Abstract
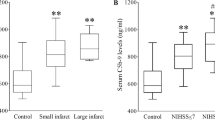
This study analyzed the relationship between LOX-1 and CX3CR1 and vascular endothelial function, fibrinolytic activity, and recurrence rate after thrombolysis in patients with cerebral infarction. Sixty patients with cerebral infarction who visited our hospital between May 2019 and April 2021 were enrolled as the study group, and 45 healthy individuals who underwent health checkups at our hospital during the same period were selected as the control group. The serum levels of LOX-1 and CX3CR1 in the study group were higher than those in the control group. The levels of serum LOX-1 and CX3CR1 were higher in the recurrence group than in the non-recurrence group. The study group had significantly lower plasma tPA and vWFp; higher plasma PAI-1; lower FMD levels; higher ba-PWV and ABI; and higher serum S100β, NSE, and NGF levels than those of the control group (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that LOX-1 and CX3CR1 levels in patients with cerebral infarction were positively correlated with PAI-1, ba-PWV, ABI, S100β, NSE, and NGF (r > 0, P < 0.05), and negatively correlated with tPA, vWF, and FMD (r < 0, P < 0.05). Serum LOX-1 and CX3CR1 levels are closely related to endothelial function, fibrinolytic activity, and neurological function in patients with cerebral infarction, and their combined detection can effectively predict the occurrence of cerebral infarction and recurrence after thrombolysis, which can be used to identify high-risk groups.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sveinsson, O.A., Kjartansson, O., and Valdimarsson, E.M., Laeknabladid, 2014, vol. 100, no. 5, pp. 271–279.
Takeda, H., Yamaguchi, T., Yano, H., and Tanaka, J., J. Pharmacol. Sci., 2021, vol. 145, no. 1, pp. 130–139.
Shin, T.H., Lee, D.Y., Basith, S., Manavalan, B., Paik, M.J., Rybinnik, I., Mouradian, M.M., Ahn, J.H. and Lee, G., Cells, 2020, vol. 9, no. 7, pp. 1630.
Lee, S.U., Kim, T., Kwon, O.K., Bang, J.S., Ban, S.P., Byoun, H.S., and Oh, C.W., J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc., 2020, vol. 63, no. 1, pp. 69–79.
Heo, N.H., Lee, M.R., Yang, K.H., Hong, O.R., Shin, J.H., Lee, B.Y., Lee, J.Y., Ahn, J.M., Oh, H.J., and Oh, J.S., Medicine (Baltimore), 2021, vol. 100, no. 44, pp. e27652.
Güneş, Y., Sincer, I., and Erdal, E., Anatol. J. Cardiol, 2019, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 54–59.
Pawelec, P., Ziemka-Nalecz, M., Sypecka, J. and Zalewska, T., Cells, 2020, vol. 9, no. 10, pp. 2277.
Kattoor, A.J., Kanuri, S.H., and Mehta, J.L., Curr. Med. Chem., 2019, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. 1693–1700.
Lu, J., Mitra, S., Wang, X., Khaidakov, M., and Mehta, J.L., Antioxid. Redox Signal, 2011, vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 2301–2333.
Chinese Society of Neurology; Chinese Society of Neurology Cerebrovascular Disease Group, Chinese Journal of Neurology, 2015, vol. 48, no. pp. 246–257.
Gao, T.L., Zhang, Z., Wen, S.J., and Zhang, N., Beijing Med. J., 2004, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 86–89.
Pothineni, N.V.K., Karathanasis, S.K., Ding, Z., Arulandu, A., Varughese, K.I., and Mehta, J.L., J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2017, vol. 69, no. 22, pp. 2759–2768.
Stancel, N., Chen, C.C., Ke, L.Y., Chu, C.S., Lu, J., Sawamura, T., and Chen, C.H., Clin. Chem., 2016, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 320–327.
Zeya, B., Arjuman, A., and Chandra, N.C., Biochemistry, 2016, vol. 55, no. 32, pp. 4437–4444.
Gliozzi, M., Scicchitano, M., Bosco, F., Musolino, V., Carresi, C., Scarano, F., Maiuolo, J., Nucera, S., Maretta, A., Paone, S., Mollace, R., Ruga, S., Zito, M.C., Macrì, R., Oppedisano, F., Palma, E., Salvemini, D., Muscoli, C., and Mollace, V., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, vol. 20, no. 13, pp. 3294.
Wang, X.L., Yu, T., Yan, Q.C., Wang, W., Meng, N., Li, X.J., and Luo, Y.H., J. Mol. Neurosci., 2015, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 449–460.
Lin, F., Pei, L., Zhang, Q., Han, W., Jiang, S., Lin, Y., Dong, B., Cui, L., and Li, M., J. Cell Physiol., 2018, vol. 233, no. 10, pp. 6683–6692.
Kobayashi, N., Takano, M., Hata, N., Kume, N., Yamamoto, M., Yokoyama, S., Shinada, T., Tomita, K., Shirakabe, A., Otsuka, T., Seino, Y., and Mizuno, K., Int. J. Cardiol, 2013, vol. 168, no. 4, pp. 3217–3223.
Luo, P., Chu, S.F., Zhang, Z., Xia, C.Y., and Chen, N.H., Brain Res. Bull., 2019, vol. 146, no. pp. 12–21.
Ding, Z., Liu, S., Wang, X., Dai, Y., Khaidakov, M., Romeo, F., and Mehta, J.L., Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 2014, vol. 92, no. 7, pp. 524–530.
Hofmann, A., Brunssen, C., and Morawietz, H., Vascul. Pharmacol., 2017, pp. S1537–1891(17)30171-4.
Aoyama, T., Inokuchi, S., Brenner, D.A. and Seki, E., Hepatology, 2010, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 1390–1400.
Yokota, C., Sawamura, T., Watanabe, M., Kokubo, Y., Fujita, Y., Kakino, A., Nakai, M., Toyoda, K., Miyamoto, Y., and Minematsu, K., J. Atheroscler. Thromb., 2016, vol. 23, no. 10, pp. 1222–1226.
Skarpengland, T., Skjelland, M., Kong, X.Y., Skagen, K., Holm, S., Otterdal, K., Dahl, C.P., Krohg-Sørensen, K., Sagen, E.L., Bjerkeli, V., Aamodt, A.H., Abbas, A., Gregersen, I., Aukrust, P., Halvorsen, B., and Dahl, T.B., J. Am. Heart Assoc., 2018, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. e006479.
Apostolakis, S. and Spandidos, D., Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 2013, vol. 34, no. 10, pp. 1251–1256.
Funding
No external funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of The First People’s Hospital of Wenling (approval number 2020PS58K) and was performed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent. The research subjects and their families were informed, and they signed a fully informed consent form.
Additional information
Corresponding author: Department of Neurology, The First People’s Hospital of Wenling, No. 333, Chuanan South Road, Chengxi Street, Wenling, Zhejiang 317500, China; Phone: +86-13486878880; e-mail: jinxinchun@tom.com.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, X.L., Shao, J.H., Wang, L.S. et al. Correlation between LOX-1 and CX3CR1 and Vascular Endothelial Function, Fibrinolytic Activity, and Recurrence after Thrombolysis in Patients with Cerebral Infarction. Neurochem. J. 16, 498–503 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712422040109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712422040109