Abstract
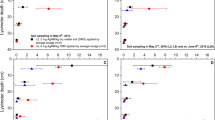
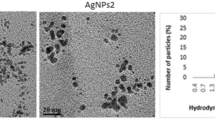
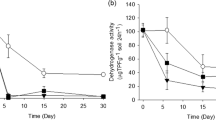
The ecotoxicity of Ag particles of different size has been assessed by microbiological, biochemical, and phytotoxic indicators for the upper layer (0–20 cm) of ordinary chernozem (Haplic Chernozem) in a laboratory model experiment. The effect has been studied of nano- (10 and 100 nm) and microparticles (1000 nm) of Ag at concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 mg/kg on the biological parameters of ordinary chernozem 30 days after contamination: the activity of catalase, dehydrogenases, ferrireductase, urease, peroxidase, polyphenol oxidase, invertase, phosphatase, the total number of bacteria, the abundance of bacteria of Azotobacter genus, the number of germinated seeds and the length of radish roots. It was found that the ecotoxicity of Ag particles depended on their size: in most cases, Ag particles 10 nm in size had a stronger ecotoxic effect on the biological parameters than particles 100 and 1000 nm in size. There were no significant differences in the ecotoxicity of 100 and 1000 nm Ag particles. The difference in the effects of Ag particles of different sizes increased with increasing Ag concentration in the soil: the higher the Ag concentration was in the soil (from 1 to 100 mg/kg), the more pronounced the difference was in ecotoxicity between 10 nm Ag particles and 100 and 1000 nm Ag particles. Phytotoxic indicators were more sensitive to contamination by Ag nanoparticles at all concentrations studied (1, 10 and 100 mg/kg); the total number of bacteria, invertase and phosphatase activity at 10 and 100 mg/kg; the abundance of bacteria of Azotobacter genus and the activity of dehydrogenases at 100 mg/kg. It is advisable to use these indicators in biodiagnostics of the ecotoxicity of Ag nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
I. P. Bab’eva and G. M. Zenova, Soil Biology (Mosk. Univ., Moscow, 1983) [in Russian].
A. Sh. Galstyan, “Enzymatic soil diagnostics. Problems and methods of biological diagnostics and indication of soils,” in Proceedings of the All-Union Meeting (Moscow, 1976), pp. 22–24.
A. V. Dikarev, V. G. Dikarev, and N. S. Dikareva, “Study of lead phytotoxicity for radish and lettuce plants when grown on different types of soil,” Agrokhimiya, No. 6, 72–80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0002188119030050
T. G. Dobrovol’skaya, D. G. Zvyagintsev, I. Yu. Chernov, A. V. Golovchenko, G. M. Zenova, L. V. Lysak, N. A. Manucharova, O. E. Marfenina, L. M. Polyanskaya, A. L. Stepanov, and M. M. Umarov, “The role of microorganisms in the ecological functions of soils,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 48 (9), 959–967 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229315090033
D. G. Zvyagintsev, I. P. Bab’eva, and G. M. Zenova, Soil Biology (Mosk. Univ., Moscow, 2005) [in Russian].
K. Sh. Kazeev, S. I. Kolesnikov, Yu. V. Akimenko, and E. V. Dadenko, Methods for Biodiagnostics of Terrestrial Ecosystems (Izd. Yuzhn. Fed. Univ., Rostov-on-Don, 2016) [in Russian].
L. A. Karyagina and N. A. Mikhailova, “Determination of polyphenoloxidase and peroxidase activity,” Vestn. Akad. Nauk BSSR. Ser. Sel’skogaspad. Nauk, No. 2, 40–41 (1986).
S. I. Kolesnikov, K. Sh. Kazeev, and V. F. Val’kov, Ecological Consequences of Soil Pollution with Heavy Metals (Izd. Sev.-Kavk. Nauchn. Tsentra Vyssh. Shk., Rostov-on-Don, 2000) [in Russian].
