Abstract
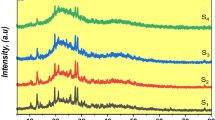
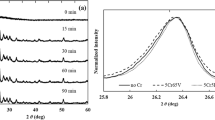
Glasses with compositions of stoichiometric and nonstoichiometric (with an excess of lithium oxide) Li-aegirine (LiFeSi2O6), as well as nonstoichiometric Li-aegirine with the addition of carbon and copper, are synthesized. The processes of the formation of crystalline phases and their evolution during the heat treatment of initial quenched glasses in the temperature range of 600–1100°C are studied by X-ray diffraction analysis. The phase composition of the initial glasses is different: the stoichiometric Li-aegirine glass contains cubic nanocrystals of magnetite, Fe3O4, ~ 21 nm in size, formed during the casting and quenching of the initial glass. An increase in the quenching rate leads to diminishing the magnetite crystal size to ~ 8 nm and to a decrease in their number. Glasses of nonstoichiometric composition are X-ray amorphous. The X-ray diffraction analysis of the crystals formed during the heat treatment of quenched glasses in a gradient furnace showed that, in all glasses at temperatures of 700 to 1040°C, crystals of monoclinic Li-aegirine (space group С2/c) are formed. At heat treatment temperatures above 1040°C, incongruent melting of Li-aegirine occurs with the formation of cristobalite and/or magnetite. The obtained results will form the base for the development of an electrode material for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tarascon, J.-M. and Armand, M., Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries, Nature (London, U.K.), 2001, vol. 414, pp. 359–367.
Nagaura, T. and Tozawa, K., Lithium ion rechargeable battery, Prog. Batter. Sol. Cells, 1990, vol. 9, pp. 209–212.
A Dream Comes True: The Lithium-Ion Rechargeable Battery. www.sony.com/en/SonyInfo/CorporateInfo/History/SonyHistory/2-13.html#block3. Accessed July 17, 2021.
Mizushima, K., Jones, P.C., Wiseman, P.J., and Goodenough, J.B., LixCoO2 (0 < x <= 1): A new cathode material for batteries of high energy density, Mater. Res. Bull., 1980, vol. 15, pp. 783–789.
Togashi, T., Honma, T., and Komatsu, T., Electrochemical performance of composites of spinel-type LiFe1-x MnxSiO4 nanocrystals and glassy phase synthesized by quenching of melts, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2015, vol. 123, no. 1, pp. 26–32.
Qian Cheng, Lu Wei, Zhe Liu, Nan Ni, Zhe Sang, Bin Zhu, Weiheng Xu, Meijie Chen, Yupeng Miao, Long-Qing Chen, Wei Min, and Yuan Yang, Operando and three-dimensional visualization of anion depletion and lithium growth by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy, Nat. Commun., 2018, vol. 9, p. 2942.
Sony to Initiate Global Replacement Program for Notebook Computer Battery Packs. www.sony.com/en/SonyInfo/News/Press/200609/06-090E. Accessed July 17, 2021.
Goodenough, J.B., Manganese oxides as battery cathodes, in Proceedings of the Symposium on Manganese Dioxide Electrode Theory and Practice for Electrochemical Applications, Schumm, B., Jr., Middaugh, R.L., Grotheer, M.P., and Hunter, J.C., Eds., N.J.: Electrochem. Soc., 1985, vol. 85-4, pp. 77–96.
Manthiram, A. and Goodenough, J.B., Lithium-based polyanion oxide cathodes, Nat. Energy, 2021, vol. 6, pp. 844–845.
Padhi, A.K., Nanjundaswamy, K., and Goodenough, J.B., Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, vol. 144, no. 4, pp. 1188–1194.
Liivat, A. and Thomas, J., Minerals as a source of novel Li-ion battery electrode materials, Macedon. J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2015, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 145–149.
