Abstract
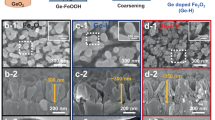
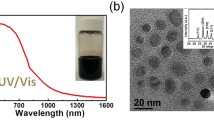
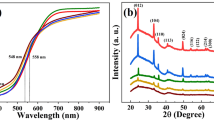
The recent accomplishments in using Sn or Ge, Mn and Ti-doped hematite photoanodes for solar water splitting are highlighted in this paper. Magnetron sputtering and hydrothermal methods were applied for depositing the alloyed films on Fluorine doped Tin Oxide (FTO) glasses. Results were compered by structural and morphology analysis using scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) images and XRD. Similarly, a comparison was done by using optical properties and photocatalytic activities. Doping elements for all samples illustrated higher photocurrent density to compare un-doped hematite. This research confirms that doped elements enhance the charge carriers and reduce the recombination losses, and it emphasizes that these treatment results in better photoelectrochemistry performance of Fe2O3 nanostructured photoanodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mao, S.S. and Shen, S., Hydrogen production: catalysing artificial photosynthesis, Nat. Photonics, 2013, vol. 7, pp. 944–946.
Fujishima, A. and Honda, K., Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode, Nature, 1972, vol. 238, pp. 37–38.
Sun, K., Shen, S., Liang, Y., Burrows, P.E., Mao, S.S., and Wang, D., Enabling silicon for solar-fuel production, Chem. Rev., 2014, vol. 14, pp. 8662–8719.
Murphy, A.B., Barnes, P.R.F., Randeniya, L.I.K., Plumb, I.C., Grey, I.E., Horne, M.D., and Glasscock, J.A., Efficiency of solar water splitting using semiconductor electrodes, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2006, vol. 31, pp. 1999–2017.
Azad, A., Kang, W., and Kim, S.J., Preparation and photoelectrochemical properties of Fe2O3–TiO2 based photoanode for water splitting, in Manufacturing Nanostructures, Waqar, A. and Nasar, A., Eds., One Central Press, UK, 2014, Ch. 3, pp. 79–107.
Yang, T.Y., Kang, H.Y., Sim, U., Lee, Y.J., Lee, J.H., Koo, B., Nam, K.T., and Joo, Y.C., A new hematite photoanode doping strategy for solar water splitting: oxygen vacancy generation, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, vol. 15, pp. 2117–2124.
Azad, A., Noh, E., Yun, K.S., Jeong, H.J., Jung, S.C., Kang, W.S., Moc, N.T., and Kim, S.J., Effect of doping of Fe into TiO2 layer in Fe2O3–TiO2–FTO system for high performance of water splitting, Adv. Sci. Technol. (Faenza, Italy), 2014, vol. 93, pp. 82–89.
Sivula, K., Zboril, R., Le Formal, F., Robert, R., Weidenkaff, A., Tucek, J., Frydrych, J., and Grätzel, M., Photoelectrochemical water splitting with mesoporous hematite prepared by a solution-based colloidal approach, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, vol. 132, pp. 7436–7444.
Zhen, C., Wang, L., Liu, L., Liu, G., Lu, G.Q., and Cheng, H.-M., Nonstoichiometric rutile TiO2 photoelectrodes for improved photoelectrochemical water splitting, Chem. Commun., 2013, vol. 49, pp. 6191–6193.
Pu, Y.C., Wang, G., Chang, K.D., Ling, Y., Lin, Y.K., Fitzmorris, B.C., Liu, C.M., Lu, X., Tong, Y., Zhang, J.Z., Hsu, Y.J., and Li, Y., Au nanostructure-decorated TiO2 nanowires exhibiting photoactivity across entire UV–visible region for photoelectrochemical water splitting, Nano Lett., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 3817–3823.
Wang, G., Ling, Y., Wang, H., Yang, X., Wang, C., Zhang, J.Z., and Li, Y., Hydrogen-treated WO3 nanoflakes show enhanced photostability, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, vol. 5, pp. 6180–6187.