S. I. Kolesnikov, K. Sh. Kazeev, M. L. Tatosyan, and V. F. Val’kov, “The effect of pollution with oil and oil products on the biological status of ordinary chernozems,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 39 (5), 552–556 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229306050127
S. I. Kolesnikov, A. N. Timoshenko, K. Sh. Kazeev, Yu. V. Akimenko, and M. A. Myasnikova, “Ecotoxicity of copper, nickel, and zinc nanoparticles assessment on the basis of biological indicators of chernozems,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 52 (8), 982–987 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106422931908009X
N. A. Kulikova, “Silver nanoparticles in soil: input, transformation, and toxicity,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 54 (3), 352–365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229321030091
Methods of Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry (Mosk. Univ., Moscow, 1980) [in Russian].
F. Kh. Khaziev, Methods of Soil Enzymology (Nauka, Moscow, 2005) [in Russian].
R. Aznar, F. Barahona, O. Geiss, J. Ponti, T. J. Luis, and J. Barrero-Moreno, “Quantification and size characterisation of silver nanoparticles in environmental aqueous samples and consumer products by single particle-ICPMS,” Talanta 175, 200–208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.048
S. Balandeh, A. Lakzian, and A. Javadmanesh, “Effects of silver nanoparticles on soil microbial activity and bacterial populations in a calcareous soil using qPCR,” J. Water Soil 35 (6), 859–843 (2022). https://doi.org/10.22067/JSW.2021.67908.1004
A. Bhattacharyya, P. Duraisamy, M. Govindarajan, A. A. Buhroo, and R. Prasad, “Nano-biofungicides: emerging trend in insect pest control,” in Advances and Applications through Fungal Nanobiotechnology (2016), pp. 307–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42990-8_15
S. Chernousova and M. Epple, “Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal,” Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 52, 1636–1653 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201205923
O. Choi and Z. Hu, “Size-dependent and reactive oxygen species nanoselective toxicity to nitrifying bacteria,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 4583–4588 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/es703238h
P. Courtois, A. Vaufleury, A. Grosser, C. Lors, and F. Vandenbulcke, “Transfer of sulfidized silver from silver nanoparticles, in sewage sludge, to plants and primary consumers in agricultural soil environment,” Sci. Total Environ. 777, 145900 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145900
P. Cvjetko, A. Milošić, A-M. Domijan, I. Vinković Vrček, S. Tolić, P. Peharec Štefanić, I. Letofsky-Papst, M. Tkalec, and B. Balen, “Toxicity of silver ions and differently coated silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa roots,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 137, 8–28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.009
F. Eivazi, Z. Afrasiabi, and E. Jose, “Effects of silver nanoparticles on the activities of soil enzymes involved in carbon and nutrient cycling,” Pedosphere 28, 209–214 (2018).
F. Eivazi and M. A. Tabatabai, “Phosphatases in soils,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 9 (3), 167–172 (1977).
W. F. Falco, M. D. Scherer, S. L. Oliveir, H. Wender, I. Colbeck, T. Lawson, A. R. L. Caires, “Phytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on Vicia faba: evaluation of particle size effects on photosynthetic performance and leaf gas exchange,” Sci. Total Environ. 701, 134816 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134816
C. Forstner, T. G. Orton, P. Wang, P. M. Kopittke, and P. G. Dennis, “Soil chloride content influences the response of bacterial but not fungal diversity to silver nanoparticles entering soil via wastewater treatment processing,” Environ. Pollut. 255, 113274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113274
A. R. Gliga, S. Skoglund, I. Odnevall, B. Fadeel, and H. Karlsson, “Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: the role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release,” Part. Fibre Toxicol. 11, 11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-11-1
A. Grün, S. Straskraba, S. Schulz, M. Schloter, and C. Emmerling, “Long-term effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of silver nanoparticles on microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and functional genes involved in the nitrogen cycle of loamysoil,” J. Environ. Sci. 69, 12–22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.04.013
