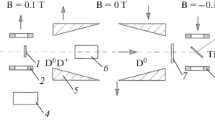
Abstract
The prototype of polarized deuteron source was made for the Van de Graaff accelerator of the Czech Technical University in Prague with aim to create full scale setup for producing polarized neutron beam for experiments on measurement \(\Delta {{\sigma }_{{\text{L}}}}\) and \(\Delta {{\sigma }_{{\text{T}}}}\), longitudinal and transversal spin asymmetries in transmission polarized neutron beam through frozen polarized deuteron target. It is based on Kaminsky’s experiment on channeling deuterons through a magnetized Ni single crystal foil of 1–2 μm. It is proposed to use the reaction T\({{(d,n)}^{4}}\)He with polarized deuterons of an energy 150–200 keV. For a nonchanneled beam (the goniometer in a random position), the tensor polarization measurements were carried out with a TiT target. Our result is \({{P}_{{zz}}} = - 0.10 \pm 0.02\). This result indicates that deuterium atoms that have passed outside the channels also become polarized due to the capture of polarized electrons from the nickel crystal.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. A. Coon, M. D. Scadron, P. C. McNamee, B. R. Barrett, D. W. E. Blatt, and B. H. J. McKellar, “Two-pion-exchange three-nuclear potential and nuclear matter,” Nucl. Phys. A 317, 242–278 (1979).
H. Primakoff and T. Holstein, “Many-body interactions in atomic and nuclear systems,” Phys. Rev. 55, 1218 (1939).
J. Fujita and H. Miyazawa, “Pion theory of three-body forces,” Prog. Theor. Phys. 17, 360–365 (1957).
B. S. Pudliner, V. R. Pandharipande, J. Carlson, and R. B. Wiringa, “Quantum Monte Carlo calculations of A ≤ 7 nuclei,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4396–4399 (1995).
Yu. N. Uzikov, “Three-Nucleon Forces and Some Aspects of Nuclear Astrophysics,” in The Universe Evolution, Ed. by I. Strakovsky and L. Blokhintsev (Nova Science Publisher, New York, 2013), pp. 269–292.
D. Huber and J. L. Friar, “The Ay puzzle and nuclear force,” Phys. Rev. C 58, 674—685 (1998).
H. Witala, W. Glöckle, J. Golak, D. Huber, H. Kamada, and A. Nogga, “Scaling properties of the longitudinal and transversal asymmetries of the \(\vec {n}\vec {d}\) total cross section,” Phys. Lett. B 447, 216–220 (1999).
R. D. Foster, C. R. Gould, D. G. Haase, J. M. Kelley, D. M. Markoff, and W. Tornow, “Measurement of the relative longitudinal spin-dependent total cross-section difference in \(\vec {n} - \vec {d}\) scattering,” Phys. Rev. C 73, 034002 (2006).
I. Wilhelm, P. Murali, and Z. Doležal, “Production of monoenergetic neutrons from the T(d, n)α reaction with the associated particle method,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 317, 553–558 (1992).
N. S. Borisov, V. N. Matafonov, A. B. Neganov, Yu. A. Plis, O. N. Shchevelev, Yu. A. Usov, I. Jánský, M. Rotter, B. Sedlák, I. Wilhelm, G. M. Gurevich, A. A. Lukhanin, J. Jelínek, A. Srnka, and L. Skrbek, “Target with a frozen nuclear polarization for experiments at low energies,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 345, 421–428 (1994).
J. Brož, J. Černý, Z. Doležal, G. M. Gurevich, M. Jirásek, P. Kubík, A. A. Lukhanin, J. Švejda, I. Wilhelm, N. S. Borisov, Yu. M. Kazarinov, B. A. Khachaturov, E. S. Kuzmin, V. N. Matafonov, A. B. Neganov, I. L. Pisarev, Yu. A. Plis, Yu. A. Usov, M. Rotter, and B. Sedlák, “Measurement of spin-dependent total cross section difference in neutron-proton scattering ΔσT at 16 MeV,” Z. Phys. A 354, 401–408 (1996).
J. Brož, J. Černý, Z. Doležal, G. M. Gurevich, P. Kubík, A. A. Lukhanin, G. A. Lukhanin, J. Švejda, I. Wilhelm, N. S. Borisov, E. S. Kuzmin, V. N. Matafonov, A. B. Neganov, I. L. Pisarev, Yu. A. Plis, and Yu. A. Usov, “Measurement of spin-dependent total cross section difference in neutron-proton scattering ΔσL at 16 MeV,” Z. Phys. A 359, 23–25 (1997).
N. S. Borisov, N. A. Bazhanov, A. A. Belyaev, J. Brož, J. Černý, Z. Doležal, A. N. Fedorov, G. M. Gurevich, M. P. Ivanov, P. Kodyš, P. Kubík, E. S. Kuzmin, A. B. Lazarev, F. Lehar, O. O. Lukhanin, V. N. Matafonov, A. B. Neganov, I. L. Pisarev, J. Svejda, S. N. Shilov, Yu. A. Usov, and I. Wilhelm, “Deuteron frozen-spin-polarized target for nd experiments at the VdG Accelerator of Charles University,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 593, 177–182 (2008).
Yu. A. Usov, “Frozen spin target developed at Dubna. History and traditions,” in Proceedings of the 16 th International Workshop in Polarized Sources, Targets and Polarimetry PSTP2015, Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany, 2015, PoS 243 (2016).
