp. 105–111.
Herron, C.E., Lester, R.A.J., Coan, E.J., and Collingridge, G.L., Frequency Dependent Involvement of NMDA Receptors in the Hippocampus: a Novel Synaptic Mechanism, Nature, 1986, vol. 322, pp. 265–268.
Dreier, J. and Heinemann, U., Regional and Time Dependent Variations of Low Mg2+-Induced Epileptiform Activity in Rat Temporal Cortex Slices, Exp. Brain Res., 1991, vol. 87, P. 581–596.
Marder, C.P. and Buonomano, D.V., Differential Effects of Short- and Long-Term Potentiation on Cell Firing in the CA1 Region of the Hippocampus, J. Neurosci., 2003, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 112–121.
Albensi, B.C., Ata, G., Schmidt, E., Waterman, J.D., and Janigro, D., Activation of Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity Causes Suppression of Epileptiform Activity in Rat Hippocampal Slices, Brain Res., 2004, vol. 998, pp. 56–64.
Kuncler, P.E. and Kraig, R.P., P/Q Ca2+ Channels Blockade Stops Spreading Depression and Related Pyramidal Neuronal Ca2+ Rise in Hippocampal Organ Culture, Hippocampus, 2004, vol. 14, pp. 356–367.
Kalashnikova, N.V., Motin, V.G., and Khodorov, B.I., Contribution of AMPA- and NMDA-Receptors to Use-Dependent Potentiation and Inhibition of Experimentally-Evoked Epileptiform Activity in Rat Hippocampal Slices, Biol. Membranes, 2005, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 104–108.
Stanton, P.K., Jones, R.S.G., Mody, I., and Heinemann, U., Epileptiform Activity Induced by Lowering Extracellular [Mg2+] in Combined Hippocampal-Entorhinal Cortex Slices: Modulation by Receptors for Norepinefrine and N-Methyl-D-Aspartate, Epilepsy Res., 1987, vol. 1, pp. 53–62.
Heinemann, U., Lux, H.D., and Gutnick, M.J., Extracellular Free Calcium and Potassium During Paroxysmal Activity in the Cerebral Cortex of the Cat, Exp. Brain Res., 1977, vol. 27, pp. 237–243.
Marciani, M.G., Louvel, J., and Heinemann, U., Aspartate-Induced Changes in Extracellular Free Calcium in “in vitro” Hippocampal Slices of Rats, Brain Res., 1982, vol. 238, pp. 272–277.
Lüthi, A., van der Putten, H., Botteri, F.M., Mansuy, I.M., Meins, M., Frey, U., Sansing, G., Portet, C., Schmutz, M., Schröder, M., Nitsch, C., Laurent, J.-P., and Monard, D., Endogenous Serine Protease Inhibitor Modulates Epileptic Activity and Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation, J. Neurosci., 1997, vol. 17, no. 12, pp. 4688–4699.
Burdette, L.J. and Masukawa, L.M., Stimulus Parameters Affecting Paired-Pulse Depression of Dentate Granule Cell Field Potentials. II. Low-Frequency Stimulation, Brain Res., 1995, vol. 680, nos. 1, 2, pp. 63–72.
Lambert, J.D., Jones, R.S., Andreasen, M., Jensen, M.S., and Heinemann, U., The Role of Excitatory Amino Acids in Synaptic Transmission in the Hippocampus, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1989, vol. 93, no. 1, pp. 195–201.
Anderson, W.W., Epileptogenesis, in Cortical Plasticity, Fazeli, M.S. and Collingridge, G.L., Ed., Oxford: BIOS Scientific Publishers Ltd, 1996, pp. 149–189.
Köhling, R., Gladwell, S.J., Bracci, E., Vreugdenhil, M., and Jefferys, J.G., Prolonged Epileptiform Bursting Induced by 0 Mg2+ in Rat Hippocampal Slices Depends on Gap Junctional Coupling, Neuroscience, 2001, vol. 105, no. 3, pp. 579–587.
Basarsky, T.A., Duffy, S.N., Andrew, R.D., and MacVicar, B.A., Imaging Spreading Depression and Associated Intracellular Calcium Waves in Brain Slices, J. Neurosci., 1998, vol. 18, no. 18, pp. 7189–7199.
Somjen, G.G., Mechanisms of Spreading Depression and Hypoxic Spreading Depression-Like Depolarization, Physiol. Rev., 2001, vol. 81, no. 3, pp. 1065–1096.
Somjen, G.G., Is Spreading Depression Bad for You? Focus on “Repetitive Normoxic Spreading Depression-Like Events Result in Cell Damage in Juvenile Hippocampal Slice Cultures,” J. Neurophysiol., 2006, vol. 95, pp. 16–17.
Twyman, R.E., Rogers, C.J., and Macdonald, R.L., Differential Regulation of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Channels by Diazepam and Phenobarbital, Ann. Neurol., 1989, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 213–220.
File, S.E., Mabbutt, P.S., and Andrews, N., Diazepam Withdrawal Responses Measured in the Social Interaction Test of Anxiety and Their Reversal by Baclofen, Psychopharmacol., 1991, vol. 104, pp. 62–66.
Korpi, E.R., Grunder, G., and Luddens, H., Drug Interactions at GABA(A) Receptors, Prog. Neurobiol., 2002, vol. 67, pp. 113–159.
Moncada, S., Palmer, R.M.J., and Higgs, E.A., Nitric Oxide: Physiology, Pathophysiology and Pharmacology, Pharmacol. Rev., 1991, vol. 43, pp. 109–141.
Dawson, T.M., Zhang, J., Dawson, V.L., and Snyder, S.H., Nitric Oxide: Cellular Regulation and Neuronal Injury, Prog. Brain Res., 1994, vol. 103, pp. 365–369.
