Abstract
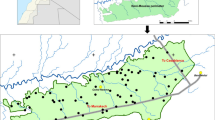
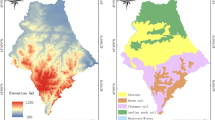
We study studied the alpine meadow soil in Gannan Prefecture. Geostatistical analysis showed that Circular [soil total nitrogen (STN), soil total potassium (STK), soil available phosphorus (SAP)] model, index [bulk density (BD), soil water content (SWC), soil organic carbon (SOC), soil available nitrogen (SAN)] model and Gaussian [soil total phosphorus (STP), soil available potassium (SAK)] model is universal Kriging Method semi-variation function optimization fitting model. In the model, the spatial correlation is weak to medium, and SOC, STN, STP, STK, SAN, SAP, SAK, and SWC have specific spatial trend effects. Then principal component analysis was used to obtain three key factors (SOC, BD, and SWC) affecting soil quality, which accounted for 81.91% of the total variation of soil quality. These factors were taken as the minimum data set (MDS) and soil quality index (SQI) was calculated. According to SQI, the whole region was divided into three soil management zones (SMZs). Recommendations are made for different management areas to ensure resource conservation and reduce environmental footprint.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Haghverdi, B. G. Leib, R. A. Washington-Allen, P. D. Ayers, and M. J. Buschermohle, “Perspectives on delineating management zones for variable rate irrigation,” Comput. Electron. Agric. 117, 154–167 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.06.019
C. J. Schollenberger and R. H. Simon, “Determination of exchange capacity and exchangeable bases in soil by ammonium acetate method,” Soil Sci. 59 (1), 13–24 (1945). https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/12.2.146
C. Ning, Z. Yangjian, Z. Juntao, L. Junxiang, L. Yaojie, Z. Jiaxing, C. Nan, H. Ke, and W. Li, “Nonlinear response of productivity and diversity of alpine meadow communities to degradation,” Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 42 (1), 50–65 (2018). https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2017.0252
C. Yanming, M. Hongbin, M. Qing, M. Ziyuan, L. Jindi, Z. Yao, and P. Wendong, “Effects of different grazing patterns on soil carbon and nitrogen storage and sequestration in desert steppe,” Acta Agrestia Sin. 31 (10), 18–27 (2022). https://doi.org/10.11686/cyxb2021412
D. L. Karlen, M. J. Mausbach, J. W. Doan, R. G. Cline, R. F. Harris and G. E. Schuman, “Soil quality: a concept, definition and framework for evaluation,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 61 (1), 4–10 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1997.03615995006100010001x
D. Lei, S. G. Zhouping, W. Gaolin, and C. Xiaofeng, “Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration in China’s grassland,” Earth Sci. Rev. 173, 84–95 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.08.008
D. Wei, L. Yuhuan, F. Weijun, J. Peikun, Z. Keli, and L. Yongfu, “Spatial variability of soil nutrients in forest areas: A case study from subtropical China,” J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 181 (6), 827–835 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800134
F. H. Westheimer, “Why nature chose phosphate,” Science 235 (4793), 1173 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2434996
G. Junjing and C. Yohay, “A global meta-analysis of grazing effects on plant richness,” Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 302 (107072), (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107072
G. S. Bhunia, P. K. Shit, and R. Chattopadhyay, “Assessment of spatial variability of soil properties using geostatistical approach of lateritic soil (West Bengal, India),” Ann. Agric. Sci. 16 (4), 436–443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.01.006
J. G. Han, Y. Zhang, C. J. Wang, W. M. Bai, Y. R. Wang, G. D. Han, L. H. Li, “Rangeland degradation and restoration management in China,” Rangeland J. 30 (2), 233–239 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1071/RJ08009
I. Bogunovic, M. Mesic, Z. Zgorelee, A. Jurisic, and D. Bilandzija, “Spatial variation of soil nutrients on sandy-loamy soil,” Soil Tillage Res. 144, 174–183 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.07.020
I. Matejovic, “Determination of carbon and nitrogen in samples of various soils by the dry combustion,” Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Analy. 28 (17–18), 1499–1511 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629709369892
L. Honglin, G. Lu, Z. Meiling, L. Zengyuan, X. Lina, and H. Yi, “Stoichiometric characteristics of soil in an Oasis on the northern edge of Tarim Basin, China,” Acta Pedol. Sin. 52 (6), 1345–1355 (2015). https://doi.org/10.11766/trxb201411220585
L. Qi, M. Hongbin, Y. Hongqian, W. Li, S. Yan, X. Dongmei, and X. Yinghzong, “Effect of rotational grazing methods on soil aggregates and organic carbon characteristics in desert grassland,” China J. Appl. Ecol. 30 (9), 3028–3038 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201909.010