In Yea Kim, Seo Yoon Shin, Jea Hwan Ko, Kang Soo Lee, Sung Pil Woo, Dong Kyu Kim, and Young Soo Yoon, Functional Li-M (Ti, Al, Co, Ni, Mn, Fe)-O energy materials, J. Korean Ceram. Soc., 2017, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 9–22.
Popovich, A.A. and Shen, V.Ts., Research technology receipt of cathode material Li2FeSiO4, Nauch.-Tekh. Vedom. SPb. Politekh. Univ., 2013, no. 2 (171), pp. 102–108.
Shen, V.Ts., Development of nanostructured cathode material based on Li2FeSiO4 for lithium-ion batteries, Cand. Sci. (Tech. Sci.) Dissertation, St. Petersburg, 2014.
Kamon-in, O., Buakeaw, S., Klysubun, W., Limphirat, W., Srilomsak, S., and Meethong, N., A study of transient phase transformation in LFS/C using in-situ time resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2014, vol. 9, pp. 4257–4267.
Honma, T., Togashi, T., and Komatsu, T., Spinel-type crystals based on LiFeSiO4 with high electrical conductivity for lithium ion battery formed by melt-quenching method, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2012, vol. 120, no. 3, pp. 93–97.
Zhou, S., Kin, G., Scanlon, D.O., Sougrati, M.T., and Melota, B.C., Low temperature preparation and electrochemical properties of LiFeSi2O6, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, vol. 161, no. 10, pp. A1642–A1647.
Ishida, N., Sakatsume, K., Kitamura, N., and Idemoto, Y., Improvement of electrochemical property of pyroxene-type LiFeSi2O6 and crystal-structure analysis, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2017, vol. 125, no. 4, pp. 281–286.
Ishida, N., Tajima, T., Kitamura, N., and Idemoto, Y., Single-phase synthesis, average, electronic, and local structure and cathode properties of pyroxene type LiFeSi2O6, Ionics, 2021, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 925–933.
Morimoto, N., Nomenclature of pyroxenes, Can. Mineral., 1989, vol. 27, pp. 143–156.
Iezzi, G., Bromiley, G.D., Cavallo, A., Das, P.P., Karavassili, F., Margiolaki, I., Stewart, A.A., Tribaudino, M., and Wright, J.P., Solid solution along the synthetic LiAlSi2O6–LiFeSi2O6 (spodumene-ferri-spodumene) join: A general picture of solid solutions, bond lengths, lattice strains, steric effects, symmetries, and chemical compositions of Li clinopyroxenes, Am. Mineral., 2016, vol. 101, pp. 2498–2513.
Rawat, R., Singh, R.S., and Bindu, R., Structural response to the magnetic pre-ordering in LiFeSi2O6, Eur. Phys. J. B, 2019, vol. 92, p. 162.
Eitel, W., Physical Chemistry of the Silicates, Chicago: Chicago Univ., 1954.
Redhammer, G.J., Roth, G., Paulus, W., Andre, G., Lottermoser, W., Amthauer, G., Treutmann, W., and Koppenhuber-Bitschnau, B., The crystal and magnetic structure of Li-aegirine LiFe3+Si2O6: A temperature-dependent study, Phys. Chem. Miner., 2001, vol. 28, pp. 337–346.
Nytén, A., Kamali, S., Häggström, L., Gustafsson, T., and Thomas, J.O., The lithium extraction/insertion mechanism in Li2FeSiO4, J. Mater. Chem., 2006, vol. 16, pp. 2266–2272.
Jodlauk, S., Becker, P., Mydosh, J.A., Khomskii, D.I., Lorenz, T., Streltsov, S.V., Hezel, D.C., and Bohat, L., Pyroxenes: A new class of multiferroics, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2007, vol. 19, no. 43, p. 432201.
Redhammer, G.J. and Roth, G., Structural variation and crystal chemistry of LiMe3+Si2O6 clinopyroxenes Me3+ = AI, Ga, Cr, V, Fe, Sc and In, Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater., 2004, vol. 219, pp. 278–294.