S. T. Goertz, J. Harmsen, and J. Heckmann, Ch. Heß, W. Meyer, E. Radtke, and G. Reicherz, “Highest polarizations in deuterated compounds,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 526, 43–52 (2004).
M. Kaminsky, “Polarization of channeled particles,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 23, 819–822 (1969); in Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Polarization Phenomena in Nuclear Reactions, Madison, 1970, pp. 803–809.
M. Kaminsky, US Patent No. 3,569, 705 (March 9, 1971).
E. K. Zavoiskii, “Concerning a possible method for the polarization of a proton beam,” Sov. Phys. JETP 5, 338—339 (1957).
D. S. Gemmel, “Channeling,” Rev. Mod. Phys. 46, 129 (1974).
D. S. Gemmel and J. N. Worthington, “An apparatus for “channeling” experiments,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 91, 15–28 (1971).
L. C. Feldman, D. W. Mingay, and J. P. F. Sellschop, “Another measurement of the polarization of deuterons channeled through thin Ni foils,” Radiat. Eff. 13, 145–151 (1972).
M. E. Ebel, “Polarization of channeled deuterons,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 24, 1395–1398 (1970).
W. Brandt and R. Sizmann, “Capture of polarized electrons by deuterons emerging from a magnetized nickel foil,” Phys. Lett. A 37, 115–116 (1971).
S. Kreussler and R. Sizmann, “Neutralization of 50–230-keV hydrogen ions which have penetrated Al, Au, C, and Cs films,” Phys. Rev. B 26, 520–529 (1982).
W. Gleich, G. Regenfus, and R. Sizmann, “Spin polarization of field-emitter electrons from monocrystalline nickel,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 27, 1066–1069 (1971).
C. Rau and R. Sizmann, “Measurement of predominant electron spin orientation at single crystal surfaces of ferromagnetic nickel,” Phys Lett. A 43, 317–318 (1973).
C. Rau, “Electron spin polarization ESP at surfaces of ferromagnetic metals,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 30, 141–174 (1982).
K.-H. Speidel, M. Knopp, W. Karle, P. Maier-Komor, H.-J. Simonis, F. Hagelberg, J. Gerber, and P. N. Tandom, “Evidence for spin-polarized electrons of highly stripped fluorine ions emerging from thin ferromagnetic layers,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2616–2619 (1988).
L. N. Libermann, D. R. Fredkin, and H. B. Shore, “Two-dimensional “ferromagnetism” in iron,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 22, 539–541 (1969).
L. Liebermann, J. Clinton, D. M. Edwards, and J. Mathon, ““Dead” layers in ferromagnetic transition metals,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 25, 232–235 (1970).
P. G. Sona, “A new method proposed to increase polarization in polarized ion sources of H- and D-,” Energia Nucleare 14, 295–299 (1967).
Yu. A. Plis, J. Černý, A. N. Fedorov, I. V. Gapienko, G. M. Gurevich, Z. Kohout, J. Petrík, S. Pospíšil, M. Solar, J. Šveida, Yu. A. Usov, and I. Wilhelm, “Research and development of the polarized deuteron source for the Van De Graaff accelerator,” Part. Nucl. Lett. 16, 256—263 (2019), Preprint JINR E13-2018-69 (JINR, Dubna).
D. von Ehrenstein, US Patent, No. 3,723,741 (March 27, 1973).
G. G. Ohlsen, “Polarization transfer and spin correlation experiments in nuclear physics,” Rep. Prog. Phys. 35, 717—801 (1972).
E. M. Gunnersen and G. James, “On the efficiency of the reaction 3H(d, n)4He in titanium tritide bombarded with deuterons,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 8, 173–184 (1960).
A. Galonsky, H. B. Willard, and T. A. Welton, “S-wave detector of deuteron polarization and 14-MeV polarized-neutron source,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 2, 349–351 (1959).
W. Haeberli, “Polarized Beams,” in Nuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions. Ed. by J. Cerny (Academic Press, New York, 1974), p. 152.
A. A. Naqvi and G. Clausnitzer, “Measurement of beam polarization using the reaction,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 324, 429–432.
G. G. Ohlsen and P. W. Keaton, “Techniques for measurement of spin-1/2 and spin-1 polarization analyzing tensors,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 109, 41–59 (1973).
B. P. Ad’yasevich, V. G. Antonenko, and V. N. Bragin, “Research of the reactions 2H(d, p)3H and 2H(d, p)3He with a polarized deuteron beam. extrapolation of the cross sections into the low energy region,” Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 33, 313 (1981).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Ivan Štekl for useful discussion.
J. Černý, Z. Kohout, J. Petrík, S. Pospíšil, M. Solar, R. Sykora, J. Šveida, and I. Wilhelm from Czech Technical University in Prague, Institute for Experimental and Applied Physics participated in the research.
Funding
The work was supported from European Regional Development Fund-Project “Van de Graaff Accelerator – a Tunable Source of Monoenergetic Neutrons and Light Ions” (no. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16-013/0001785).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gapienko, I.V., Belov, D.V., Fedorov, A.N. et al. Research and Development of the Polarized Deuteron Source for the Electrostatic Accelerator. Phys. Part. Nuclei Lett. 20, 1409–1418 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1547477123060146
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1547477123060146