Abstract
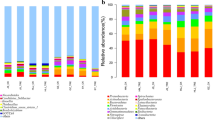
In order to explore the responses of soil enzyme activities and microbial community compositions to long-term nitrogen (N) addition in both bulk soil and microaggregate of chestnut soil, we conducted a 7-year urea addition experiment with N treatments at 6 levels (0, 56, 112, 224, 392 and 560 kg N ha–1 yr–1) in a temperate steppe of Inner Mongolia in China. Soil properties and the activities of four enzymes involved in carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) cycling were measured in both bulk soil and microaggregate, and phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) were measured in bulk soil. The results indicated that: 1) in bulk soil, N addition significantly decreased β-1,4-glucosidase (BG) and leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) activities at the treatment amounts of 224, 392 and 560 kg N ha–1 yr–1, and obviously suppressed β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG) activity at the treatment amount of 560 kg N ha–1 yr–1. N addition enhanced total PLFAs (totPLFAs) and bacterial PLFAs (bacPLFAs) at the treatment amounts of 392 and 560 kg N ha–1 yr–1, respectively, but fungal PLFAs showed no response to N addition. The activities of BG, NAG and LAP were positively correlated with soil pH, but negatively correlated with the concentration of NH +4 -N; 2) in microaggregate (53–250 μm), the activities of BG, NAG and AP showed no response to increased addition of N, but the significantly decreased LAP activity was observed at the treatment amount of 392 kg N ha–1 yr–1. These results suggested that enzyme activities were more sensitive to N addition than PLFA biomarkers in soil, and LAP activity in microaggregate may be a good indicator for evaluating N cycle response to long-term N addition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. D. Allison and J. D. Jastrow, “Activities of extracellular enzymes in physically isolated fractions of restored grassland soils,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 38 (11), 3245–3256 (2006).
C. J. Alster, D. P. German, Y. Lu, and S. D. Allison, “Microbial enzymatic responses to drought and to nitrogen addition in a southern California grassland,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 64 (9), 68–79 (2013).
M. P. Babaev and N. I. Orujova, “Assessment of the biological activity of soils in the subtropical zone of Azerbaijan,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 42 (10), 1163–1169 (2009).
E. M. Bach and K. S. Hofmockel, “Soil aggregate isolation method affects measures of intra-aggregate extracellular enzyme activity,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 69 (1), 54–62 (2014).
Y. Bai, J. Wu, C. M. Clark, et al., “Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from Inner Mongolia grasslands,” Global Change Biol. 16 (1), 358–372 (2010).
P. Baldrian, J. Voríšková, P. Dobiášová, V. Merhautová, L. Lisá, and V. Valášková, “Production of extracellular enzymes and degradation of biopolymers by saprotrophic microfungi from the upper layers of forest soil,” Plant Soil 338 (1–2), 111–125 (2011).
J. Bi, N. Zhang, Y. Liang, H. Yang, and K. Ma, “Interactive effects of water and nitrogen addition on soil microbial communities in a semiarid steppe,” J. Plant Ecol. 5 (3), 320–329 (2012).
S. A. Billings, C. M. Brewer, and B. L. Foster, “Incorporation of plant residues into soil organic matter fractions with grassland management practices in the North American Midwest,” Ecosystems 9 (5), 805–815 (2006). NH4+
S. Bittman, T. A. Forge, and C. G. Kowalenko, “Responses of the bacterial and fungal biomass in a grassland soil to multi-year applications of dairy manure slurry and fertilizer,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 37 (4), 613–623 (2005).
D. A. Bossio and K. M. Scow, “Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns,” Microb. Ecol. 35 (3–4), 265–278 (1998).
T. M. Bowles, V. Acosta-Martínez, F. Calderón, and L. E. Jackson, “Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 68 (1), 252–262 (2014).
R. G. Burns, J. L. DeForest, J. Marxsen, et al., “Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 58 (2), 216–234 (2013).
R. Cahan, E. Hetzroni, M. Nisnevitch, and Y. Nitzan, “Purification and Identification of a novel leucine aminopeptidase from Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis,” Curr. Microbiol. 55 (5), 413–419 (2007).
R. Cardelli, R. Levi-Minzi, A. Saviozzi, and R. Riffaldi, “Organically and conventionally managed soils: biochemical characteristics,” J. Sustainable Agric. 25 (2), 63–74 (2005).
F. T. De Vries, E. Hoffland, N. van Eekeren, L. Brussaard, and J. Bloem, “Fungal/bacterial ratios in grasslands with contrasting nitrogen management,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 38 (8), 2092–2103 (2006).
