Abstract
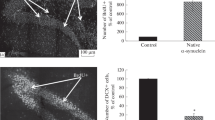
Hyperproduction and disturbance of the protein conformation of α-synuclein that are associated with the formation of aggregated forms, which have a neurotoxic effect, are the key link in the mechanisms of the pathogenesis of synucleinopathies, which are chronic progressive neurodegenerative diseases. We studied the effects of chronic intranasal administration of fibrillar forms of α-synuclein on the processes of neurogenesis in the hippocampus, the content of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, motor and exploratory activity, short- and long-term memory, and anxiety in ageing animals. The experiments were performed with 12-month-old male C57Bl/6 mice, which were administered intranasally once a day with a solution of α-synuclein fibrils or physiological solution for 14 days. Behavioral experiments included the Open field, novel object recognition, passive avoidance, and elevated plus maze tests. We used antibodies against bromodeoxyuridine, doublecortin, and tyrosine hydroxylase to stain proliferating cells, immature neurons, and dopaminergic nerve cells. We found that α-synuclein fibrils do not cause significant changes in indices of neurogenesis, the number of proliferating cells and immature neurons in the hippocampal dentate gyrus; nor do they have a significant effect on exploratory behavior, short- and long-term memory, and anxiety in mice. However, animals that were treated with fibrils of α-synuclein had a significant increase in the number of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta and an increase in some indices of general motor activity. We compared the data on the effects of α-synuclein fibrils and the results of a previous study of the action of α-synuclein oligomers under the conditions of a similar experimental protocol. We discuss possible mechanism of the revealed effect of α-synuclein fibrils on dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra of ageing mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breydo, L., Wu, J.W., and Uversky, V.N., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2012, vol. 1822, pp. 261–285.
Goedert, M., Jakes, R., and Spillantini, M.G., J. Parkinsons D., vol. 7, no. S1, pp. S53–S69.
Spillantini, M.G. and Goedert, M., Cell Tissue Res., 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2706-9.
McCann, H., Stevens, C.H., Cartwright, H., and Halliday, G.M., Parkinsonism Relat. D., no. Suppl 1, pp. 62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70017-8.
Horgusluoglu, E., Nudelman, K., Nho, K., and Saykin, A.S., Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet., 2017, vol. 174, pp. 93–112.
Le Grand, J.N., Gonzales-Cano, L., Pavlou, M.A., and Schwamborn, J.C., Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2015, vol. 72, pp. 773–797.
Yang, W. and Yu, S., Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2017, vol. 74, pp. 1485–1501.
Sherstnev, V.V., Kedrov, A.V., Solove`va, O.A., Gruden’, M.A., Konovalova, E.V., Kalinin, I.A., and Proshin, A.T., Neurochem. J., 2017, vol. 11, pp. 282–289.
Gruden, M.A., Davydova, T.V., Narkevich, V.B., Fomina, V.G., Wang, C., Kudrin, V.S., Morozova-Roche, L.A., and Sewell, R.D., Behav. Brain Res., 2014, vol. 263, pp. 158–168.
Encinas, J.M. and Enikolopov, G., Methods Cell Biol., 2008, vol. 85, pp. 243–272.
Franklin, K. and Paxinos, G., The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Third edition, New York, London, Burlington, San Diego: Academic PRESS, 2007.
Luk, K.C., Kehm, V., Carroll, J., Zhang, B., OBrien, P., Trojanowski, J.O., and Lee, V.M.J., Science, 2012, vol. 338, pp. 949–958.
Mor, D.E., Tsika, E., Mazzulli, J.R., Gould, N.S., Kim, H., Daniels, M.J., Doshi, S., Gupta, P., Grossman, J.L., Tan, V.X., Kalb, R.G., Caldwell, K.A., Caldwell, G.A., Wolfe, J.H., and Ischiropoulos, H., Nat. Naurosci., 2017, vol. 20, pp. 1560–1568.
Post, M.R., Lieberman, O.J., and Mosharov, E.V., Front. Neurosci., 2018, vol. 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00161.
Peelaerts, W., Bousset, L., Van der Perren, A., Moskalyuk, A., Pulizzi, R., Guigliano, M., Van der Haute, C., Melki, R., and Baekelandt, V., Nature, 2015, vol. 522, pp. 340–344.
Peelaerts, W. and Baekelandt, V., J. Neurochem., 2016, vol. 139, pp. 256–274.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.V. Sherstnev, O.A. Solov’eva, M.A. Gruden’, A.V. Kedrov, E.V. Konovalova, A.M. Ratmirov, 2018, published in Neirokhimiya, 2018, Vol. 35, No. 4, pp. 363–370.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherstnev, V.V., Solov’eva, O.A., Gruden’, M.A. et al. The Effects of Fibrillar Forms of α-Synuclein Protein on Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus, Dopaminergic Neurons of the Substantia Nigra, and the Behavior of Ageing Mice. Neurochem. J. 12, 359–365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712418040062
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712418040062