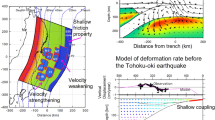
Abstract
The model of elastic rebound of thin plates is considered to account for GPS-inferred surface deformation of plates during subduction earthquakes on the example of the M9 earthquake that occurred in Japan in 2011. Due to the fact that the oceanic plate moves together with a great mass of the convective mantle, it dips into the mantle at constant velocity all the time, both during the earthquakes and in the periods between them, although its coupling with the continental plate changes. The edge of the continental plate behaves as an elastic plate that permanently bends under the action of the friction force on contact with the diving oceanic plate. The bent plate unbends after the earthquake. This leads to its thrusting over the subducting oceanic plate. As a result, the island plate moves towards the ocean, its island part sinks, and the oceanic plate uplifts leading to a tsunami. The coordinates and magnitudes of the rise and subsidence correspond to the universal relations in the elastic plate model. The breaking of coupling of the continental plate with the submarine mountains and a basaltic plateau of the dipping plate is considered as a possible explanation of the anomalous properties of the strongest earthquakes. The main earthquake can be produced by partial destruction of a plateau or a large mountain. After this, the locked plates become free along a great area in an avalanche-like manner, and the friction of rest gives place to sliding friction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keilis-Borok, V., Gabrielov, A., and Soloviev, A., Geo-Complexity and Earthquake Prediction, in Encyclopedia of Complexity and Systems Science, Meyers, R., Ed., New York: Springer, 2009, pp. 4178–4194. doi: 10.1007/978-0387-30440-3-246
Levitt, D.A. and Sandwell, D.T., Lithospheric Bending at Subduction Zones Based on Depth Soundings and Satellite Gravity, J. Geophys. Res., 1995, vol. 100, pp. 379–400.
Miura, S., Takahashi, N., Nakanishi, A., Ito, A., Kodaira, S., Tsuru, T., and Kaneda, Y., Seismic Velocity Structure off Miyagi Fore-Arc Region, Japan Trench, using Ocean Bottom Seismographic Data, Frontier Res. Earth Evolut., 2001, vol. 1, pp. 337–340.
Okada, Y., Surface Deformation due to Shear and Tensile Faults in a Half-Space, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am., 1985, vol. 75, pp. 1135–1154.
Pacific Ocean Floor Map, National Geographic, 1969, http://www.maps.com/map.aspx?pid=15902.
Poster of the Great Tohoku Earthquake (northeast Honshu, Japan) of March 11, 2011—Magnitude 9.0, US Geological Survey, 2011, http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqar-chives/poster/2011/20110311.php.
Preliminary Geodetic Slip Model of the 2011 M9.0 Tohokuchiho Taiheiyo-oki Earthquake, ARIA team at JPL and Caltech, 2011. http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/world/japan/031111_M9.0prelim_geodetic_slip.php.
Rogozhin, E.A., Japan Tohoku 11.03.2011 (M = 9.0) Earthquake Source Structure, Its Macroseismic, Seismological, and Geodynamic Manifestations, Probl. Eng. Seismol., 2011, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 5–20.
Sato, M., Ishikawa, T., Ujihara, N., Yoshida, Sh., Fujita, M., Mochizuki, M., and Asada, A., Supporting Online Material for Displacement above the Hypocenter of the 2011 Tohoku-Oki Earthquake, http://www.sciencemag. org/content/suppl/2011/05/18/science.1207401.DC1/Sato. SOM.pdf
Savage, J.C., A Dislocation Model for Strain Accumulation and Release at a Subduction Zone, J. Geophys. Res., 1983, vol. 88, pp. 4984–4996.
Simons, M., Minson, S., Sladen, A., Ortega, F., Jiang, J., Owen, S., Meng, L., Ampuero, J.-P., Wei, Sh., Chu, R., Helmberger, D., Kanamori, H., Hetland, E., Moore, A., and Webb, F., The 2011 Magnitude 9.0 Tohoku-Oki Earthquake: Mosaicking the Megathrust from Seconds to Centuries, http://www.sciencemag.org/content/early/2011/05/18/science.1206731.full.pdf
Tectonic Plates Boundaries, Wikimedia Commons, 2006, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tectonic_plates_boundaries_detailed-fr.svg
Trubitsyn, V.P. and Rykov, V.V., Mechanism of Formation of an Inclined Subduction Zone, Izv. Phys. Earth, 1997, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 427–437.
Trubitsyn, V.P. and Rykov, V.V., A numerical Model of Marginal Seas and Japan Islands Formation Caused by Eurasia Moving to a Subduction Zone, Comput. Seismol. Geodynam., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 208–215.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Geodynamic Model of the Evolution of the Pacific Ocean, Izv. Phys. Earth, 2006, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 93–114.
Tsuji, H., Sendai M9.0 Earthquake Information, March 11, 2011, http://geodesy.unr.edu/sendai_20110311.html
Turcotte, D. and Schubert, G., Geodynamics, New York: Wiley, 1982.
Zhao, D., Wang, Z., Umino, N., and Hasegawa, A., Tomographic Imaging Outside a Seismic Network: Application to the Northeast Japan Arc, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am., 2007, vol. 97, pp. 1121–1132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.P. Trubitsyn, 2012, published in Fizika Zemli, 2012, No. 2, pp. 3–13.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trubitsyn, V.P. Bending deformations of plates in the model of strong subduction earthquakes. Izv., Phys. Solid Earth 48, 93–103 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351312010119
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351312010119