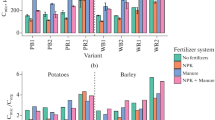
Abstract
The loss of soil organic matter (SOM) due to agricultural land use has a negative impact on soil properties and is one of the major contributors to the increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations. An appropriate way for simultaneous restoration of SOM stocks and deposition of sequestered carbon is the straw application into the soil. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effect of straw application on the quantitative indicators of different groups of microorganisms in a soddy-podzolic soil (Umbric Retisol) in a long-term field experiment. Straw application increased microbial biomass carbon (Cmic) by 1.25–2 times, with the greatest increase in microbial biomass in trials without mineral fertilizer. Basal respiration and metabolic quotient (qCO2) increased in the sequence: control < NPK < NPK + straw < straw. Application of straw increased the gene copy number of fungi and bacteria up to 2 times and archaea up to 1.5 times. Application of mineral fertilizers without straw reduced qCO2, fungi biomass, and archaeal gene copy number by 1.5–3.0 times. The fungi/bacteria ratio varied from 4 to 15 as determined by the fluorescent microscopy and from 0.17 to 0.33 as determined by quantitative PCR. The lowest values of fungi/bacteria ratios were found in soils with the application of mineral fertilizers, and the highest ones, in soils with the straw application. Thus, the regular application of fresh organic matter of straw is an important technological procedure to increase the soil microbiological activity and mitigate the negative impact of mineral fertilizers on soil microbiota.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. D. Anan’eva, E. V. Blagodatskaya, and T. S. Demkina, “Estimating the resistance of soil microbial complexes to natural and anthropogenic impacts,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 35 (5), 514–521 (2002).
N. D. Ananyeva, E. V. Stolnikova, E. A. Susyan, and A. K. Khodzhaeva, “The fungal and bacterial biomass (selective inhibition) and the production of CO2 and N2O by soddy-podzolic soils of postagrogenic biogeocenoses,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 43 (11), 1287–1293 (2010).
N. D. Ananyeva, E. A. Susyan, and E. G. Gavrilenko, “Determination of the soil microbial biomass carbon using the method of substrate-induced respiration,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 44 (11), 1215–1221 (2011).
E. V. Blagodatskaya, M. V. Semenov, and A. V. Yakushev, Activity and Biomass of Soil Microorganisms under Changing Environmental Conditions (Tov. Nauchn. Izd. KMK, Moscow, 2016) [in Russian].
D. G. Zvyagintsev, Methods of Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry (Mosk. Univ., Moscow, 1991) [in Russian].
E. V. Lavrent’eva, A. M. Semenov, V. V. Zelenev, Yu. Chzhun, E. V. Semenova, V. M. Semenov, B. B. Namsaraev, and A. H. C. Van Bruggen, “Daily dynamics of cellulase activity in arable soils depending on management practices,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 42 (8), 885–893 (2009).
S. M. Lukin, “The history of scientific research on soil fertility and the use of fertilizers (to the 105th anniversary of the formation of the Sudogda experimental field of All-Russian Research Institute of Organic Fertilizers and Peat),” Istor. Nauki Tekh., No. 3, 3–17 (2018).
D. A. Nikitin, T. V. Chernov, A. D. Zhelezova, A. K. Tkhakakhova, S. A. Nikitina, M. V. Semenov, N. A. Xenofontova, and O. V. Kutovaya, “Seasonal dynamics of microbial biomass in soddy-podzolic soil,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 52 (11), 1414–1421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229319110073
D. A. Nikitin, E. A. Ivanova, A. D. Zhelezova, M. V. Semenov, R. G. Gadzhiumarov, A. K. Tkhakakhova, T. I. Chernov, N. A. Ksenofontova, and O. V. Kutovaya, “Assessment of the impact of no-till and conventional tillage technologies on the microbiome of southern agrochernozems,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 53 (12), 1782–1793 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106422932012008X
D. A. Nikitin, M. V. Semenov, T. I. Chernov, N. A. Ksenofontova, A. D. Zhelezova, E. A. Ivanova, N. B. Khitrov, and A. L. Stepanov, “Microbiological indicators of soil ecological functions: a review,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 55 (2), 221–234 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322020090
L. M. Polyanskaya and D. G. Zvyagintsev, “The content and composition of microbial biomass as an index of the ecological status of soils,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 38 (6), 625–633 (2005).
