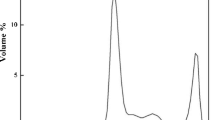
Abstract
A copper-based electrical-contact composite material hardened by disperse zinc oxide and zinc titanate is studied by scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis. The distribution of oxide phases in the samples containing 2.5 wt % oxide nanopowder mixture in an initial charge is found to be uniform. An increase in the amount of oxides leads to an increase in their sized in sintering. A relation between the sample wear and the sample composition is obtained during laboratory tests. It is shown that the introduction of more than 2.5 wt % oxide mixture results in intense wear of the working surface of the sample and an increase in the running-in period of contacts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Braunovic, V. V. Konchits, and N. K. Myshkin, Electrical Contacts: Fundamentals, Applications, and Technology (CRC, Tailor and Francis, London–New York, 2007).
Sintered Materials for Electrical Engineering and Electronics: a Handbook, Ed. by G. G. Gnesin (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1981).
L. T. Denisova, N. V. Belousova, V. M. Denisov, et al., Zh. Sib. Fed. Univ., Ser. Tekh., Tekhnol. 3, 250 2009.
H. Holm, Electric Contacts (Springer, Berlin, 2010).
S. Kulas, “Welding of contacts when closing electrical circuits,” in Electrical contacts and electrodes, Tr. Inst. Probl. Mater. im. I. N. Frantsevich Nats. Akad. Nauk Ukr., 145 (2010).
I. P. Rad’ko, Aktual. Vopr. Sovr. Nauki, No. 31, 174 2014.
V. I. Milykh and T. P. Pavlenko, Elektrotekh. Komp’yut. Sist., No. 3, 325 2011.
Yu. I. Gordeev, G. M. Zeer, E. G. Zelenkova, et al., Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Poroshk. Metallurg. Funkts. Pokrytiya, No. 4, 47 2010.
G. M. Zeer, E. G. Zelenkova, A. V. Sidorak, O. N. Ledyaeva, and M. Yu. Kuchinskii, Tech. Phys. 58, 710 2013.
D. Zhou, F. Qiu, H. Wan, and Q. Jian, Acta Metall. Sin. 27, 798 2014.
G. P. Luchinskii, Chemistry of Titanium (Khimiya, Moscow, 1971).
M. P. Afonin and M. N. Ovchinnikova, Electrical Contacts and Electrodes, Tr. Inst. Probl. Mater. im. I. N. Frantsevich Nats. Akad. Nauk Ukr., 116 (2010).
M. Abbaoui, A. Lefort, D. Sallais, and N. Benjemaa, in Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, The Delta Centre, Montreal, 2006, pp. 103–109.
G. M. Zeer, E. G. Zelenkova, O. N. Ledyaeva, et al., RF Patent No. 2 52 5882, Byull. Izobret. No. 23 (2014).
F. H. Dulin and D. E. Rase, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 43, 125 1960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.M. Zeer, E.G. Zelenkova, V.V. Beletskii, S.V. Nikolaev, A.N. Kozhurin, M.Yu. Kuchinskii, O.A. Grigor’eva, 2015, published in Zhurnal Tekhnicheskoi Fiziki, 2015, Vol. 60, No. 12, pp. 88–93.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeer, G.M., Zelenkova, E.G., Beletskii, V.V. et al. Microstructure and properties of an electrocontact Cu–(ZnO/TiO2) material. Tech. Phys. 60, 1823–1828 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784215120270
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784215120270