L. Yaqiong, H. Yanshuang, Z. Yian, and B. Tao, “Effects of different measures for improving degraded grassland on the soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in steppe of inner Mongolia,” Acta Prataculturae Sin. 38 (5), 91–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.16742/j.zgcdxb.2016-05-15
L. Yuzhen, S. Caicai, L. Wenting, Y. Xiaoxia, F. Bin, S. Guang, Z. Xue, L. Caidi, Y. Zengzeng, G. Jie, Z. Xiaofang, Y. Yang, Z. Chunping, and D. Quanming, “Response of keystone species changes in alpine grassland plant communities to different herbivore assemblage grazing,” Acta Ecol. Sin. 42 (18), 7529–7540 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb202110072757
L. Xiaoyan, W. Dongyan, R. Yongxing, W. Zongming, and Z. Yongheng, “Soil quality assessment of croplands in the black soil zone of Jilin Province, China: establishing a minimum data set model,” Ecol. Indic. 107 (105251), (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind
M. S. Askari and N. M. Holden, “Quantitative soil quality indexing of temperate arable management systems,” Soil Tillage Res. 150, 57–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.01.010
M. Jifu, C. Yiping, Z. Jie, W. Kaibo, and W. Junhua, “Soil quality should be accurate evaluated at the beginning of lifecycle after land consolidation for eco-sustainable development on the Loess Plateau,” J. Cleaner Prod. 267 (122244), (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122244
N. Huayue and G. Jixi, “Research progress on ecological impact and spreading mechanism of weeds on degraded grassland,” Chin. J. Grassl. 44 (7), 101–113 (2022). https://doi.org/10.16742/j.zgcdxb.20210317
R. B. Harris, “Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: a review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes,” J. Arid Environ. 74 (1), 1–12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.06.014
R. J. Huggett, “Soil chronosequences, soil development, and soil evolution: a critical review,” Catena 32 (3–4), 155–172 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(98)00053-8
R. K. Singh, A. Singh, and P. C. Sharma, Successful Adaptations in Salt Affected Agroecosystems of India (2019).
R. M. Lark, “Estimation of the variograms of soil properties by the method of moments and maximum likelihood; a comparison,” Eur. J. Soil Sci. 51 (4), 717–728 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00345.x
R. Srivastava, M. Sethi, R. K. Yadav, D. S. Bundela, M. Singh, S. Chattaraj, S. K. Singh, R. A. Nasre, S. R. Bishnoi, S. Dhale, D. S. Mohekar, and A. K. Barthwal, “Visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for rapid characterization of salt-affected soil in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of Haryana,” J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 45 (2), 307–315 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-016-0587-0
S. Ayoubi, A. Mehnatkesh, A. Jalalian, K. L. Sahrawat, and M. Gheysari, “Relationships between grain protein, Zn, Cu, Fe and Mn contents in wheat and soil and topographic attributes,” Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 60 (5), 625–638 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2013.825899
S. Jian, Z. Zhenchao, and D. Shikui, “Adaptive management of alpine grassland ecosystems over Tibetan Plateau,” Pratac. Sci. 36 (4), 933–938 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2019-0224
S. Jiandong, Y. Yulin, C. Bing, and W. Hongqi, “Spatial variability of soil total salt, pH and total alkalinity,” Soils 37 (1), 69–73 (2005). https://doi.org/10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2005.01.014
S. Nawar, R. Corstanje, G. Halcro, D. Mulla, and A. Mouazen, “Delineation of soil management zones for variable-rate fertilization: a review,” Adv. Agron. 143, 175–245 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2017.01.003
S. Ravi, D. D. Breshears, T. E. Huxman, and P. D’Odorico, “Land degradation in drylands: interactions among hydrologic-aeolian erosion and vegetation dynamics,” Geomorphology 116 (3–4), 236–245 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.11.023
S. S. Andrews, D. L. Karlen, and J. P. Mitchell, “A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California,” Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 90 (1), 25–45 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00174-8
Z. Sun, Y. B. Wang, G. H. Liu, and Z. Gao, “Heterogeneity analysis of soil particle size distribution in the process of degradation of alpine meadow in the permafrost regions based on multifractal theory,” J. Glaciol. Geocryology 37 (4), 980–990 (2015). https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2015.0109
T. Zhen, S. Chende, G. Quanzhou, S. Yanmin, Y. Weixi, and L. Yingnian, “Soil organic carbon storage and vertical distribution of alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau,” Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 7, 720–728 (2006). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.07.006