L. M. Polyanskaya, N. I. Sukhanova, K. V. Chakmazyan, and D. G. Zvyagintsev, “Changes in the structure of soil microbial biomass under fallow,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 45 (7), 710–716 (2012).
L. M. Polyanskaya, D. D. Yumakov, Z. N. Tyugay, and A. L. Stepanov, “Fungi and bacteria in the dark-humus forest soil,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 53 (9), 1255–1259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229320090124
I. V. Rusakova, “Influence of straw of cereals and leguminous crops on carbon content, agrochemical properties and nutrient balance in soddy-podzolic soil,” Agrokhim. Vestn., No. 6, 6–10 (2015).
I. V. Rusakova, “Microbiological and ecophysiological parameters of soddy-podzolic soil with long-term use of straw and mineral fertilizers, their relationship with productivity,” S-kh. Biol., No. 55(1), 153–162 (2020). https://doi.org/10.15389/agrobiology.2020.1.153rus
B. M. Semenov and A. K. Khodzhaeva, “Agroecological functions of plant residues in soil,” Agrokhimiya, No. 7, 63–81 (2006).
V. M. Semenov and B. M. Kogut, Soil Organic Matter (GEOS, Moscow, 2015) [in Russian].
V. M. Semenov, N. B. Pautova, T. N. Lebedeva, D. P. Khromychkina, N. A. Semenova, and V. O. Lopes de Gerenyu, “Plant residues decomposition and formation of active organic matter in the soil of the incubation experiments,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 52 (10), 1183–1194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229319100119
M. V. Semenov, “Metabarcoding and metagenomics in soil ecology research: achievements, challenges, and prospects,” Biol. Bull. Rev. 11 (1), 40–53 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086421010084
M. V. Semenov, D. A. Nikitin, A. L. Stepanov, and V. M. Semenov, “The structure of bacterial and fungal communities in the rhizosphere and root-free loci of gray forest soil,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 52 (3), 319–332 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229319010137
M. V. Semenov, N. A. Manucharova, G. S. Krasnov, D. A. Nikitin, and A. L. Stepanov, “Biomass and taxonomic structure of microbial communities in soils of the right-bank basin of the Oka River,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 52 (8), 971–981 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106422931908012X
T. I. Chernov and M. V. Semenov, “Management of soil microbial communities: opportunities and prospects (a review),” Eurasian Soil Sci. 54 (12), 1888–1902 (2021).
G. Angst, K. E. Mueller, K. G. Nierop, and M. J. Simpson, “Plant-or microbial-derived? A review on the molecular composition of stabilized soil organic matter,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 156, 108189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108189
V. L. Bailey, J. L. Smith, and H. Bolton Jr., “Fungal-to-bacterial ratios in soils investigated for enhanced C sequestration,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 34, 997–1007 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00033-0
M. Berhane, M. Xu, Z. Liang, J. Shi, G. Wei, and X. Tian, “Effects of long-term straw return on soil organic carbon storage and sequestration rate in North China upland crops: a meta-analysis,” Global Change Biol. 26, 2686–2701 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15018
X. Chen, M. Liu, Y. Kuzyakov, W. Li, J. Liu, C. Jiang, Wu. Meng, and Z. Li, “Incorporation of rice straw carbon into dissolved organic matter and microbial biomass along a 100-year paddy soil chronosequence,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 130, 84–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.06.004
X. Chen, Y. Xia, Y. Rui, Z. Ning, Y. Hu, H. Tang, H. He, H. Li, Y. Kuzyakov, T. Ge, J. Wu, and Y. Su, “Microbial carbon use efficiency, biomass turnover, and necromass accumulation in paddy soil depending on fertilization,” Agric., Ecosyst. Environ. 292, 106816 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.106816
J. Craine, A. J. Elmore, L. Wang, J. Aranibar, M. Bauters, P. Boeckx, et al., “Isotopic evidence for oligotrophication of terrestrial ecosystems,” Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2, 1735–1744 (2018).