Y. N. Huang, T. T. Qian, F. Dang, Y. G. Yin, M. Li, and D. M. Zhou, “Significant contribution of metastable particulate organic matter to natural formation of silver nanoparticles in soils” Nat. Commun. 10, 4–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11643-6
A. Ivask, I. Kurvet, K. Kasemets, I. Blinova, V. Aruoja, S. Suppi, H. Vija, A. Kakinen, T. Titma, M. Heinlaan, M. Visnapuu, D. Koller, V. Kisand, and A. Kahru, “Size-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles to bacteria, yeast, algae, crustaceans and mammalian cells in vitro,” PLoS One 9 (7), e102108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.01021080
X. Jin, M. Li, J. Wang, C. Marambio-Jones, F. Peng, X. Huang, R. Damoiseaux, and E. M. V. Hoek, “High-throughput screening of silver nanoparticle stability and bacterial inactivation in aquatic media: influence of specific ions,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 7321–7328 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/es100854g
S. I. Kolesnikov, N. I. Tsepina, T. V. Minnikova, K. Sh. Kazeev, S. S. Mandzhieva, S. N. Sushkova, T. M. Minkina, M. Mazarji, R. K. Singh, and V. D. Rajput, “Influence of silver nanoparticles on the biological indicators of haplic chernozem,” Plants 10, 1022 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10051022
S. I. Kolesnikov, N. I. Tsepina, L. V. Sudina, T. V. Minnikova, K. Sh. Kazeev, and Yu. V. Akimenko, “Silver ecotoxicity estimation by the soils state biological indicators,” Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2020, 1207210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1207210
S. I. Kolesnikov, M. V. Yaroslavtsev, N. A. Spivakova, and K. Sh. Kazeev, “Comparative assessment of the biological tolerance of chernozems in the south of Russia towards contamination with Cr, Cu, Ni, and Pb in a model experiment,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 46, 176–181 (2013).
M. Kuamri, V. Ernest, A. Mukherjee, and N. Chandrasekaran, “In vivo nanotoxicity assays in plant models,” Nanotoxicity 926, 399–410 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-002-1_26
N. A. Kulikova, D. S. Volkov, A. B. Volikov, D. P. Abroskin, A. I. Krepak, and I. V. Perminova, “Silver nanoparticles stabilized by humic substances adversely affect wheat plants and soil,” J. Nanopart. Res. 22, 100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-020-04788-9
T. Künniger, A. C. Gerecke, A. Ulrich, A. Huch, R. Vonbank, M. Heeb, A. Wichser, R. Haag, P. Kunz, and M. Faller, “Release and environmental impact of silver nanoparticles and conventional organic biocides from coated woodenfaçades,” Environ. Pollut. 184, 464–471 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.030
L. B. Lahuta, J. Szablinska-Piernik, K. Stalanowska, K. Głowacka, M. Horbowicz, “The size-dependent effects of silver nanoparticles on germination, early seedling development and polar metabolite profile of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.),” Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 13255 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113255
S. Makama, J. Piella, A. Undas, W. J. Dimmers, R. Peters, V. F. Puntes, and N. W. Brink, “Properties of silver nanoparticles influencing their uptake in and toxicity to the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus following exposure in soil,” Environ. Pollut. 218, 870–878 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.016
C. Michels, S. Perazzoli, and M. Soares, “Inhibition of the enriched culture of ammonium-oxidizing bacteria by two different nanoparticles: silver and magnetite,” Common Environ. Sci. 586, 995–1002 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.080
P. Mishra, Y. Xue, F. Eivazi, and Z. Afrasiabi, “Size, concentration, coating, and exposure time effects of silver nanoparticles on the activities of selected soil enzymes,” Geoderma 381, 114682 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114682
G. Montes de Oca-Vásquez, F. Solano-Campos, J. R. Vega-Baudrit, R. López-Mondéjar, A. Vera, J. L. Morenof, and F. Bastidaf, “Organic amendments exacerbate the effects of silver nanoparticles on microbial biomass and community composition of a semiarid soil,” Sci. Total Environ. 744, 140919 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122224
J. R. Morones, J. L. Elechiguerra, A. Camacho, K. Holt, J. B. Kouri, J. T. Ramirez, and M. J. Yacaman, “The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles,” Nanotechnology 16, 2346–2353 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/059
