Abstract
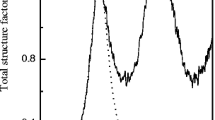
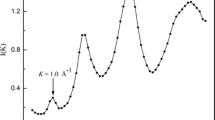
Chalcogenide Ge20Se80 glass was prepared using the melt-quench technique. The radial distribution function is obtained from X-ray diffraction data in the scattering vector interval 0.28 ≤ K ≤ 6.87 Å−1. Reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) simulations are useful to compute the partial pair distribution functions, partial structure factors, S ij(K), and total structure factor. Values of r 1/r 2 ratio and bond angle (Θ) indicate that Ge(Se½)4 tetrahedra units connected by chains of the chalcogen atoms are present. The partial structure factors have shown that homopolar Ge—Ge and Se—Se bonds are behind the appearance of the first sharp diffraction peak in the total structure factor. Tetrahedral Ge(Se½)4 structural units connected by Se-Se chains have been confirmed by the simulated values of the partial coordination numbers and the bond angle distributions. Finally, Raman spectra measurements have strongly supported the conclusions obtained either from the calculated Fourier data or from RMC simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inam, F., Shatnawi, M.T., Tafen, D., Billinge, S.J.L., Chen, P., and Drabold, D.A., An intermediate phase in GexSe1 − x glasses: Experiment and simulation, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2007, vol. 19, no. 45, p. 455206.
Sharma, D., Sampath, S., Lalla, N.P., and Awasthi, A.M., Mesoscopic organization and structural phases in network-forming GexSe1 − x glasses, Physica B (Amsterdam), 2005, vol. 357, pp. 290–298.
Wang, Y., Ohata, E., Hosokawa, S., Sakurai, M., and Matsubara, E., Intermediate-range order in glassy GexSe1 − x around the stiffness transition composition, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2004, vol. 337, no. 1, pp. 54–61.
Tafen, D. and Drabold, D.A., Models and modeling schemes for binary IV—VI glasses, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter, 2005, vol. 71, no. 5, pp. 54206–54220.
Rao, N.R., Krishna, P.S.R., Basu, S., Dasannacharya, B.A., Sangunni, K.S., and Gopal, E.S.R., Structural correlations in GexSe1 − x glasses—A neutron diffraction study, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1998, vol. 240, nos. 1–3, pp. 221–231.
Machado, K.D., de Lima, J.C., Campos, C.E.M., Gasperini, A.A.M., de Souza, S.M., Maurmann, C.E., Grandi, T.A., and Pizani, P.S., Reverse Monte Carlo simulations and Raman scattering of an amorphous GeSe alloy produced by mechanical alloying, Solid State Commun., 2005, vol. 133, no. 6, pp. 411–416.
Hosokawa, S., Wang, Y., Sakurai, M., Bèrar, J.-F., Pilgrim, W.-C., and Murase, K., Rigidity transitions and intermediate structures of Ge–Se glasses—An anomalous X-ray scattering study, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B, 2003, vol. 199, pp. 165–168.
Gulbrandsen, E., Johnsen, H.B., Endregaard, M., Grande, T., and Stølen, S., Short-range order in Serich Ge–Se glasses—An EXAFS study, J. Solid State Chem., 1999, vol. 145, pp. 253–259.
Susman, S., Price, D.L., Volin, K.J., Dejus, R.J., and Montague, D.G., Intermediate-range order in binary chalcogenide glasses: The first sharp diffraction peak, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1988, vol. 106, pp. 26–29.
Salmon, P.S. and Petri, I., Structure of glassy and liquid GeSe2, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2003, vol. 15, no. 16, pp. S1509–S1528.
Warren, B.E., Krutter, H., and Morningstar, O., Fourier analysis of X-ray patterns of vitreous SiO2 and B2O2, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1936, vol. 19, nos. 1–12, pp. 202–206.
McGreevy, R.L., Reverse Monte Carlo modelling, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2001, vol. 13, pp. R877–R913.
McGreevy, R.L. and Pusztai, L., Reverse Monte Carlo simulation: A new technique for the determination of disordered structures, Mol. Simul., 1988, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 359–367.
Faber, T.E. and Ziman, J.M., A theory of the electrical properties of liquid metals, Philos. Mag., 1965, vol. 11, no. 109, pp. 153–173.
Elliott, S.R., Physics of Amorphous Materials, 2nd ed. New York: Longman, 1990.
Moharram, A.H. and Abdel-Basit, A.M., Structural correlations of AsGeSe glasses, Physica A (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2005, vol. 358, nos. 1–4, pp. 279–284.
Szczygielska, A., Burian, A., Dore, J.C., Honkimäki, V., and Duber, S., Local structure of saccharoseand anthracene-based carbons studies by wide-angle highenergy X-ray scattering, J. Alloys Compd., 2004, vol. 362, nos. 1–2, pp. 307–313.
Keen, D.A. and McGreevy, R.L., Structural modelling of glasses using reverse Monte Carlo simulation, Nature (London), 1990, vol. 344, pp. 423–425.
http://wwwisis2.isis.rl.ac.uk/rmc.
Johnson, R.W., Price, D.L., Susman, S., Arai, M., Morrison, T.I., and Shenoy, G.K., The structure of silicon-selenium glasses: I. Short-range order, J. NonCryst. Solids, 1986, vol. 83, pp. 251–271.
Kaplow, R., Strong, S.L., and Averbach, B.L., Radial density functions for liquid mercury and lead, Phys. Rev., 1965, vol. 138, no. 5A, pp. A1336–A1345.
Machado, K.D., de Lima, J.C., Campos, C.E.M., Grandi, T.A., and Pizani, P.S., Reverse Monte Carlo simulations and Raman scattering of an amorphous GeSe4 alloy produced by mechanical alloying, J. Chem. Phys., 2004, vol. 120, no. 1, pp. 329–336.
Fuoss, P.H., Eisenberger, P., Warburton, W.K., and Bienestock, A., Application of differential anomalous X-ray scattering to structural studies of amorphous materials, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1981, vol. 46, no. 23, pp. 1537–1540.
Dwivedi, P.K., Tripathi, S.K., Pradhan, A., Kulkarni, V.N., and Agarwal, S.C., Raman study of ion irradiated GeSe films, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2000, vol. 266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moharram, A.H. Short-range order of germanium selenide glass. Glass Phys Chem 41, 453–459 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659615050090
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659615050090