Abstract
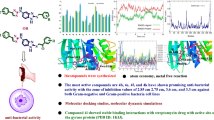
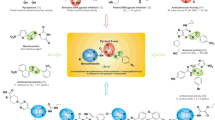
A series of novel 1,4-benzodioxan derivatives containing Schiff base are synthesized by the method of splicing active substructures. All compounds are assayed for antimicrobial activity. The preliminary results indicate that most of the products demonstrate higher antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria strains than Gram-positive bacteria strains. Compounds 4d and 4m exhibit better antibacterial activity against E. coli (MIC = 0.78 and 0.17 μg/mL), respectively; compound 4g displays better antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa (MIC = 0.78 μg/mL). Eleven common antibacterial targets are selected for molecular docking of target compounds. The results demonstrate that all target compounds have the strongest binding energy to Tyrosine-tRNA synthetase (-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY, kcal/mol: 47.1486 and 47.3776). Therefore, it is speculated that the target compounds can be used as novel tyrosine-tRNA synthetase inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischbach, M.A. and Walsh, C.T. Science, 2009, vol. 325, p. 1089. doi https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176667
Khalilullah, H., Ahsan, M.J., Hedaitullah, M., Khan, S., and Ahmed, B., Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, vol. 12, p. 789. doi https://doi.org/10.2174/138955712801264800
Ahmed, B., Ahsan, M.J., Khan, S., Khalilullah, H., Anti-Infective Agents 2012, vol. 10, p. 142. doi https://doi.org/10.2174/2211362611208020142
Song, X., Yang, Y., Zhao, J., and Chen, Y., Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, vol. 62, p. 1110. doi https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c14-00485
Yang, F., Han, J., Wang, Y., Chen, F., Chinese J. Appl. Chemi. 2015, vol. 32, p. 392. doi https://doi.org/10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2015.04.140286
More, P.G., Bhalvankar, R.B., and Patter, S.C.J., Indian Chem. Soc. 2001, vol. 78, p. 474.
Desai, S.B., Desai, P.B., and Desai, K.R., Heterocycl. Commun. 2001, vol. 7, p. 83. doi 10.1515/HC
Samadhiya, S. and Halve, A., Orient J. Chem. 2001, vol. 17, p. 119.
Kabeer, A.S., Baseer, M.A., and Mote, N.A., Asian. J. Chem. 2001, vol. 13, p. 496.
El-Masry, A.H., Fahmy, H.H., and Abdelwahed, S.H.A., Molecules 2000, vol. 5, p. 1429. doi https://doi.org/10.3390/51201429
Oliva, M.A., Trambaiolo, D., and Löwe, J., J. Mol. Biol., 2007, vol. 373, p. 1229. doi https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.056
Sheldrick, G.M., SHELXS 97. Program for Crystal Structure Determinations, University of Göttingen, Germany, 1997.
Wu, G., Robertson, D.H., Brooks, C.L. III, and Vieth, M., J. Comput. Chem., 2003, vol. 24, p. 1549. doi https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.10306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
Supplementary materials are available from authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HY., Wang, TR., Sheng, GH. et al. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking of 1,4-Benzodioxan Derivatives as Potential Antibacterial Agents. Russ J Gen Chem 88, 2601–2610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363218120228
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070363218120228