Abstract
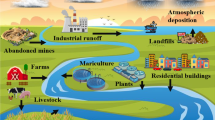
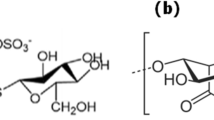
Calcium alginate nanoparticles (CANPs) were synthesized to remove lead ion [Pb(ІІ)] as pollutant of environment from aqueous solutions. The produced CANPs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), particle size analysis (PSA) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). Various factors, which affected adsorption efficiency of lead ions by CANPs, such as pH (pH from 1 to 8), initial ions concentration (in the range of 25 to 125 mg L–1), contact time (varying from 5 to 120 min), and adsorbent dose (50 to 500 mg L–1), were investigated for determination of optimum experimental conditions. The result of tests showed that the investigated factors had significant effects on adsorption of Pb(ІІ) ions and the maximum adsorption percentage of lead at pH = 6~7, 25 mg L–1 initial ions concentration, contact time of more than 140 min. and for adsorbent dose at 500 mg L–1. Also these results demonstrated the effective adsorption of Pb2+ ions by synthesized CANPs that occurred due to a high surface area of CANPs and the presence of anionic carboxylate functional groups and allowed effective absorbing and removing Pb(ІІ) ions from aqueous solutions. Thus, these nanoparticles were able to remove over 99% of lead ions from solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baturova, L.P., et al., Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2015, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 59–64.
Tarasenko, S.A., et al., Russ. J. Appl. Chem., vol. 80, no. 3, pp. 372–375.
Li, Z., et al., Sci. Total Environ., 2014, vols. 468, 469, pp. 843–53.
Tchounwou, P.B., et al., Heavy Metals Toxicity & Environment. EXS, 2012, vol. 101, pp. 133–164.
Markus, J. and McBratney, A.B., Environ. Int., 2001, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 399–411.
Silbergeld, E.K., Waalkes, M., and Rice, J.M., Am. J. Ind. Med., 2000, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 316–23.
White, J.M., Postgraduate Med. J., 1975, vol. 51, no. 601, pp. 755–756.
Telisman, S., et al., Am. J. Ind. Med., 2004, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 446–54.
Flora, G., Gupta, D. and Tiwari, A., Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 2012, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 47–58.
Moradi, O., et al., Iranian J. Env. Health Sci. & Eng., 2012, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 31–31.
Barakat, M.A., Arabian J. Chem., 2011, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 361–377.
Amin, M.T., Alazba, A.A. and Manzoor, U., Adv. Mater. Sci. & Eng., 2014, p. 24.
Qu, X., Alvarez, P.J.J., and Li, Q., Water Research, 2013, vol. 47, no. 12, pp. 3931–3946.
Sobhanardakani, S., et al., Iranian J. Toxicol., 2014, vol. 8, no. 26, pp. 1145–1151.
John, M.J. and Thomas, S., Chemistry, R.S.O. Natural Polymers, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2012.
Lee, K.Y. and Mooney, D.J., Progress in Polymer Science, 2012, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 106–126.
Goh, C.H., Heng, P.W.S., and Chan, L.W., Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 1–12.
Sun, J. and Tan, H., Alginate–Based Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine Applications, Materials, 2013, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 1285–1309.
Daemi, H. and Barikani, M., Scientia Iranica, 2012, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 2023–2028.
Callow, J.A., et al., Colloids & Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2003, vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 315–321.
Shakeri, A., et al., Iranian J. Chem. & Chem. Eng., 2012, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 45–50.
Shashkova, I.L., et al., Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2009, vol. 82, no. 6, pp. 940–946.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khezri, M., Jalilpour, Y., Abedi, S. et al. Synthesis of calcium alginate nanoparticles for removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions. Russ J Appl Chem 89, 1177–1182 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427216070181
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427216070181