Abstract
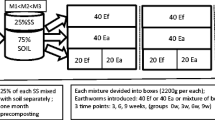
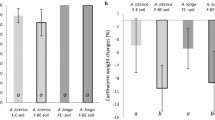
The influence of earthworms (Aporrectodea caliginosa, Lumbricus rubellus, L. terrestris, and Eisenia fetida) on the mobility of microelements and their availability for plants was studied. The contents of water-soluble Fe and Mn compounds extracted from the coprolites were 5–10 times higher than that in the soil (enriched in calcium carbonate and dried) consumed by the earthworms. This digestion-induced effect became higher with the age of the coprolites (up to 9 days) and took place under their alkalization. In the excreta (surface + enteric) of earthworms, the Fe concentration exceeded those of Mn and Zn by many times. Iron and manganese were mostly concentrated (>80% and >60%, respectively) in the organic part of the excrements. In the tests with hydroponics, the excreta were found to be a source of iron compounds available for plants that were similar to Fe2(SO4)3 or Fe-citrate by their physiological effect in the case when the Fe concentration in the excretions was above 0.7 μM. However, the single application of excreta of different earthworm species into the CaCO3 enriched soil did not significantly affect the plant (cucumber) nutrition. The analysis of the transport of microelements with xylem sap showed that this fact appeared to be due to the absence of an Fe deficit in the cucumber plants because of their high capability for the absorption of weakly soluble iron compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. P. Bityutskii, Essential Microelements of Plants (DEAN, St. Petersburg, 2005) [in Russian].
N. P. Bityutskii, I. N. Lapshina, E. I. Lukina, et al., “Role of Earthworms in Mineralization of Organic Nitrogen Compounds in Soil,” Pochvovedenie, No. 10, 1242–1250 (2002) [Eur. Soil Sci. 35 (10), 1100–1107 (2002)].
N. P. Bityutskii, A. N. Solov’eva, E. I. Lukina, et al., “Stimulating Effect of Earthworm Excreta on the Mineralization of Nitrogen Compounds in Soil,” Pochvovedenie, No. 4, 468–473 (2007) [Eur. Soil Sci. 40 (4), 426–431 (2007)].
A. I. Zrazhevskii, Earthworms as a Fertility Factor of Forest Soils (Akad. Nauk Ukr. SSR, Kiev, 1957) [in Russian].
A. V. Tiunov, Extended Abstract of Doctoral Dissertation in Biology (Moscow, 2007).
V. M. Churbanov and D. M. Alekseeva,“Determination of Small Iron Amounts in Plants,” Agrokhimiya, No. 12, 123–128 (1969).
A. A. Shlyk, “Determination of Chlorophylls and Carotinoids in Extracts from Green Leaves,” in Biochemical Methods in Plant Physiology, Ed. by O. A. Pavlinova (Nauka, Moscow, 1971), pp. 154–170 [in Russian].
A. M. M. Abdul Rida, Concentrations et croissance de lombriciens et de plantes dans des sols contamines ou non par Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb et Zn: interactions plantesollombricien, Soil Biol. Biochem. 28, 1029–1035 (1996).
O. Atlavinyte and Y. Vanagas, “The Effect of Earthworms on the Quality of Barley and Rye Grain,” Pedobiologia 23, 256–262 (1982).
S. S. Bhattacharya and G. N. Chattopadhyay, “Effect of Vermicomposting on the Transformation of Some Trace Elements in Fly Ash,” Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst 75, 223–231 (2006).
J. Cheng and M. H. Wong, “Effects of Earthworms on Zn Fraction in Soils” Biol. Fertil. Soils 36, 72–78 (2002).
M. Coeurdassier, R. Scheifler, de Vaufleury, et al., “Earthworms Influence Metal Transfer from Soil to Snails,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 35, 302–310 (2007).
W. Devliegher and W. Verstraete, “The Effect of Lumbricus terrestris on Soil in Relation to Plant Growth: Effects of Nutrient-Enrichment Processes (NEP) and Gut-Associated Processes (GAP),” Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 341–346 (1997).
J. Dominguez, C. A. Edwards, and S. A. Subler, “A Comparison of Vermicomposting and Composting,” BioCycle 38, 57–58 (1997).
H. Marschner, Mineral Plant Nutrition (Academic, London, 1997).
A. Noguchi, I. Hasegawa, and J. Yazaki, “Use of Xylem Sap to Determine Differences in the Availability of Mineral Elements in Soils,” in Plant Nutrition: Food Security and Sustainability of Agro-Ecosystems (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 2001), pp. 734–735.
W. J. G. M. Peijnenburg and T. Jager, “Monitoring Approaches to Assess Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Metals: Matrix Issues,” Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 56, 63–77 (2003).
S. Scheu, “Effects of Earthworms on Plant Growth: Patterns and Perspectives,” Pedobiologia 47 (2003).
U. Tomati, E. Galli, A. Grappelli, and G. Di Lena, “Effect of Earthworm Casts on Protein Synthesis in Radish (Raphanus Sativum) and Lettuce (Lactuga sativa) Seedlings,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 9, 288–289 (1990).
U. Tomati, E. Galli, and L. Pasetti, “Effect of Earthworms on Molybdenum-Depending Activities,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 23, 359–361 (1996).
B. Wen, X. Y. Hu, B. Wen Liu, et al., “The Role of Earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in Influencing Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Soils,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 40, 181–187 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.P. Bityutskii, P.I. Kaidun, 2008, published in Pochvovedenie, 2008, No. 12, pp. 1479–1486.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bityutskii, N.P., Kaidun, P.I. The influence of earthworms on the mobility of microelements in soil and their availability for plants. Eurasian Soil Sc. 41, 1306–1313 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229308120089
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229308120089