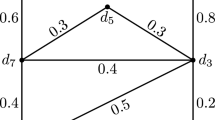
Abstract
Changes in the values of the maximal permissible flows that can be transmitted between nodes in the case of network damage are analyzed through computational experiments. At the initial stage, the maximal single-product flow is independently determined for each pair of source–sink vertices. The maximal flow vector is used to estimate the functional capability limit of the original, intact network. In the course of computational experiments, each damage from the given set is considered sequentially; for all source–sink pairs, the maximal flows in the damaged network are found. For each pair of nodes, all damage are determined for which the maximal flow is either zero or less than the permissible value. Based on the data obtained, diagrams of possible damage for all pairs of source–sink are formed. Computational experiments are carried out for networks with radial-ring structures and coincident sets of nodes. The resulting diagrams allow us to compare and find the most vulnerable pairs with nondominated vector damage estimates.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yu. E. Malashenko and I. A. Nazarova, “Analysis of critical damage in the communication network. I. Model and computational experiment,” J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 59, 745 (2020).
Yu. E. Malashenko and I. A. Nazarova, “Analysis of critical damage in the communication network. II. Guaranteed functional performance estimates,” J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 59, 918 (2020).
Yu. B. Germeier, Introduction to the Theory of Operations Research (Nauka, Moscow, 1971) [in Russian].
J. M. Danskin, The Theory of Max-Min and its Application to Weapons Allocation Problems (Springer, Berlin, 1967).
J. J. Cochran, L. A. Cox, Jr., P. Keskinocak, et al., Wiley Encyclopedia of Operations Research and Management Science (Wiley, New York, 2010).
Yu. E. Malashenko, I. A. Nazarova, and N. M. Novikova, “Express analysis and aggregated representation of the set of reachable flows for a multicommodity network system,” J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 58, 889 (2019).
P. Jensen and W. J. Barnes, Network Flow Programming (Wiley, New York, 1980).
T. H. Grubesic, T. C. Matisziw, A. T. Murray, et al., “Comparative approaches for assessing network vulnerability,” Int. Region. Sci. Rev. 31, 88 (2008).
A. T. Murray, “An overview of network vulnerability modeling approaches,” Geo J. 78, 209–221 (2013).
J. Johansson, “Risk and vulnerability analysis of interdependent technical infrastructures. Addressing sociotechnical systems,” Doctoral Thesis (Lund Univ., Lund, 2010).
T. Gomes, C. Esposito, D. Hutchison, et al., “Survey of strategies for communication networks to protect against large-scale natural disasters,” in Proceedings of the International Workshop on Reliable Networks Design and Modeling RNDM, Halmstad, 2016, pp. 11–22.
J. O. Royset and R. K. Wood, “Solving the bi-objective maximum-flow network-interdiction problem,” INFORMS J. Comput. 19, 175–184 (2007).
J. Walteros and P. Pardalos, “Selected topics in critical element detection,” Optimiz. Appl. 71, 9–26 (2012).
Yu. E. Malashenko, I. A. Nazarova, and N. M. Novikova, “An approach to the analysis of possible structural damages in multicommodity network systems,” Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 59, 1562 (2019).
A. Veremyev, O. A. Prokipyev, and E. L. Pasiliao, “Critical nodes for distance-based connectivity and related problems in graphs,” Networks 66, 170–195 (2015).
M. Ventresca, K. R. Harrison, and B. M. Ombuki-Berman, “The bi-objective critical node detection problem,” Eur. J. Oper. Res. 265, 895–908 (2018).
J. Li, P. M. Pardalos, B. Xin, and J. Chen, “The bi-objective critical node detection problem with minimum pairwise connectivity and cost: Theory and algorithms,” Soft Comput. 23, 1–16 (2019).
M. Lalou, M. A. Tahraoui, and H. Kheddouci, “The critical node detection problem in networks: A survey,” Comput. Sci. Rev. 28, 92–117 (2018).
A. Kuhnle, N. P. Nguyen, T. N. Dinh, et al., “Vulnerability of clustering under nodes failure in complex networks,” Social Network Anal. Mining 7, 8–24 (2017).
Yu. E. Malashenko, I. A. Nazarova, and N. M. Novikova, “Analysis of cluster damages in network systems,” Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 60, 341 (2020).
Th. H. Cormen, Ch. Leiserson, R. L. Rivest, et al., Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd ed. (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malashenko, Y.E., Nazarova, I.A. Analysis of Critical Damage in the Communication Network: III. Analysis of Internode Flows. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 60, 576–584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064230721030102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064230721030102