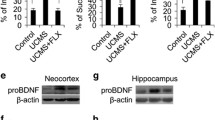
Abstract—Recently, it has become apparent that the interaction between the serotonin (5-HT) system and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) system plays an important role in the regulation of behavior, and in various physiological and neuroplasticity processes. Moreover, there is data indicating the involvement of the 5-HT1A receptor, a key regulator of the central serotonergic system, in the control of the BDNF system. Recently, we have created new recombinant mouse strains, B6.CBA-D13Mit76C (B6-M76C) and B6.CBA-D13Mit76B (B6-M76B) in which 5-HT1A receptors have different sensitivity to chronic activation. In this paper, using these mice, we studied acute stress-induced changes in the levels of BDNF protein and its precursor proBDNF. It was shown that B6-M76C mice with reduced sensitivity of presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors differ from B6-M76B mice; B6-M76C mice have a lower level of proBDNF in the midbrain and hippocampus and an increased BDNF/proBDNF ratio in the hippocampus. Acute stress caused a decrease in the level of proBDNF in the midbrain of mice of the control B6-M76B line leading to a significant increase in the BDNF/proBDNF ratio, which reflects the intensity of “maturation” of BDNF. Thus, it was discovered that changes in the sensitivity of the key regulator of the central serotonergic system, 5-HT1A receptor, lead to significant changes in the response of the BDNF system to acute stress. It was also revealed that the function of the 5-HT1A receptor is associated with the pattern of basal expression of elements of the BDNF system, namely, the expression of the proBDNF precursor protein. In addition, the data suggest that the changes in the functional activity of the BDNF system caused by acute stress are associated primarily with neuroplasticity mechanisms that determine the emotional and behavioral response to emotional stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Popova, N.K., Ilchibaeva, T.V., and Naumenko, V.S., Biochemistry (Moscow), 2017, vol. 82, no. 3, pp. 308–317.
Popova, N.K., Il’chibaeva, T.V., and Naumenko, V.S., Biokhimiya, 2017, vol. 82, no. 3, pp. 449–459.
Benarroch, E.E., Neurology, 2015, vol. 84, no. 16, pp. 1693–1704.
Lu, B., Pang, P.T., and Woo, N.H., Nat. Reviews. Neurosci., 2005, vol. 6, no. 8, pp. 603–614.
Kenchappa, R.S., Tep, C., Korade, Z., Urra, S., Bronfman, F.C., Yoon, S.O., and Carter, B.D., J. Biol. Chem., 2010, vol. 285, no. 26, pp. 20358–20368.
Deinhardt, K. and Chao, M.V., Neuropharmacol., 2014, vol. 76, Pt. C, pp. 603–609.
Borodinova, A.A. and Salozhin, S.V., Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I.P. Pavlova, 2016, vol. 66, no. 1, pp. 3–23.
Popova, N.K. and Naumenko, V.S., Rev. Neurosci., 2013, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 191–204.
Kulikova, E.A., Bazovkina, D.V., Akulov, A.E., Tsybko, A.S., Fursenko, D.V., Kulikov, A.V., Naumenko, V.S., Ponimaskin, E., and Kondaurova, E.M., Br. J. Pharmacol., 2016, vol. 173, no. 13, pp. 2147–2161.
Kulikova, E.A., Bazovkina, D.V., Antonov, Y.V., Akulov, A.E., Kulikov, A.V., and Kondaurova, E.M., Neurosci. Res., 2017, vol. 117, pp. 14–21.
Kondaurova, E.M., Bazovkina, D.V., and Kulikov, A.V., Ross. Fiziol. Zhurn. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2015, vol. 101, no. 6, pp. 670–677.
Dixon, W.J., Biometrics, 1953, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 74–89.
Popova, N.K. and Naumenko, V.S., Exp. Opin. Ther. Targ., 2019, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 227–239.
Jiang, D.G., Jin, S.L., Li, G.Y., Li, Q.Q., Li, Z.R., Ma, H.X., Zhuo, C.J., Jiang, R.H., and Ye, M.J., Neural Regen. Res., 2016, vol. 11, no. 9, pp. 1471–1479.
Nibuya, M., Morinobu, S., and Duman, R.S., J. Neurosci., 1995, vol. 15, no. 11, pp. 7539–7547.
Altar, C.A., Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 1999, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 59–61.
Castren, E. and Rantamaki, T., Dev. Neurobiol., 2010, vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 289–297.
Barnes, N.M. and Sharp, T., Neuropharmacol., 1999, vol. 38, no. 8, pp. 1083–1152.
Ilchibaeva, T.V., Kondaurova, E.M., Tsybko, A.S., Kozhemyakina, R.V., Popova, N.K., and Naumenko, V.S., Behav. Brain Res., 2015, vol. 290, pp. 45–50.
Selye, H., J. Hum. Stress, 1975, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 37–44.
Popova, N.K., Ponimaskin, E.G., and Naumenko, V.S., Ross. Fiziol. Zhurn. Im. I.M. Sechenova, 2015, vol. 101, no. 11, pp. 1270—1278.
Funding
The animals were maintained at the expense of the budget project no. 0324-2019-0041-C-01; this study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 19-15-00025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval. The maintenance of the experimental animals and all procedures were performed in accordance with the international rules for the treatment of animals of the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publications No. 80023), 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondaurova, E.M., Il’chibaeva, T.V., Bazovkina, D.V. et al. The Influence of Stress on the Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Precursor proBDNF in Mice with Different Sensitivity of Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptors. Neurochem. J. 14, 262–267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712420030071
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712420030071