F. Fan, B. Yu, B. Wang, T. S. George, H. Yin, D. Xu, D. Li, and A. Song, “Microbial mechanisms of the contrast residue decomposition and priming effect in soils with different organic and chemical fertilization histories,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 135, 213–221 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.05.001
D. Francioli, E. Schulz, G. Lentendu, T. Wubet, F. Buscot, and T. Reitz, “Mineral vs. organic amendments: microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies,” Front. Microbiol. 7, 1446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01446
P. Han, W. Zhang, G. Wang, W. Sun, and Y. Huang, “Changes in soil organic carbon in croplands subjected to fertilizer management: a global meta-analysis,” Sci. Rep. 6 (1), 1–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27199
J. Z. He, H. W. Hu, and L. M. Zhang, “Current insights into the autotrophic thaumarchaeal ammonia oxidation in acidic soils,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 55, 146–154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.06.006
M. He, W. Ma, V. V. Zelenev, A. K. Khodzaeva, A. M. Kuznetsov, A. M. Semenov, V. M. Semenov, W. W. Blok, and A. H. C. van Bruggen, “Short-term dynamics of greenhouse gas emissions and cultivable bacterial populations in response to induced and natural disturbances in organically and conventionally managed soils,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 119, 294–306 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.07.011
P. Heděnec, L. O. Nilsson, H. Zheng, P. Gundersen, I. K. Schmidt, J. Rousk, and L. Vesterdal, “Mycorrhizal association of common European tree species shapes biomass and metabolic activity of bacterial and fungal communities in soil,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 149, 107933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107933
D. Geisseler and K. M. Scow, “Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—a review,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 75, 54–63 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.03.023
Y. Geng, G. Cao, L. Wang, and S. Wang, “Effects of equal chemical fertilizer substitutions with organic manure on yield, dry matter, and nitrogen uptake of spring maize and soil nitrogen distribution,” PLoS One 14, e0219512 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219512
Z. Jin, T. Shah, L. Zhang, H. Liu, S. Peng, and L. Nie, “Effect of straw returning on soil organic carbon in rice–wheat rotation system: a review,” Food Energy Secur. 9 (2), e200 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.200
P. Iovieno, L. Morra, A. Leone, L. Pagano, and A. Alfani, “Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil respiration and enzyme activities of two Mediterranean horticultural soils,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 45, 555–561 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0365-z
H. K. Landenmark, D. H. Forgan, and C. S. Cockell, “An estimate of the total DNA in the biosphere,” PLoS Biol. 13, e1002168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002168
Y. Liang, M. Al-Kaisi, J. Yuan, J. Liu, H. Zhang, L. Wang, H. Cai, and J. Ren, “Effect of chemical fertilizer and straw-derived organic amendments on continuous maize yield, soil carbon sequestration and soil quality in a Chinese Mollisol,” Agric., Ecosyst. Environ. 314, 107403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107403
C. Liu, M. Lu, J. Cui, B. Li, and C. Fang, “Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis,” Global Change Biol. 20, 1366–1381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12517
F. Lu, “How can straw incorporation management impact on soil carbon storage? A meta-analysis,” Mitigation Adapt. Strategies Global Change 20, 1545–1568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-014-9564-5
A. A. Malik, S. Chowdhury, V. Schlager, A. Oliver, J. Puissant, P. G. Vazquez, N. Jehmlich, M. Bergen, R. I. Griffiths, and G. Gleixner, “Soil fungal: bacterial ratios are linked to altered carbon cycling,” Front. Microbiol. 7, 1247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01247
M. C. Morais, B. M. Ferrari, C. D. Borges, M. R. Cherubin, S. M. Tsai, C. C. Cerri, C. E. P. Cerri, and B. J. Feigl, “Does sugarcane straw removal change the abundance of soil microbes?,” BioEnergy Res. 12, 901–908 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-10018-5
M. Saleem, A. D. Law, M. R. Sahib, Z. H. Pervaiz, and Q. Zhang, “Impact of root system architecture on rhizosphere and root microbiome,” Rhizosphere 6, 47–51 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2018.02.003
M. V. Semenov, G. S. Krasnov, V. M. Semenov, and A. H. van Bruggen, “Long-term fertilization rather than plant species shapes rhizosphere and bulk soil prokaryotic communities in agroecosystems,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 154, 103641 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103641
M. V. Semenov, G. S. Krasnov, V. M. Semenov, N. Ksenofontova, N. B. Zinyakova, and A. H. van Bruggen, “Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota?,” J. Environ. Manage. 294, 113018 (2021).