Park, H.S., Lee, H.C., Leonard, K.C., Liu, G., and Bard, A.J., Unbiased photoelectrochemical water splitting in Z-scheme device using W/Mo-doped BiVO4 and Zn(x)Cd(1–x)Se, ChemPhysChem, 2013, vol. 14, pp. 2277–2287.
Lin, Y., Zhou, S., Sheehan, S.W., and Wang, D., Nanonet-based hematite heteronanostructures for efficient solar water splitting, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, vol. 133, pp. 2398–2401.
Mulmudi, H.K., Mathews, N., Dou, X.C., Xi, L.F., Pramana, S.S., Lam, Y.M., and Mhaisalkar, S.G., Controlled growth of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanorod array on fluorine doped tin oxide: synthesis and photoelectrochemical properties, Electrochem. Commun., 2011, vol. 13, pp. 951–954.
Launay, J.C. and Horowitz, G., Crystal growth and photoelectrochemical study of Zr-doped α-Fe2O3 single crystal, J. Cryst. Growth, 1982, vol. 57, pp. 118–124.
Kennedy, J.H. and Frese, K.W., Photooxidation of water at α-Fe2O3 electrodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1978, vol. 125, pp. 709–714.
Ling, Y., Wang, G., Wheeler, D.A., Zhang, J.Z., and Li, Y., Sn-Doped hematite nanostructures for photoelectrochemical water splitting, Nano Lett., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 2119–2125.
Morrish, R., Rahman, M., MacElroy, J.M.D., and Woldon, C.A., Activation of hematite nanorod arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting, ChemSus-Chem, 2011, vol. 4, pp. 474–479.
Van de Krol, R., Liang, Y., and Schoonman, J., Solar hydrogen production with nanostructured metal oxides, J. Mater. Chem., 2008, vol. 18, pp. 2311–2320.
Glasscock, J.A., Barnes, P.R.F., Plumb, I.C., and Savvides, N., Enhancement of photoelectrochemical hydrogen production from hematite thin films by the introduction of Ti and Si, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, vol. 111, pp. 16477–16488.
Mayer, M.T., Du, C., and Wang, D., Hematite/Si nanowire dual-absorber system for photoelectrochemical water splitting at low applied potentials, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, vol. 134, pp. 12406–12409.
Le Formal, F., Sivula, K., and Grätzel, M., The transient photocurrent and photovoltage behavior of a hematite photoanode under working conditions and the influence of surface treatments, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, vol. 116, pp. 26707–26720.
Zhang, M., Luo, W., Li, Z., Yu, T., and Zou, Z., Improved photoelectrochemical responses of Si and Ti codoped α-Fe2O3 photoanode films, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, vol. 97, 042105. doi 10.1063/1.3470109
Maeda, K., Teramura, K., Lu, D., Takata, T., Saito, N., Inoue, Y., and Domen, K., Photocatalyst releasing hydrogen from water, Nature, 2006, vol. 440, p. 295.
Varghese, O.K., Paulose, M., LaTempa, T.J., and Grimes, C.A., High-rate solar photocatalytic conversion of CO2 and water vapor to hydrocarbon fuels, Nano Lett., 2009, vol. 9, pp. 731–737.
Chen, X. and Mao, S.S., Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications, Chem. Rev., 2007, vol. 107, pp. 2891–2959.
Ohmori, T., Takahashi, H., Mametsuka, H., and Suzuki, E., Photocatalytic oxygen evolution on α-Fe2O3 films using Fe3+ ion as a sacrificial oxidizing agent, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2000, vol. 2, pp. 3519–3522.
Ling, Y. and Li, Y., Review of Sn-doped hematite nanostructures for photoelectrochemical water splitting, Part. Part. Syst. Charact., 2014, vol. 31, pp. 1113–1121.
