Abstract
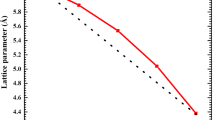
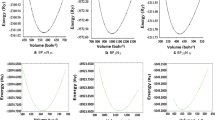
In order to extract structural and electronic properties of BxIn1 – xAs ternary alloys and enrich the database of materials based on boron and indium, we have used full-potential augmented plane wave (FP-LAPW) method through the density function theory (DFT) and within generalized gradient approximation (GGA), local density approximation (LDA), and Tran–Blaha modified Becke–Johnson approximation (TB–mBJ). We have optimized the cohesive energy of our binary compound and ternary alloys versus volume of the unit cell firstly, and we have found that the optimum volume, lattice parameter, and the bulk modulus vary for different boron concentrations. Using DFT–mBJ calculations, we found that InAs possess direct band-gap energy and an indirect gap semiconductor for BAs and B0.75In0.25As. However, B0.25In0.75As and B0.5In0.5As ternary alloys have a metallic and semi metallic characters, respectively. We also studied the optical properties of our BAs and InAs binary and B0.75In0.25As ternary semiconductors and their behaviors are also investigated under the application of hydrostatic pressure in a range of 0 to 25 GPa. In summary, we conclude that the incorporation of boron atom in InAs increase its hardness and affects the band-gap energy considerably, and therefore provides a novel research perspective. We note that InAs binary compound loses its semiconductor character and becomes semi-metal at 5 GPa.

















Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N. Chimot, J. Even, H. Folliot, and S. Loualiche, Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 364, 263 (2005).
F. El Haj Hassan and H. Akbarzadeh, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 121, 171 (2005).
M. Guemou, B. Bouhafs, A. Abdiche, R. Khenata, Y. Al Douri, and S. Bin Omran, Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 407, 1292 (2012).
R. Ahmed, S. J. Hashemifar, H. Akbarzadeh, M. Ahmed, and F. Aleem, Comput. Mater. Sci. 39, 580 (2007).
M. Ferhat, A. Zaoui, M. Certier, and H. Aourag, Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 252, 229 (1998).
R. Bhat, P. S. Dutta, and S. Guha, J. Cryst. Growth 310, 1910 (2008).
V. N. Brudnyi, N. G. Kolin, and A. I. Potapov, Semiconductors 37, 390 (2003).
J. A. Perri, S. Laplaca, and B. Post, Acta Crystallogr. 11, 310 (1958).
T. L. Chu and A. E. Hyslop, J. Appl. Phys. 43, 276 (1972).
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G. K. H. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, and J. Luitz, WIEN2k, An Augmented Plane Wave Plus Local Orbital Program for Calculating Crystal Properties (Vienna Univ. Technol., Vienna, Austria, 2001).
F. D. Murnaghan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 30, 244 (1947).
Y. Yan, Q. Wang, W. Shu, Z. Jia, X. Ren, X. Zhang, and Y. Huang, Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 407, 4570 (2012).
R. W. G. Wyckoff, Crystal Structures, 2nd ed. (Krieger, Malabar, 1986).
K. H. Hellwege and O. Madelung, Landolt–Börnstein, New Series, Group III (Springer, Berlin, 1982), Vol. 17, Pt. A.
M. Vubcevich, Phys. Status Solidi B 54, 219 (1972).
H. Meradji, S. Labidi, S. Ghemid, S. Drablia, and B. Bouhafs, Phys. Proc. 2, 933 (2009).
H. Bross and R. Bader, Phys. Status Solidi B 191, 369 (1995).
O. Madelung, Landolt-Börnstein, New Series, Group III (Springer, Berlin, 1982), Vol. 17a.
R. Wentzcovitch, M. L. Cohen, and P. K. Lam, Phys. Rev. B 36, 6058 (1987).
M. Briki, M. Abdelouhab, A. Zaoui, and M. Ferhat, Superlatt. Microstruct. 45, 80 (2009).
N. Tayebi, K. Benkabou, and F. Z. Aoumeur-Benkabou, Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 407, 2739 (2012).
P. P. Paskov, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 1890 (1997).
T. Hofmann, M. Schubert, G. Leibiger, and V. Gottschalch, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 182110 (2007).
S. Adachi, J. Appl. Phys. 61, 4869 (1987).
H. Baaziz, Z. Charifi, and N. Bouarissa, Mater. Chem. Phys. 68, 197 (2001).
M. Merabet, D. Rached, R. Khenata, S. Benalia, B. Abidri, N. Bettahar, and S. BinOmran, Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 406, 3247 (2011).
A. Zaoui and F. El Haj Hassan, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 253 (2001).
V. M. Daniel’tsev, N. V. Vostokov, Yu. N. Drozdov, M. N. Drozdov, A. V. Murel, D. A. Pryakhin, O. I. Khrykin, and V. I. Shashkin, J. Surf. Invest. 2, 514 (2008).
M. Rabah, B. Abbar, Y. Al-Douri, B. Bouhafs, and B. Sahraoui, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 100, 163 (2003).
F. Tran and P. Blaha, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 226401 (2009).
P. J. L. Hervé and L. K. J. Vandamme, J. Appl. Phys. 77, 5476 (1995).
N. M. Ravindra, S. Auluck, and V. K. Srivastava, Phys. Status Solidi B 93, 155 (1979).
D. E. Aspnes and A. A. Studna, Phys. Rev. B 27, 985 (1983).
M. Othman, E. Kasap, and N. Korozlu, J. Alloys Compd. 496, 230 (2010).
N. Amrane and M. Benkraouda. J. Adv. Phys. 13, 5041 (2017).
M. I. Ziane, Z. Bensaad, B. Labdelli, and H. Bennacer, Sens. Transducers 27 (Spec. Iss.), 374 (2014).
R. Wentzcovitch, M. L. Cohen, and P. K. Lam, Phys. Rev. B 36, 6058 (1987).
H. Meradji, S. Labidi, S. Ghemid, S. Drablia, and B. Bouhafs, Phys. Proc. 2, 933 (2009).
S. Adachi, Properties of Group IV, III–V, and II–VI Semiconductors (Wiley, New York, 2005), Chap. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guemou, M., Khelil, M. & Abdiche, A. Pressure Effect Study on the Electronic and Optical Properties of BxIn1 – xAs Alloys Using DFT Calculation. Phys. Solid State 62, 1815–1829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378342010011X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378342010011X