Abstract
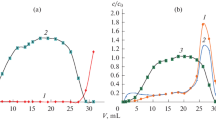
An attempt at eliminating the nonspectral matrix effect leading to suppression of the analytic signal intensity at instrument output has been made using an Agilent-7700 mass spectrometer with inductively coupled plasma with a quadrupole analyzer for several elements in blood and urine. It is shown that acid and salt compositions, as well as organic substances in the composition of the sample itself, play a decisive role in the emergence of the nonspectral matrix effect. The role of acid, salt, and organic compositions of the entire blood matrix and urine in underrating the results of determination of several elements has been estimated. It has also been shown that the internal standard must be chosen proceeding from the closeness of its first ionization potential to the first ionization potential of the element being determined. The contributions of nonspectral matrix effects to the distortion of the results of analysis of biological liquids have been analyzed and estimated. It has been found that the dependence of the matrix effect on salts in the acidic matrix and on the operating regime of the instrument is additive.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. A. Pupyshev and V. T. Surikov, Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ion Production (Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Yekaterinburg, 2006).
Agilent 7700 ICP-MS Specifications (Agilent Technologies, 2012).
P. J. Parsons and F. Barbosa, Spectrochim. Acta B 62, 992 (2007).
D. V. Yaroshenko and L. A. Kartsova, J. Anal. Chem. 69, 311 (2014).
R. Xu, L. Fan, M. Rieser, and T. El-Shourbagy, J. Pharm. Biomed. 44, 342 (2007).
A. Ciric, H. Prosen, M. Jelikic-Stankov, and P. Durdevic, Talanta 99, 780 (2012).
R. King, R. Bonfiglio, C. Fernandez-Metzler, C. Miller-Stein, and T. Olah, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 11, 942 (2000).
R. Dams, M. Huestis, W. Lambert, and C. Murphy, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 14, 1290 (2003).
I. I. Stewart and J. W. Olesik, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 13, 1313 (1998).
J.-L. Todoli and J.-M. Mermet, Spectrochim. Acta B 54, 895 (1999).
M. A. Kartasheva, V. G. Borovitskii, and S. Yu. Dubnikov, RF Patent No. 2039970 (1995).
T. W. May and R. H. Wiedmeyer, At. Spectrosc. 19, 150 (1998).
T. K. Nurubeyli, Z. K. Nurubeyli, K. Z. Nuriyev, and K. B. Gurbanov, Tech. Phys. 62, 305 (2017).
G. I. Ramendik, E. V. Fatyushina, A. I. Stepanov, and V. S. Sevast’yanov, J. Anal. Chem. 56, 500 (2001).
A. M. Gashimov, K. Z. Nuriev, S. Manuchar, K. B. Gurbanov, and Z. K. Nurubeili, Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 44, 159 (2008).
Z. K. Nurubeili, K. Z. Nuriev, and G. M. Kerimov, Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 49, 331 (2013).
A. F. Pupyshev and E. V. Semenova, Anal. Kontrol’ 4, 120 (2000).
J. Emsley, The Elements (Clarendon, 1998).
C. Tanaselia, T. Frentiu, M. Ursu, M. Vlad, M. Chintoanu, E. Cordos, L. David, M. Paul, and D. Gomoiescu, Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2, 99 (2008).
D. R. Lide and B. Raton, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 89th ed. (CRC, 2008).
S. Awad, S. P. Allison, and D. N. Lobo, Clin. Nutr. 27, 179 (2008).
A. V. Skal’nyi, Chemical Elements in Human Physiology and Ecology (Oniks 21 Vek, Moscow, 2004).
V. K. Karandashev, A. Yu. Leykin, and K. Z. Zhernokleeva, J. Anal. Chem. 69, 22 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by N. Wadhwa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nurubeyli, T.K., Nuriyev, K.Z., Nurubeyli, Z.K. et al. Role of the Matrix Effect in Analysis of Biological Objects Using Mass Spectrometry with Inductively Coupled Plasma. Tech. Phys. 64, 909–915 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784219060148
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784219060148