Abstract
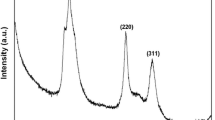
Colloidal chemistry techniques at elevated temperatures (250–300°C) have been used to synthesize big (up to 20 nm) quantum dots (QDs) based on indium antimonide (InSb). In respect to their optical and electrical characteristics, the obtained big QDs exhibit properties similar to those of QDs with usual dimensions (4–5 nm), except the spectral maximum of luminescence being shifted inadequately to the size difference. This circumstance, together with the QD shape as measured by transmission electron microscopy, can be indicative of a less perfect crystalline structure of obtained big QDs, probably resulting from insufficiently high temperature of synthesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. B. Brichkin and V. F. Razumov, Russ. Chem. Rev. 85, 1297 (2016).
P. Reiss, M. Carriere, C. Lincheneau, L. Vaure, and S. Tamang, Chem. Rev. 116, 10731 (2016).
S. Tamang, K. Kim, H. Choi, Y. Kim, and S. Jeong, Dalton Trans. 44, 16923 (2015).
W. Liu, A. Y. Chang, R. D. Schaller, and D. V. Talapin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 20258 (2012).
V. Ya. Aleshkin, Modern Physics of Semiconductors. http://www.pnn.unn.ru/UserFiles/lectures/Aleshkin_lectures.pdf.
A. I. Mikhailov, V. F. Kabanov, N. D. Zhukov, and E. G. Glukhovskoy, Nanosyst.: Phys. Chem., Math. 8, 596 (2017).
K. Yaemsunthorn, T. Thongtem, S. Thongtem, and C. Randorn, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 68, 53 (2017).
M. Yarema and M. V. Kovalenko, Chem. Mater. 25, 1788 (2013).
D. V. Kryl’skii and N. D. Zhukov, Tech. Phys. Lett. 45, 801 (2019).
W. Shen, H. Tang, X. Yang, Z. Cao, T. Cheng, X. Wang, Z. Tand, J. You, and Z. Deng, J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 8243 (2017).
A. V. Lukashin and A. A. Eliseev, Chemical Methods of Nanoparticle Synthesis (Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 2007) [in Russian]. http://www.ignorik.ru/ign/660/d-659553/7z-docs/3.pdf.
N. D. Zhukov, D. S. Mosiyash, I. V. Sinev, A. A. Khazanov, A. V. Smirnov, and I. V. Lapshin, Tech. Phys. Lett. 43, 1124 (2017).
N. D. Zhukov, A. A. Khazanov, and Ya. E. Pereverzev, Tech. Phys. Lett. 43, 547 (2017).
A. Kurzmann, P. Stegmann, J. Kerski, R. Schott, A. Ludwig, A. D. Wieck, J. König, A. Lorke, and M. Geller, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 247403 (2019).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to S.V. Dezhurov for manufacturing nanoparticles, M.V. Gavrikov for conducting the STM measurements, and I.T. Yagudin for the SEM and TEM measurements.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, projects no. 18-07-00586-a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by P. Pozdeev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krylsky, D.V., Zhukov, N.D. Synthesis and Properties of Indium Antimonide Big Quantum Dots. Tech. Phys. Lett. 46, 901–904 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785020090205
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785020090205