N. Musee, M. Thwala, and N. Nota, “The antibacterial effects of engineered nanomaterials: implications for wastewater treatment plants,” J. Environ. Monit. 13, 1164–1183 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1em10023h
C. A. Ottoni, NetoM. C. Lima, P. Leo, B. D. Ortolan, E. Barbieri, and A. O. De Souza, “Environmental impact of biogenic silver nanoparticles in soil and aquatic organisms,” Chemosphere 239, 124698 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124698
C. Peyrot, K. J. Wilkinson, M. Desrosiers, and S. Sauvé, “Effects of silver nanoparticles on soil enzyme activities with and without added organic matter,” Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 33, 115–125 (2014). .https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2398
J. Pulit-Prociak and M. Banach, “Silver nanoparticles–a material of the future…?,” Open Chem. 14, 76–91 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2016-0005
S. Rahmatpour, M. Shirvani, M. R. Mosaddeghi, N. Farshid, and M. Bazarganipour, “Dose–response effects of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate on microbial and enzyme activities in calcareous soils,” Geoderma 285, 313–322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.10.006
A. D. Samarajeewa, J. R. Velicogna, J. I. Princz, R. M. Subasinghe, R. P. Scroggins, and L. A. Beaudette, “Effect of silver nano-particles on soil microbial growth, activity and community diversity in a sandy loam soil,” Environ. Pollut. 220, 504–513 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.094
W. A. Shoults-Wilson, B. B. Reinsh, O. V. Tsyusko, P. M. Bertsh, G. V. Lowry, and J. M. Unrin, “Role of particle size and soil type in the toxicity of silver nanoparticles to worms,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 75, 365–377 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2010.0127nps
R. G. Sibbald, J. Contreras-Ruiz, P. Coutts, M. Fierheller, A. Rothman, and K. Woo, “Bacteriology, inflammation, and healing: a study of nanocrystalline silver dressings in chronic venous leg ulcers,” Adv. Skin Wound Care 20, 549–558 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASW.0000294757.05049.85
U. Song, H. Jun, B. Waldman, J. Roh, Y. Kim, J. Yi, and E. J. Lee, “Functional analyses of nanoparticle toxicity: a comparative study of the effects of TiO2 and Ag on tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum),” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 93, 60–67 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.03.033
M. A. Tabatabai and J. M. Bremner, “Use of p-nitrophenol phosphate in assay of soil phosphatase activity,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 1, 301–307 (1969).
P. Thuesombat, S. Hannongbua, S. Akasit, and S. Chadchawan, “Effect of silver nanoparticles on rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. KDML 105) seed germination and seedling growth,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 104, 302–309 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.022
World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014. Update 2015. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps (FAO, Rome, 2015).
C. Yan, J. Huang, C. Cao, R. Li, Y. Ma, and Y. Wang, “Effects of PVP-coated silver nanoparticles on enzyme activity, bacterial and archaeal community structure and function in a yellow-brown loam soil,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 8058–8070 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07347-5
H. Yu, X. Xu, X. Chen, T. Lu, and P. Zhang, “Preparation and antibacterial effects of PVA-PVP hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 103, 125–133 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.24835
L. Zhang, L. Wu, Y. Si, and K. Shu, “Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to Azotobacter vinelandii: growth inhibition, cell injury, oxidative stress and internalization,” PLoS One 13 (12), e0209020 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0209020
Funding
This work was supported by Russian Science Foundation, project no. 22-74-00054 in Southern Federal University (https://rscf.ru/project/22-74-00054/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
This work does not contain any studies involving human and animal subjects.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by T. Chicheva
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsepina, N.I., Kolesnikov, S.I., Minnikova, T.V. et al. Assessment of Ecotoxicity of Silver Particles Different in Size according to Biological Indicators in Haplic Chernozem. Eurasian Soil Sc. 57, 865–874 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323603645
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323603645