Bohn, C.D., Agrawal, A.K., Walter, E.C., Vaudin, M.D., Herzing, A.A., Haney, P.M., Talin, A.A., and Szalai, V.A., Effect of tin doping on α-Fe2O3 photoanodes for water splitting, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, vol. 116, pp. 15290–15296.
Sivula, K., Le Formal, F., and Grätzel, M., Solar water splitting: Progress using hematite (α-Fe2O3) photoelectrodes, ChemSusChem, 2011, vol. 4, pp. 432–449.
Sing, G., Chiam, Y., Kumar, M.H., Bassi, P.S., Seng, H.L., Barber, J., and Wong, L.H., Improving the efficiency of hematite nanorods for photoelectrochemical water splitting by doping with manganese, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, vol. 6, pp. 5852–5859.
Liao, P. and Carter, E.A., Hole transport in pure and doped hematite, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, vol. 112, 013701. doi 10.1063/1.4730634
Balko, B.A. and Clarkson, K.M., The effect of doping with Ti(IV) and Sn(IV) on oxygen reduction at hematite electrodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2001, vol. 148, pp. E85–E91.
Hiralal, P., Saremi-Yarahmadi, S., Bayer, B.C., Wang, H., Hofmann, S., Upul Wijayantha, K.G., Amaratunga, G.A.J., Nanostructured hematite photoelectrochemical electrodes prepared by the low temperature thermal oxidation of iron, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2011, vol. 95, pp. 1819–1825.
Chernomordik, B.D., Russell, H.B., Cvelbar, U., Jasinski, J.B., Kumar, V., Deutsch, T., and Sunkara, M.K., Photoelectrochemical activity of asgrown,α-Fe2O3 nanowire array electrodes for water splitting, Nanotecnology, 2012, vol. 23, 194009. doi 10.1088/0957-4484/23/19/194009
Vincent, T., Gross, M., Dotan, H., and Rothschild, A., Thermally oxidized iron oxide nanoarchitectures for hydrogen production by solar-induced water splitting, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012, vol. 37, pp. 8102–8109.
Yang, B., Qin, G., Pei, W., Li, S., Ren, Y., and Ishio, S., Effect of phosphor addition on intergranular exchange coupling of Co–Pt thin films, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 398–402.
Li, S., Cai, J., Mei, Y., Ren, Y., and Qin, G., Thermal oxidation preparation of doped hematite thin films for photoelectrochemical water splitting, Int. J. Photoenergy, 2014, pp. 794370–794376. doi 10.1155/2014/794370
Deng, J., Zhong, J., Pu, A., Zhang, D., Li, M., Sun, X., and Lee, S.T., Ti-doped hematite nanostructures for solar water splitting with high efficiency, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, vol. 112, p. 084312. doi 10.1063/1.4759278
Wen, X., Wang, S., Ding, Y., Lin Wang, Z., and Yang, S., Controlled growth of large-area, uniform, vertically aligned arrays of α-Fe2O3 nanobelts and nanowires, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, vol. 109, pp. 215–220.
Wei, Q., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., Zhou, Q., and Zhu, Y., Enhanced photocatalytic activity of porous α-Fe2O3 films prepared by rapid thermal oxidation, J. Phys. D, 2008, vol. 41, no. 20, p. 20002. doi 10.1088/0022-3727/41/20/202002
Prabhakar, R.R., Mathews, N., Jinesh, K.B., Karthik, K.R.G., Pramana, S.S., Varghese, B., Sow, C.H., and Mhaisalkar, S., Efficient multispectral photodetection using Mn doped ZnO nanowires, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, vol. 22, pp. 9678–9683.
Dotan, H., Sivula, K., Gratzel, M., Rothschild, A., and Warren, S.C., Probing the photoelectrochemical properties of hematite (α-Fe2O3) electrodes using hydrogen peroxide as a hole scavenger, Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, vol. 4, pp. 958–964.
Zhang, H., Chen, G., and Bahnemann, D.W., Photoelectrocatalytic materials for environmental applications, J. Mater. Chem., 2009, vol. 19, pp. 5089–5121.
