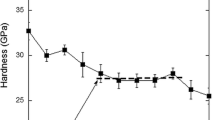
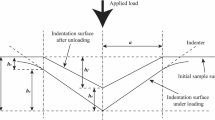
Abstract
The size hardness effects are studied via the micro- and nanoindentation methods over the wide range of the depth of print h (from dozens of nanometers to several dozen micrometers) for several classes of materials, such as ionic and covalent single crystals (sapphire, silicon, lithium fluoride); metals (single-crystal Al, polycrystalline Cu, Ni, and Nb); ceramics (high-strength nanostructured TZP-ceramic based on the natural zirconium dioxide–baddeleyite mineral); amorphous materials (fused quartz); and polymers (polycarbonate and polytetrafluoroethylene). As is shown, some of them possess severe size hardness effects, whereas the others reveal the weak ones or even a lack of these effects. The thermoactivation analysis is implemented, as well, and the activating and energy characteristics of local deformation processes induced by an indenter are compared with the dominant plasticity micromechanisms of the studied materials at different stages of the print formation and with the size peculiarities. The materials with low hardness coefficients and meeting the requirements of ISО 14577 and GOST R 8.748-2011 standards in the nanohardness measurements are highlighted, as well. In the established load ranges, these materials are the promising candidates for their use as reference samples, which are designed to ensure the uniformity of the hardness measurements at the nano- and microscales, as well as for calibrating and testing the nanoindentometers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology, Ed. by B. Bhushan (Springer, Berlin, 2010).
Yu. I. Golovin, Principles of Nanotechnology (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 2012) [in Russian].
A. C. Fischer-Cripps, Nanoindentation (Springer, New York, 2011).
Yu. I. Golovin, Nanoindentation and Its Possibilities (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
A. S. Grashchenko, S. A. Kukushkin, and A. V. Osipov, Tech. Phys. Lett. 40, 1114 (2014).
W. D. Nix and H. Gao, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 411 (1998).
L. A. Berla, S. W. Lee, Yi. Cui, and W. D. Nix, J. Power Sources 273, 41 (2015).
X. Qiao, L. Han, W. Zhang, and J. Gu, Mater. Characteriz. 110, 86 (2015).
T. Csanádi, S. Grasso, A. Kovalcíková, J. Dusza, and M. Reece, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 36, 239 (2016).
D. Wu, J. S. C. Jang, and T. G. Nieh, Intermetallics 68, 118 (2016).
Yu. I. Golovin, Phys. Solid State 50, 2205 (2008).
Yu. I. Golovin, V. M. Vasyukov, V. V. Korenkov, P. A. Stolyarov, A. V. Shuklinov, and L. E. Polyakov, Tech. Phys. 56, 642 (2011).
Yu. I. Golovin, V. I. Ivolgin, A. I. Tyurin, S. V. Potapov, V. Z. Bengus, and E. D. Tabachnikova, Crystallogr. Rep. 50, 291 (2005).
M. Sh. Akchurin, R. V. Gainutdinov, E. A. Garibin, Yu. I. Golovin, A. A. Demidenko, K. V. Dukel’skii, S. V. Kuznetsov, I. A. Mironov, V. V. Osiko, A. N. Smirnov, N. Yu. Tabachkova, A. I. Tyurin, P. P. Fedorov, and V. V. Shindyapin, Perspekt. Mater., No. 5, 5 (2010).
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
D. M. Dimiduk, M. D. Uchic, and T. A. Parthasarathy, Acta Mater. 53, 4065 (2005).
J. Biener, A. M. Hodge, J. R. Hayes, C. A. Volkert, L. A. Zepeda-Ruiz, Al. V. Hamza, and F. F. Abraham, Nano Lett. 6, 2379 (2006).
F. Xu, Y. H. Ding, X. H. Deng, P. Zhang, and Z. L. Long, Physica B 450, 84 (2014).
D. Maharaj and B. Bhushan, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 95, 1 (2015).
K. Herrmann, N. M. Jennett, S. Kuypers, I. McEntegaart, C. Ingelbrecht, U. Hangen, T. Chudoba, F. Pohlenz, and F. Menelaoa, Z. Metallk. 94, 802 (2003).
Hardness Testing: Principles and Applications, Ed. by K. Herrmann (ASM Int., Materials Park, Ohio, 2011).
Yu. I. Golovin, A. I. Tyurin, and V. V. Khlebnikov, Tech. Phys. 50, 479 (2005).
Yu. I. Golovin, A. I. Tyurin, and B. Ya. Farber, Philos. Mag. A 82, 1857 (2002).
Yu. I. Golovin, A. I. Tyurin, and B. Ya. Farber, J. Mater. Sci. 37, 895 (2002).
Yu. I. Golovin, V. I. Ivolgin, A. I. Tyurin, and V. A. Khonik, Phys. Solid State 45, 1267 (2003).
Yu. I. Golovin, A. A. Shibkov, Yu. S. Boyarskaya, M. S. Kats, and A. I. Tyurin, Sov. Phys. Solid State 30, 2005 (1988).
S. D. Viktorov, Yu. I. Golovin, A. N. Kochanov, A. I. Tyurin, A. V. Shuklinov, I. A. Shuvarin, and T. S. Pirozhkova, Fiz.-Tekh. Probl. Razrab. Polezn. Iskopaemykh 50, 46 (2014).
Yu. I. Golovin, R. B. Morgunov, D. V. Lopatin, A. A. Baskakov, and Ya. E. Evgen’ev, Phys. Solid State 40, 1870 (1998).