J. L. DeForest, D. R. Zak, K. S. Pregitzer, and A. J. Burton, “Atmospheric nitrate deposition, microbial community composition, and enzyme activity in northern hardwood forests,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 68 (1), 132–138 (2004).
F. Demoling, D. Figueroa, and E. Bååth, “Comparison of factors limiting bacterial growth in different soils,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 39 (10), 2485–2495 (2007).
F. Demoling, L. Ola Nilsson, and E. Bååth, “Bacterial and fungal response to nitrogen fertilization in three coniferous forest soils,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 40 (2), 370–379 (2008).
W. A. Dick, L. Cheng, and P. Wang, “Soil acid and alkaline phosphatase activity as pH adjustment indicators,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 32 (13), 1915–1919 (2000).
E. T. Elliott, “Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50 (3), 627–633. 1986.
Å. Frostegård and E. Bååth, “The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil,” Biol. Fertil. Soils. 22 (1–2), 59–65. 1996.
J. N. Galloway, F. J. Dentener, D. G. Capone, E. W. Boyer, R. W. Howarth, S. P. Seitzinger, and C. J. Vöos-marty, “Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future,” Biogeochemistry 70 (2), 153–226 (2004).
D. P. German, M. N. Weintraub, A. S. Grandy, C. L. Lauber, Z. L. Rinkes, and S. D. Allison, “Optimization of hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme methods for ecosystem studies,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 43 (7), 1387–1397 (2011).
G. W. Gooday, in Biochemistry of Microbial Degradation (Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht, 1994), pp. 279–312.
N. He, Q. Yu, R. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Gao, and G. Yu, “Enhancement of carbon sequestration in soil in the temperature grasslands of Northern China by addition of nitrogen and phosphorus,” PloS One 8 (10), 1002–1004 (2013).
D. Hiltbrunner, S. Zimmermann, S. Karbin, F. Hagedorn, and P. A. Niklaus, “Increasing soil methane sink along a 120-year afforestation chronosequence is driven by soil moisture,” Global Change Biol. 18 (12), 3664–3671 (2012).
S. E. Hobbie, “Contrasting effects of substrate and fertilizer nitrogen on the early stages of litter decomposition,” Ecosystems 8 (6), 644–656 (2005).
S. J. Horn, G. Vaaje-Kolstad, B. Westereng, and V. G. Eijsink, “Novel enzymes for the degradation of cellulose,” Biotechnol. Biofuels 5 (1), 1–13 (2012).
S. Jagadamma and R. Lal, “Distribution of organic carbon in physical fractions of soils as affected by agricultural management,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 46 (6), 543–554 (2010).
J. D. Jastrow, J. E. Amonette, and V. L. Bailey, “Mechanisms controlling soil carbon turnover and their potential application for enhancing carbon sequestration,” Clim. Change 80 (1–2), 5–23 (2007).
P. N. Kamble, J. Rousk, S. D. Frey, and E. Bååth, “Bacterial growth and growth-limiting nutrients following chronic nitrogen additions to a hardwood forest soil,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 59 (2), 32–37 (2013).
L. Kang, X. Han, Z. Zhang, and O. J. Sun, “Grassland ecosystems in China: review of current knowledge and research advancement,” Phil. R. Soc. B 362 (1482), 997–1008 (2007).
B. L. Keeler, S. E. Hobbie, and L. E. Kellogg, “Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition,” Ecosystems 12 (1), 1–15 (2009).
K. Y. Khan, A. I. Pozdnyakov, and B. K. Son, “Structure and stability of soil aggregates,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 40 (4), 409–414 (2007).
J. Kohler, G. Tortosa, J. Cegarra, F. Caravaca, and A. Roldán, “Impact of DOM from composted “alperujo” on soil structure, AM fungi, microbial activity and growth of Medicago sativa,” Waste Manage. 28 (8), 1423–1431 (2008).
A. Y. Kong, K. Hristova, K. M. Scow, and J. Six, “Impacts of different N management regimes on nitrifier and denitrifier communities and N cycling in soil microenvironments,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 42 (9), 1523–1533 (2010).
A. Y. Kong, K. M. Scow, A. L. Córdova-Kreylos, W. E. Holmes, and J. Six, “Microbial community composition and carbon cycling within soil microenvironments of conventional, low-input, and organic cropping systems,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 43 (1), 20–30 (2011).
A. Kulmatiski and K. H. Beard, “Long-term plant growth legacies overwhelm short-term plant growth effects on soil microbial community structure,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 43 (4), 823–830 (2011).