M. V. Semenov, G. S. Krasnov, V. M. Semenov, and A. van Bruggen, “Mineral and organic fertilizers distinctly affect fungal communities in the crop rhizosphere,” J. Fungi 8, 251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8030251
J. Six, S. D. Frey, R. K. Thiet, and K. M. Batten, “Bacterial and fungal contributions to carbon sequestration in agroecosystems,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 70 (2), 555–569 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.0347
M. Soares and J. Rousk, “Microbial growth and carbon use efficiency in soil: Links to fungal-bacterial dominance, SOC-quality and stoichiometry,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 131, 195–205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.01.010
M. T. Suzuki, L. T. Taylor, and E. F. DeLong, “Quantitative analysis of small-subunit rRNA genes in mixed microbial populations via 5′-nuclease assays,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66 (11), 4605–4614 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.11.4605-4614.2000
A. Tiefenbacher, T. Sandén, H.-P. Haslmayr, J. Miloczki, W. Wenzel, and H. Spiegel, “Optimizing carbon sequestration in croplands: a synthesis,” Agronomy 11, 882 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050882
A. H. C. van Bruggen, M. He, V. V. Zelenev, V. M. Semenov, A. M. Semenov, E. V. Semenova, T. V. Kuznetsova, A. K. Khodzaeva, A. M. Kuznetsov, and M. V. Semenov, “Relationships between greenhouse gas emissions and cultivable bacterial populations in conventional, organic and long-term grass plots as affected by environmental variables and disturbances,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 114, 145–159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.07.014
D. Wang, Z. Zhu, M. Shahbaz, L. Chen, S. Liu, K. Inubushi, J. Wu, and T. Ge, “Split N and P addition decreases straw mineralization and the priming effect of a paddy soil: a 100-day incubation experiment,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 55, 701–712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-019-01383-6
Y. Wang, P. Wu, F. Mei, Y. Ling, Y. Qiao, C. Liu, S. J. Legharic, X. Guan, and T. Wang, “Does continuous straw returning keep China farmland soil organic carbon continued increase? A meta-analysis,” J. Environ. Manage. 288, 112391 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112391
E. Wessén, K. Nyberg, J. K. Jansson, and S. Hallin, “Responses of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidizers to soil organic and fertilizer amendments under long-term management,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 45, 193–200 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.04.003
L. Wu, W. Zhang, W. Wei, Z. He, Y. Kuzyakov, R. Bol, and R. Hu, “Soil organic matter priming and carbon balance after straw addition is regulated by long-term fertilization,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 135, 383–391 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.06.003
D. Yan, X. E. Long, L. Ye, G. Zhang, A. Hu, D. Wang, and S. Ding, “Effects of salinity on microbial utilization of straw carbon and microbial residues retention in newly reclaimed coastal soil,” Eur. J. Soil Biol. 107, 103364 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2021.103364
H. Yang, C. Fang, Y. Meng, Y. Dai, and J. Liu, “Long-term ditch-buried straw return increases functionality of soil microbial communities,” Catena 202, 105316 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105316
C. Yansheng, Z. Fengliang, Z. Zhongyi, Z. Tongbin, and X. Huayun, “Biotic and abiotic nitrogen immobilization in soil incorporated with crop residue,” Soil Tillage Res. 202, 104664 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104664
X. M. Zhao, L. He, Z. D. Zhang, H. B. Wang, and L. P. Zhao, “Simulation of accumulation and mineralization (CO2 release) of organic carbon in chernozem under different straw return ways after corn harvesting,” Soil Tillage Res. 156, 148–154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.11.001
M. Zhao, J. Zhao, J. Yuan, L. Hale, T. Wen, Q. Huang, J. M. Vivanco, J. Zhou, G. A. Kowalchuk, and Q. Shen, “Root exudates drive soil-microbe-nutrient feedbacks in response to plant growth,” Plant, Cell Environ. 44, 613–628 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13928
L. Q. Zhu, J. Li, B. R. Tao, and N. J. Hu, “Effect of different fertilization modes on soil organic carbon sequestration in paddy fields in South China: a meta-analysis,” Ecol. Indic. 53, 144–153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.01.038
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 21-76-10025.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Klyueva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikitin, D.A., Semenov, M.V., Ksenofontova, N.A. et al. Effect of Fresh Organic Matter of Straw on Microbiological Parameters of Soddy-Podzolic Soil. Eurasian Soil Sc. 56, 651–662 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322601950
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229322601950