Turianicova, E., Witte, R., Da Silva, K.L., Zorkovska, A., Senna, M., Hahn, H., Heitjans, P., and Sepelak, V., Combined mechanochemical/thermal synthesis of microcrystalline pyroxene LiFeSi2O6 and one-step mechanosynthesis of nanoglassy LiFeSi2O6 based composite, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 707, pp. 310–314.
Skurikhin, O., Senna, M., Fabián, M., Witte, R., Tarasenko, R., Tkáč, V., Orendáč, M., Kaňuchová, M., Girman, V., Harničárova, M., Valíček, J., Šepelák, V., and Tóthová, E., A sustainable reaction process for phase pure LiFeSi2O6 with goethite as an iron source, Ceram. Int., 2020, vol. 46, pp. 14894–14901.
Ji, Y., Honma, T., and Komatsu, T., Crystallization of the Na2FexNi1-xP2O7 glass and ability of cathode for sodium-ion batteries, Front. Mater., 2020, vol. 7, pp. 1–9.
Honma, T., Oku, D., and Komatsu, T., Formation and its mechanism of copper metal layers at surface by annealing in reduced atmosphere in CuO-Li2O-Nb2O5-SiO2 glass, Solid State Ionics, 2009, vol. 180, pp. 1457–1462.
Komatsu, T., Design and control of crystallization in oxide glasses (review), J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2015, vol. 428, pp. 156–175.
Evstrop'ev, K.S. and Toropov, N.A., Khimiya kremniya i fizicheskaya khimiya silikatov (Silicon Chemistry and Physical Chemistry of Silicates), Moscow: Izdat. Liter. Stroit. Mater., 1950, pp. 60–62.
Mezentseva, L.P., Popova, V.F., Al’myashev, V.I., Lomanova, N.A., Ugolkov, V.L., Beshta, S.V., Khabenskii, V.B., and Gusarov, V.V., Phase and chemical transformations in the SiO2-Fe2O3(Fe3O4) system at various oxygen partial pressures, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem., 2006, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 118–125.
Holand, W. and Beall, G.H., Glass Ceramic Technology, Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2012.
Min’ko, N.I. and Zhernovaya, N.F., Some features of crystallization of glasses in the Na2O-FeO-SiO2 and Na2O-Fe2O3-SiO2 systems, Fiz. Khim. Stekla, 1987, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 496–501.
Min’ko, N.I. and Zhernovaya, N.F., Glass formation and properties of glasses in Na2O-FeO-SiO2 and Na2O-Fe2O3-SiO2 systems, Fiz. Khim. Stekla, 1985, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 415–419.
Min’ko, N.I. and Zhernovaya, N.F., Influence of additives of calcium, magnesium and aluminum oxides on aegirine crystallization in glasses of the Na2O–Fe2O3–SiO2 system, Fiz. Khim. Stekla, 1985, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 286–291.
Advanced Battery Materials, Sun, Ch.-W., Ed., New York: Wiley, 2019, pp. 171–173.
Heubner, C., Nikolowski, K., Reuber, S., Schneider, M., Wolter, M., and Michaelis, A., Recent insights into rate performance limitations of Li-ion batteries, Batter. Supercaps, 2021, vol. 4, pp. 268–285.
Rusan, V.V., Agafonov, D.V., Polyakova, L.S., and Dymshits, O.S., Synthesis of an electrode material for LIB based on Li-aegirine (LiFe3+Si2O6) by the ‘glass melt–ceramic’ method, in Fiziko-khimicheskie problemy vozobnovlyaemoi energetiki: sbornik trudov rossiiskoi konferentsii (Proceedings of the Russia Conference on Physical and Chemical Problems of Renewable Energy, St. Petersburg, Nov. 22–24, 2021), St., Petersburg: Politekh-press, 2021, pp. 68–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rusan, V.V., Alekseeva, I.P., Dymshits, O.S. et al. Phase Transformations and Electrochemical Properties of Heat-Treated Glasses with the Composition of Li-Aegirine. Glass Phys Chem 48, 558–569 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659622600405
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659622600405