Jacoby, S., Sims, R.E., and Hartell, N.A., Nitric Oxide is Required for the Induction and Heterosynaptic Spread of Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Cerebellar Slices, J. Physiol., 2001, vol. 535, part 3, pp. 825–839.
Hardingham, N. and Fox, K., The Role of Nitric Oxide and GluR1 in Presynaptic and Postsynaptic Components of Neocortical Potentiation, J. Neurosci., 2006, vol. 26, no. 28, pp. 7395–7404.
Raevsky K.S., Nitric oxide, a New Physiological Messenger: Possible Role in Pathology of Control Nerwous System, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. (Rus.), 1997, vol. 123, pp. 484–490.
Schuchmann, S., Albrecht, D., Heinemann, U., and von Bohlen und Halbach, O., Nitric Oxide Modulates Low-Mg2+-Induced Epileptiform Activity in Rat Hippocampal-Entorhinal Cortex Slices, Neurobiol. Dis., 2002, vol. 11, pp. 96–105.
Yasuda, H., Fujii, M., Fujisawa, H., Ito, H., and Suzuki, M., Changes in Nitric Oxide Synthesis and Epileptic Activity in the Contralateral Hippocampus of Rats Following Intrahippocampal Kainite Injection, Epilepsia, 2001, vol. 42, pp. 13–20.
Bashkatova, V., Narkevich, V., Vitskova, G., and Vanin, A., The Influence of Anticonvulsant and Antioxidant Drugs on Nitric Oxide Level and Lipid Peroxidation in the Rat Brain During Penthylenetetrazole-Induced Epileptiform Model Seizures, Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2003, vol. 27, pp. 487–492.
Penix, L.P., Davis, W., and Subramaniam, S., Inhibition of NO Synthase Increases the Severity of Kainic Acid-Induced Seizures in Rodents, Epilepsy Res., 1994, vol. 18, pp. 177–184.
Przegaliinski, E., Baran, L., and Siwanowicz, J., The Role of Nitric Oxide in Chemically- and Electrically-Induces Seizures in Mice, Neurosci. Lett., 1996, vol. 217, pp. 145–148.
Hablitz, J.J., Picritoxin-Induced Epileptiform Activity in Hippocampus: Role of Endogenous Versus Synaptic Factors, J. Neurophysiol., 1984, vol. 51, pp. 1011–1027.
Fellin, T., Gomez-Gonzalo, M., Gobbo, S., Carmignoto, G., and Haydon, P.G., Astrocytic Glutamate is not Necessary for the Generation of Epileptiform Neuronal Activity in Hippocampal Slices, J. Neurosci., 2006, vol. 26, no. 36, pp. 9312–9322.
Köhr, G. and Heinemann, U., Effects of NMDA Antagonists on Picrotoxin-, Low Mg2+- and Low Ca2+-Induced Epileptogenesis and on Evoked Changes in Extracellular Na+ and Ca2+ Concentrations in Rat Hippocampal Slices, Epilepsy Res., 1989, vol. 4, pp. 187–200.
Goda, M., Kovac, S., Speckmann, E.J., and Gorji, A., Glutamate and Dopamine Receptors Contribute to the Lateral Spread of Epileptiform Discharges in Rat Neocortical Slices, Epilepsia, 2008, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 237–247.
Heinemann, U., Hamon, B., Konnerth, A., and Wadman, W.J., Stimulus-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Area CA1 of the in vitro Hippocampal Slice of Rats, Exp. Brain Res., 1986, vol. 14, pp. 291–299.
Hablitz, J.J. and Heinemann, U., Alterations in the Microenvironment During Spreading Depression Associated with Epileptiform Activity in the Immature Neocortex, Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res., 1989, vol. 46, pp. 243–252.
Hoyt, K.R., Tang, L.H., Aizenman, E., and Reynolds, I.J., Nitric Oxide Modulates NMDA-Induced Increases in Intracellular Ca2+ in Cultured Rat Forebrain Neurons, Brain Res., 1992, vol. 592, nos. 1, 2, pp. 310–316.
Davies, C.H., Starkey, S.J., Pozza, M.F., and Collingridge, G.L., The GABA Autoreceptors Regulate the Induction of LTP, Nature, 1991, vol. 349, no. 6310, pp. 609–611.
Brown, J.T., Davies, C.H., and Randall, A.D., Synaptic Activation of GABA(B) Receptors Regulates Neuronal Network Activity and Entrainment, Eur J Neurosci., 2007, vol. 25, no. 10, pp. 2982–2990.
Mori, M., Abegg, M.H., Gähwiler, B.H., and Gerber, U., A Frequency-Dependent Switch from Inhibition to Excitation in a Hippocampal Unitary Circuit, Nature, 2004, vol. 431, no. 7007, pp. 453–456.
Mann, E.O. and Paulsen, O., Role of GABAergic Inhibition in Hippocampal Network Oscillations, Trends Neurosci., 2007, vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 343–349.
Thompson, S.M., Capogna, M., and Scanziani, M., Presynaptic Inhibition in the Hippocampus, Trends Neurosci., 1993, vol. 16, pp. 222–227.
Jensen, K., Lambert, J.D.C., and Jensen, M.S., Activity-Dependent Depression of GABAergic IPSCs in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons, J. Neurophysiol., 1999, vol. 82, pp. 42–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalashnikova, N.V., Motin, V.G. & Khodorov, B.I. Synaptic mechanisms of use-dependent potentiation and use-dependent inhibition of evoked burst discharges in rat hippocampal slices. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. A 3, 206–215 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747809020147
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747809020147