Abstract
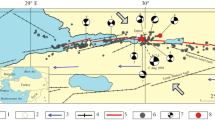
The results of modeling the stress-strain state for the epicentral zone of the earthquake that occurred on December 26, 2003 in the southeast of Iran in the city of Bam, Kerman province, before and after the rupture are presented. It is shown that the source of the earthquake is located in the zone of high stresses, whereas the emerged rupture traces this zone on the surface and corresponds to its length. The aftershocks are localized in the area of the maximal stress drop after the formation of the rupture. The drop in the stress stimulates the release of the accumulated tectonic stresses during the subsequent aftershock process. The obtained results can be useful for the deterministic approach to seismic hazard assessment and forecasting, as well as for setting up the geophysical observations intended for forecasting the strong crustal earthquakes in the continental regions.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Azadmanesh, A., Gheitanchi, M.R., Azadmanesh, M., and Babaei, Mahani A.R., Analysis of the Bam earthquake, SE Iran, on 26 December 2003, The 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China, 2008.
Kanamori, H., Mechanics of earthquakes, Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 1994, vol. 22, pp. 207–237.
Manafpour, A.R., The Bam, Iran Earthquake of 26 December 2003, Field Investigation Report, Halcrow EEFIT, Report 59, 2004.
Morozov, V.N. and Manevich, A.I., Modeling the stressstrain state in the epicentral zone of the earthquake of 26.01.2001, M = 6.9 (India), Geofiz. Issled., 2016, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 23–35. doi 10.21455/gr2016.4–2
Morozov, V.N. and Manevich, A.I., Modeling the stressstrain state in the epicentral zone of the earthquake of 13.03.1992, Ms = 6.8 (Turkey), Geofiz. Issled., 2018, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 17–29. https://doi.org/10.21455/gr2018.1-2
Morozov, V.N., Kolesnikov, I.Yu., Belov, S.V., and Tatarinov, V.N., Stress-strain state of Nizhnekanskii massif—a probable region for nuclear waste disposal, Geoekologiya, 2008, no. 3, pp. 232–243.
Morozov, V.N., Kolesnikov, I.Yu., and Tatarinov, V.N., Modeling the hazard levels of stress-strain state in the structural blocks of the Nizhnekanskii granitoid massif: selecting the sites for nuclear waste disposal, Geoekologiya, 2011, no. 6, pp. 524–542.
Morozov, V.N., Kolesnikov, I.Yu., and Tatarinov, V.N., Modeling the hazard levels of stress-strain state in structural blocks in Nizhnekanskii granitoid massif for selecting nuclear waste disposal sites, Water Resour., 2012, vol. 39, no. 7, pp. 756–769. doi 10.1134/S009780781207007X
Rogozhin, E.A., The tectonics of source zones of North Eurasia—strong earthquakes of the end of the XX century, Ross. Zh. Nauk Zemle, 2000, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 37–62.
Shebalin, N.V., Sil’nye zemletryaseniya. Izbrannye trudy (Strong Earthquakes. Selected Works), Moscow: Izd-vo Akademii gornykh nauk, 1997.
Sherman, S.I., Seminskii, S.A., Bornyakov, S.A., Buddo, V.Yu., Lobatskaya, R.M., Adamovich, A.N., Truskov, V.A., and Babichev, A.A., Razlomoobrazovanie v litosfere: zony sdviga (Faulting in the Lithosphere: Shear Zones), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1992.
Talebian, M., Fielding, E.J., Funning, G.J., Ghorashi, M., Jackson, J., Nazari, H., Parsons, B., Priestley, K., Rosen, P.A., Walker, R., and Wright, T.J., The 2003 Bam (Iran) earthquake: rupture of a blind strike-slip fault, Geophys. Rev. Lett., 2004, vol. 31, L11611. doi 10.1029/2004GL02020058
Tatar, M., Hatzfeld, D., Moradi, A.S., Paul, A., Farahbod, A.M., and Mokhtari. M., Aftershocks study of the 26 December 2003 Bam earthquake, J. Seismol. Earthquake Eng., 2004, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 23–31.
Zabrodin, V.Yu., Rybas, O.V., and Gil’manova, G.Z., Razlomnaya tektonika materikovoi chasti Dal’nego Vostoka Rossii (Fault Tectonics of the Continental Part of Russian Far East), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2015.
Zubkov, A.V., Crustal stress state of the Urals, Litosfera, 2002, no. 3, pp. 3–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.N. Morozov, V.N. Tatarinov, I.Yu. Kolesnikov, A.I. Manevich, 2018, published in Fizika Zemli, 2018, No. 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morozov, V.N., Tatarinov, V.N., Kolesnikov, I.Y. et al. Modeling the Stress-Strain State in the Epicentral Zone of a Strong Earthquake in Iran (December 26, 2003, Mw = 6.6). Izv., Phys. Solid Earth 54, 602–611 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351318040080
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351318040080