Zhang, X. and Zhang, L., Electronic and band structure tuning of ternary semiconductor photocatalysts by self doping: The case of BiOI, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, vol. 114, pp. 18198–18206.
Gassenbauer, Y. and Klein, A., Electronic and chemical properties of tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) surfaces and ITO/ZnPc interfaces studied in-situ by photoelectron spectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, vol. 110, pp. 4793–4801.
Greiner, M.T. and Lu, Z.H., Thin-film metal oxides in organic semiconductor devices: their electronic structures, work functions and interfaces, NPG Asia Mater., 2013, vol. 5, p. e55. doi 10.1038/am.2013.29
Sieber, K.D., Sanchez, C., Turner, J.E., and Somorjai, G.A., Preparation, characterization and photoelectronic properties of germanium-substituted Fe2O3 single crystals, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1985, vol. 81, pp. 1263–1274.
Liao, P., Toroker, M.C., and Carter, E.A., Electron transport in pure and doped hematite, Nano Lett., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 1775–1781.
Jiang, J.Z., Lin, R., Nielsen, K., Mørup, S., Rickerby, D.G., and Clasen, R., Interstitial positions of tin ions in α-(FerichSn)2O3 solid solutions prepared by mechanical alloying, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1997, vol. 55, pp. 14830–14835.
Sorescu, M., Diamandescu, L., Tarabasanu-Mihaila, D., Teodorescu, V.S., and Howard, B.H., Hydrothermal synthesis and structural characterization of (1–x)α-Fe2O3–xSnO2 nanoparticles, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2004, vol. 65, pp. 1021–1029.
Klahr, B., Gimenez, S., Fabregat-Santiago, F., Bisquert, J., and Hamann, T.W., Photoelectrochemical and impedance spectroscopic investigation of water oxidation with “Co–Pi”-coated hematite electrodes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, vol. 134, pp. 16693–16700.
Shimizu, K., Lasia, A., and Boily, J.F., Electrochemical impedance study of the hematite/water interface, Langmuir, 2012, vol. 28, pp. 7914–7920.
Aroutiounian, V.M., Arakelyan, V.M., Shahnazaryan, G.E., Hovhannisyan, H.R., Wang, H., and Turner, J.A., Photoelectrochemistry of tin-doped iron oxide electrodes, Solar Energy, 2007, vol. 81, pp. 1369–1376.
Sanchez, H.L., Steinfink, H., and White, H.S., Solid solubility of Ge, Si, and Mg in Fe2O3 and photoelectric behavior, J. Solid State Chem., 1982, vol. 41, pp. 90–96.
Tilley, S.D., Cornuz, M., Sivula, K., and Gratzel, M., Light-induced water splitting with hematite: Improved nanostructure and iridium oxide catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, vol. 49, pp. 6405–6408.
Wang, G.M., Li, Y.C., Wheeler, D.A., George, K.E.N., Horsley, K., Heske, C., Zhang, J.Z., and Li, Y., Facile synthesis of highly photoactive α-Fe2O3-based films for water oxidation, Nano Lett., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 3503–3509.
Jang, J.S., Lee, J., Ye, H., Fan, F.R.F., and Bard, A.J., Rapid screening of effective dopants for Fe2O3 photocatalysts with scanning electrochemical microscopy and investigation of their photoelectrochemical properties, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, vol. 113, pp. 6719–6724.
Tauc, J., Grigorovici, R., and Vancu, A., Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium, Phys. Status Solidi B, 1966, vol. 15, pp. 627–637.
Bryan, J.D. and Gamelin, D.R., Doped semiconductor nanocrystals: Synthesis, characterization, physical properties, and applications, in Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, Karlin, K.D., Ed., Seattle: Univ. Washington, 2005, vol. 54, pp. 47–126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azad, A., Kim, SJ. Enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting efficiency: Increasing the photo anode’s properties by doping on the fluorine doped tin oxide glass surface. Glass Phys Chem 42, 458–472 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659616050023
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659616050023