W. Jianbing and Y. Wenjie, “Impacts of climate change on the pasture grass in border area at the north-east of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau,” J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 38 (26), 14535–14537 (2010). https://doi.org/10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2010.26.122
W. Li, G. Yantai, M. Wiesmeier, Z. Guiqin, Z. Ruiyang, H. Guodong, and H. Fujiang, “Grazing exclusion-An effective approach for naturally restoring degraded grasslands in Northern China,” Land Degrad. Dev. 29 (12), 4439–4456 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3191
W. Xing, L. Huixia, F. Bojie, J. Tiantian, and L. Guohua, “Study on soil characteristics of alpine grassland in different degradation levels in headwater regions of Three River in China,” Chin. J. Grassland 35 (3), 77–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5021.2013.03.014
W. Yuqin, W. Hongsheng, S. Meiling, and B. Gensheng, “Effect of autumn clipping on vegetation and soil ecological properties of degraded alpine grassland,” Acta Prataculturae Sin. 42 (3), 61–69 (2020). https://doi.org/10.16742/j.zgcdxb.20190120
X. Jinyu, P. Xiaopeng, and X. Changlin, “Effect of grazing prohibition on restoration of degraded grassland,” Pratac. Sci. 32 (1), 138–145 (2015). https://doi.org/10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2013-0730
X. Yudan, D. Shikui, S. Hao, X. Jiannan, L. Shuai, G. Xiaoxia, and W. Shengnan, “Degradation significantly decreased the ecosystem multifunctionality of three alpine grasslands: evidences from a large-scale survey on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,” Acta Pedol. Sin. 18 (2), 357–366 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.11.015
Y. Jinsong, “Development and prospect of the research on salt-affected soils in China,” Acta Pedol. Sin. 45 (5), 837–845 (2008). https://doi.org/trxb10.11766/200806280509
Y. Pujia, L. Qiang, J. Hongtao, L. Guangdi, Z. Wei, S. Xiangjin, D. Baba, and Z. Daowei, “Effect of cultivation on dynamics of organic and inorganic carbon stocks in Songnen plain,” Agron. J. 106 (5), 1574–1582 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj14.0113
Y. Pujia, L. Shiwei, Y. Hongtao, F. Gaohua, and Z. Daowei, “Short-term land use conversions influence the profile distribution of soil salinity and sodicity in northeastern China,” Ecol. Indic. 88, 79–87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.01.017
Y. Yali, W. Yuqin, B. Gensheng, W. Hongsheng, L. Shixiong, S. Meiling, S. Baolian, and W. Yuncun, “Characteristics of soil microbes and enzyme in degraded alpine meadows,” Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 28 (12), 3881–3890 (2017). https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.201712.040
Y. Yei, P. Xiaoyu, Y. Shuqi, Z. Yunbin, Z. Cai, and H. Yong, “Effects of land use types on soil organic carbon and soil labile organic carbon in the karst faulted basin of southern Yunnan,” Acta Ecol. Sin. 42 (17), 7105–7117 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5846 /stxb202108112216
Z. Han, O. Zhencheng, and Z. Xiaomin, “Effects of different land use types on ecological stoichiometry characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in farmland soils in Jiangxi Province, China,” Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 39 (3), 939–951 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0383
Z. Lu, W. Xiangtao, W. Jie, L. Lirong, L. Shilong, L. Guobin, and Z. Chao, “Alpine meadow degradation depresses soil nitrogen fixation by regulating plant functional groups and diazotrophic community composition,” Plant Soil, 1–17 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2167-9
Z. Qipeng, F. Ruyao, D. Cuiyan, Z. Hongjuan, S. Menghan, and W. Qian, “Slope aspect effects on plant community characteristics and soil properties of alpine meadows on Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan plateau,” Ecol. Indic. 143, 109400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109400
Z. Weibin, “Analysis of soil moisture change law in Huangshan City,” Soil Water Conser. China 9, 55–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.14123/j.cnki.swcc.2018.0206
Z. Zilu, Z. Xihong, L. Feng, and S. Xiaojun, “Spatial heterogeneity of soil readily available potassium and its influencing factors in Western Chongqing Hilly Area,” Acta Pedol. Sin. 57 (2), 307–315 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11766/trxb201902250030
Funding
We acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31760135), Gansu Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20JR10RA089), and Gansu Provincial Forestry and Grassland Science and Technology Innovation (KJCX2021005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the authors do not have any possible conflicts of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Wang, S., Mi, J. et al. Spatial Variability of Alpine Meadow Soils in Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Gansu Province, China. Eurasian Soil Sc. 56 (Suppl 2), S276–S286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323601592
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323601592