Yu. I. Golovin and R. B. Morgunov, Phys. Solid State 43, 859 (2001).
Yu. A. Osip’yan, Yu. I. Golovin, R. B. Morgunov, R.K.Nikolaev, I. A. Pushnin, and S. Z. Shmurak, Phys. Solid State 43, 1389 (2001).
Yu. Golovin, R. Morgunov, and A. Baskakov, Mol. Phys. 100, 1291 (2002).
Yu. I. Golovin and R. B. Morgunov, JETP Lett. 61, 596 (1995).
GOST (State Standard) R 8.748-2011 (Standartinform, Moscow, 2013).
ISO Standard No. 14577-1–3 (2002), ISO Standard No. 14577-4 (2007).
X. Feng, Y. Hyang, and K. Hwang, in Micro- and Nano Mechnical Testing of Materials and Devices, Ed. by F. Yang and J. C. M. Li (Springer, New York, 2008), p. 49.
Yu. R. Kolobov, Diffusion Controlled Processes on Grain Boundaries and Plasticity of Metal Polycrystals (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1998) [in Russian].
R. A. Andrievski and A. M. Glezer, Phys. Usp. 52, 315 (2009).
Y. Y. Lim and M. M. Chaudhri, Philos. Mag. A 82, 2071 (2002).
I. Manika and J. Maniks, Acta Mater. 54, 2049 (2006).
S. Qu, Y. Huang, W. D. Nix, H. Jiang, F. Zhang, and K. C. Hwang, J. Mater. Res. 19, 3423 (2004).
M. A. Meyers, A. Mishra, and D. J. Benson, Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 427 (2006).
T. P. Remington, C. J. Ruestes, E. M. Bringa, B. A. Remington, C. H. Lu, B. Kad, and M. A. Meyers, Acta Mater. 78, 378 (2014).
C. J. Ruestes, A. Stukowski, Y. Tang, D. R. Tramontina, P. Erhart, B. A. Remington, H. M. Urbassek, M. A. Meyers, and E. M. Bringa, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 613, 390 (2014).
A. E. Romanov, A. L. Kolesnikova, I. A. Ovid’ko, and E. C. Aifantis, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 503, 62 (2009).
V. L. Indenbom, JETP Lett. 12, 369 (1970).
I. C. Choi, Y. J. Kim, B. Ahn, M. Kawasaki, T. G. Langdon, and J. I. Jang, Scripta Mater. 75, 102 (2014).
Yu. I. Golovin, S. N. Dub, V. I. Ivolgin, V. V. Korenkov, and A. I. Tyurin, Phys. Solid State 47, 995 (2005).
Yu. I. Golovin, V. I. Ivolgin, V. V. Korenkov, and A. I. Tyurin, Tech. Phys. Lett. 23, 621 (1997).
Yu. I. Golovin and A. I. Tyurin, Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Fiz. 59, 49 (1995).
Yu. I. Golovin and A. I. Tyurin, Phys. Solid State 38, 1000 (1996).
Yu. I. Golovin and A. I. Tyurin, Crystallogr. Rep. 40, 818 (1995).
S. N. Zhurkov and B. N. Narzullaev, Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 23, 1677 (1953).
S. N. Zhurkov, Int. J. Fract. Mech. 1, 311 (1965).
V. R. Regel’, A. I. Slutsker, and E. E. Tomashevskii, The Kinetic Nature of the Strength of Solids (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 1974) [in Russian].
V. L. Indenbom, in Thermally Activated Processes (Mir, Moscow, 1973), p. 5 [in Russian].
V. L. Indenbom, A. N. Orlov, and Yu. Z. Estrin, in Elementary Processes of Plastic Crystal Deformation (Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 1978), p. 93 [in Russian].
V. L. Hilarov, Phys. Solid State 47, 832 (2005).
H. Conrad, Nanotechnology 18, 325701 (2007).
L. Lu, X. Chen, X. Huang, and K. Lu, Science 323, 607 (2009).
H. Somekawa, A. Singh, and C. A. Schuh, J. Alloys Compd. 685, 1016 (2016).
H. Somekawa and C. A. Schuh, Acta Mater. 59, 7554 (2011).
J. K. Mason, A. C. Lund, and C. A. Schuh, Phys. Rev. B 73, 054102 (2006).
C. A. Schuh, J. K. Mason, and A. C. Lund, Nat. Mater. 4, 617 (2005).
M. Sakai, Acta Metal. Mater. 41, 1751 (1993).
M. T. Attaf, Mater. Lett. 57, 4684 (2003).
O. Uzun, N. Güçlü, U. Kölemen, and O. Şahin, Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 5 (2008).
H. Conrad, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 341, 216 (2003).
H. J. Frost and M. F. Ashby, Deformation Mechanism Maps: The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics (Pergamon, Oxford, 1982).
S. V. Eremeev, L. Yu. Nemirovich-Danchenko, and S. E. Kul’kova, Phys. Solid State 50, 543 (2008).
J. Carrasco, N. Lopez, and F. Illas, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 225502 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Yu.I. Golovin, A.I. Tyurin, E.G. Aslanyan, T.S. Pirozhkova, V.M. Vasyukov, 2017, published in Fizika Tverdogo Tela, 2017, Vol. 59, No. 9, pp. 1778–1786.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golovin, Y.I., Tyurin, A.I., Aslanyan, E.G. et al. The physical and mechanical properties and local deformation micromechanisms in materials with different dependence of hardness on the depth of print. Phys. Solid State 59, 1803–1811 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783417090104
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783417090104