D. S. LeBauer and K. K. Treseder, “Nitrogen limitation of net primary productivity in terrestrial ecosystems is globally distributed,” Ecology. 89 (2), 371–379 (2008).
W. Liu, L. Jiang, S. Hu, L. Li, L. Liu, and S. Wan, “Decoupling of soil microbes and plants with increasing anthropogenic nitrogen inputs in a temperate steppe,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 72 (6), 116–122 (2014).
X. Liu, L. Duan, J. Mo, E. Du, J. Shen, X. Lu, Y. Zhang, X. Zhou, C. He, and F. Zhang, “Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: an overview,” Environ. Pollut. 159 (10), 2251–2264 (2011).
X. Liu, Y. Zhang, W. Han, et al., “Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China,” Nature 494 (7438), 459–462 (2013).
F. M. Lü, X. T. Lü, W. Liu, X. Han, G. M. Zhang, D. L. Kong, and X. G. Han, “Carbon and nitrogen storage in plant and soil as related to nitrogen and water amendment in a temperate steppe of northern China,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 47 (2), 187–196 (2011).
S. Malherbe and T. E. Cloete, “Lignocellulose biodegradation: fundamentals and applications,” Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 1 (2), 105–114 (2002).
N. W. Mungai, P. P. Motavalli, R. J. Kremer, and K. A. Nelson, “Spatial variation of soil enzyme activities and microbial functional diversity in temperate alley cropping systems,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 42 (2), 129–136 (2005).
Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate (U.S. Department of Agriculture Washington DC, 1954), pp. 18–19.
J. Rousk, P. C. Brookes, and E. Bååth, “Fungal and bacterial growth responses to N fertilization and pH in the 150-year “Park Grass” UK grassland experiment,” FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 76 (1), 89–99 (2011).
K. R. Saiya-Cork, R. L. Sinsabaugh, and D. R. Zak, “The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 34 (9), 1309–1315 (2002).
H. Sarula Chen, X. Hou, L. Ubugunov, O. Vishnyakova, X. Wu, et al., “Carbon storage under different grazing management in the typical steppe,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 47 (11), 1152–1160 (2014).
V. M. Semenov, L. A. Ivannikova, T. V. Kuznetsova, N. A. Semenova, and A. S. Tulina, “Mineralization of organic matter and the carbon sequestration capacity of zonal soils,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 41 (7), 717–730 (2008).
V. M. Semenov, L. A. Ivannikova, N. A. Semenova, A. K. Khodzhaeva, and S. N. Udal’tsov, “Organic matter mineralization in different soil aggregate fractions,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 43 (2), 141–148 (2010).
A. Sessitsch, A. Weilharter, M. H. Gerzabek, H. Kirchmann, and E. Kandeler, “Microbial population structures in soil particle size fractions of a long-term fertilizer field experiment,” Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 (9), 4215–4224 (2001).
R. C. Shen, M. Xu, Y. C. Gang, Y. Shen, and S. Q. Wan, “Soil microbial responses to experimental warming and nitrogen addition in a temperate steppe of northern China,” Pedosphere 24 (4), 427–436 (2014).
R. L. Sinsabaugh, M. M. Carreiro, and D. A. Repert, “Allocation of extracellular enzymatic activity in relation to litter composition, N deposition, and mass loss,” Biogeochemistry 60 (1), 1–24 (2002).
J. Six, E. T. Elliott, and K. Paustian, “Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: a mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 32 (14), 2099–2103 (2000).
R. Spaccini and A. Piccolo, “Effects of field managements for soil organic matter stabilization on water-stable aggregate distribution and aggregate stability in three agricultural soils,” J. Geochem. Explor. 129 (6), 45–51 (2013).
R. Spaccini and A. Piccolo, in Carbon Sequestration in Agricultural Soils. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Innovative Methods (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2012), pp. 61–105.
S. Steinbeißs, H. Beßler, C. Engels, et al., “Plant diversity positively affects short-term soil carbon storage in experimental grasslands,” Global Change Biol. 14 (12), 2937–2949 (2008).
C. J. Stevens, N. B. Dise, J. O. Mountford, and D. J. Gowing, “Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands,” Science 303 (5665), 1876–1879 (2004).
M. Stursova, C. L. Crenshaw, and R. L. Sinsabaugh, “Microbial responses to long-term N deposition in a semiarid grassland,” Microb. Ecol. 51 (1), 90–98 (2006).
M. Štursová, L. Žifcáková, M. B. Leigh, R. Burgess, and P. Baldrian, “Cellulose utilization in forest litter and soil: identification of bacterial and fungal decomposers,” FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 80 (3), 735–746 (2012).
K. N. Suding, S. L. Collins, L. Gough, et al., “Functional-and abundance-based mechanisms explain diversity loss due to N fertilization,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (12), 4387–4392 (2005).
K. K. Treseder, “Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: a meta-analysis of ecosystem studies,” Ecol. Lett. 11 (10), 1111–1120 (2008).
M. G. van Der Heijden, R. D. Bardgett, and N. M. van Straalen, “The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems,” Ecol. Lett. 11 (3), 296–310 (2008).
M. P. Waldrop and D. R. Zak, “Response of oxidative enzyme activities to nitrogen deposition affects soil concentrations of dissolved organic carbon,” Ecosystems 9 (6), 921–933 (2006).
M. P. Waldrop, D. R. Zak, R. L. Sinsabaugh, M. Gallo, and C. Lauber, “Nitrogen deposition modifies soil carbon storage through changes in microbial enzymatic activity,” Ecol. Appl. 14 (4), 1172–1177 (2004).
R. Z. Wang, T. R. Filley, Z. W. Xu, X. Wang, M. H. Li, Y. G. Zhang, W. T. Luo, and Y. Jiang, “Coupled response of soil carbon and nitrogen pools and enzyme activities to nitrogen and water addition in a semi-arid grassland of Inner Mongolia,” Plant Soil 381 (1–2), 323–336 (2014).
C. Wei, H. Zheng, Q. Li, et al., “Nitrogen addition regulates soil nematode community composition through ammonium suppression,” PloS One 7 (8), 1601–1620 (2012).
K. A. Whittinghill, W. S. Currie, D. R. Zak, A. J. Burton, and K. S. Pregitzer, “Anthropogenic N deposition increases soil C storage by decreasing the extent of litter decay: analysis of field observations with an ecosystem model,” Ecosystems 15 (3), 450–461 (2012).
Z. W. Xu, S. Q. Wan, H. Y. Ren, X. G. Han, and Y. Jiang, “Influences of land use history and short-term nitrogen addition on community structure in temperate grasslands,” J. Arid Environ. 87 (12), 103–109 (2012).
Z. Xu, S. Wan, G. Zhu, H. Ren, and X. Han, “The influence of historical land use and water availability on grassland restoration,” Restor. Ecol. 18 (1), 217–225 (2010).
H. Yao, D. Bowman, T. Rufty, and W. Shi, “Interactions between N fertilization, grass clipping addition and pH in turf ecosystems: implications for soil enzyme activities and organic matter decomposition,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 41 (7), 1425–1432 (2009).
Q. Yu, Q. Chen, J. Elser, et al., “Linking stoichiometric homoeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning and stability,” Ecol. Lett. 13 (11), 1390–1399 (2010).
Q. Yu, H. Wu, N. He, et al., “Testing the growth rate hypothesis in vascular plants with above-and belowground biomass,” PloS One 7 (3), e32162 (2012).
E. S. Zavaleta, M. R. Shaw, N. R. Chiariello, B. D. Thomas, E. E. Cleland, C. B. Field, and H. A. Mooney, “Grassland responses to three years of elevated temperature, CO2, precipitation, and N deposition,” Ecol. Monogr. 73 (4), 585–604 (2003).
L. H. Zeglin, M. Stursova, R. L. Sinsabaugh, and S. L. Collins, “Microbial responses to nitrogen addition in three contrasting grassland ecosystems,” Oecologia 154 (2), 349–359 (2007).
L. Zelles, “Phospholipid fatty acid profiles in selected members of soil microbial communities,” Chemosphere 35 (1–2), 275–294 (1997).
N. Zhang, W. Xu, X. Yu, D. Lin, S. Wan, and K. Ma, “Impact of topography, annual burning, and nitrogen addition on soil microbial communities in a semiarid grassland,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 77 (4), 1214–1224 (2013).
X. Zhou, C. Chen, Y. Wang, Z. Xu, H. Han, L. Li, and S. Wan, “Warming and increased precipitation have differential effects on soil extracellular enzyme activities in a temperate grassland,” Sci. Total Environ. 444 (2), 552–558 (2013).
C. Ziter and A. S. MacDougall, “Nutrients and defoliation increase soil carbon inputs in grassland,” Ecology 94 (1), 106–116 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Pochvovedenie, 2016, No. 10, pp. 1218–1229.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Sheng, L., Wang, Z. et al. Responses of soil enzyme activity and microbial community compositions to nitrogen addition in bulk and microaggregate soil in the temperate steppe of Inner Mongolia. Eurasian Soil Sc. 49, 1149–1160 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229316100124
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229316100124