Abstract
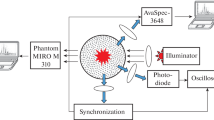
Some results from studies of microwave discharges in heavy hydrocarbons are presented. Microwave energy was introduced into liquid hydrocarbon via a coaxial line. The pressure above the liquid surface was equal to the atmospheric pressure. The discharge was ignited in a mixture of argon and hydrocarbon vapor. Argon was supplied through a channel in the central conductor of the coaxial line. The emission spectra of discharges in different liquid hydrocarbons were studied. It is shown that the emission spectra mainly consist of sequences of Swan bands, while radiation of other plasma components is on the noise level. Spectra of plasma emission are presented for discharges in liquid n-heptane, nefras, and C-9 oil used to produce chemical fibers. The rotational (gas) and vibrational temperatures are determined by processing the observed spectra.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Samukawa, M. Hori, S. Rauf, K. Tachibana, P. Bruggeman, G. Kroesen, J. C. Whitehead, A. B. Murphy, A. F. Gutsol, S. Starikovskaia, U. Kortshagen, J. P. Boeuf, T. J. Sommerer, M. J. Kushner, U. Czarnetzki, et al., J. Phys. D 45, 253001 (2012).
P. Bruggeman and C. Leys, J. Phys. D 42, 053001 (2009).
Y. Yang, Y. I. Cho, and A. Fridman, Plasma Discharge in Liquid: Water Treatment and Applications (CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 2012).
W. G. Graham and K. R. Stalder, J. Phys. D 44, 174037 (2011).
Y. Hattori, S. Mukasa, S. Nomura, and H. Toyota, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 063305 (2010).
T. Ishijima, H. Sugiura, R. Saito, H. Toyoda, and H. Sugai, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 19, 015010 (2010).
B. Wang, B. Sun, X. Zhu, Z. Yan, Y. Liu, and H. Liu, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 418, 012099 (2013).
B. Wang, B. Sun, X. Zhu, Z. Yan, Y. Liu, and H. Liu, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 53, 697 (2013).
S. Nomura, H. Toyota, S. Mukasa, Y. Takahashi, T. Maehara, A. Kawashima, and H. Yamashita, Appl. Phys. Express. 1, 046002 (2008).
T. Ishijima, H. Hotta, and H. Sugai, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 121501 (2007).
T. Ishijima, H. Sugiura, R. Satio, H. Toyada, and H. Sugai, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 19, 015010 (2010).
T. Ishijima, K. Nosaka, Y. Tanaka, Y. Uesugi, Y. Goto, and H. Horibe, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 142101 (2013).
S. Nomura and H. Toyota, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4503 (2003).
S. Nomura, H. Toyota, M. Tawara, and H. Yamashota, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 231502 (2006).
S. Nomura, H. Toyota, S. Mukasa, H. Yamashita, and T. Maehara, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 211503 (2006).
S. Nomura, H. Toyota, S. Mukasa, H. Yamashita, T. Maehara, and A. Kawashima, J. Appl. Phys. 106, 073306 (2009).
H. Toyota, S. Nomura, Y. Takahashi, and S. Mukasa, Diamond Relat. Mater. 17, 1902 (2008).
Yu. A. Lebedev, V. S. Konstantinov, M. Yu. Yablokov, A. N. Shchegolikhin, and N. M. Surin, High Energy Chem. 48, 385 (2014).
N. N. Buravtsev, V. S. Konstantinov, Yu. A. Lebedev, and T. B. Mavlyudov, in Proceedings of the VIII International Workshop “Microwave Discharges: Fundamentals and Applications,” Zvenigorod, 2012, Ed. by Yu. A Lebedev, p. 167.
H. Toyota, S. Nomura, and S. Mukasa, Int. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2 (3), 83 (2013).
Y. Hattori, S. Mukasa, H. Toyota, H. Yamashita, and S. Nomura, Surf. Coat. Technol. 206, 2140 (2012).
E. Camerotto, R. De Schepper, and A. Y. Nikiforov, J. Phys. D 45, 435201 (2012).
Yu. A. Lebedev, I. L. Epstein, V. A. Shakhatov, E. V. Yusupova, and V. S. Konstantinov, High Temp. 52, 319 (2014).
A. V. Tatarinov, Yu. A. Lebedev, and I. L. Epstein, High Energy Chem. 50, 144 (2016).
Yu. A. Lebedev, A. V. Tatarinov, I. L. Epstein, and K. A. Averin, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 36, 535 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.A. Averin, Yu.A. Lebedev, V.A. Shakhatov, 2016, published in Prikladnaya Fizika, 2016, No. 2, pp. 41–45.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Averin, K.A., Lebedev, Y.A. & Shakhatov, V.A. Some Results from Studies of Microwave Discharges in Liquid Heavy Hydrocarbons. Plasma Phys. Rep. 44, 145–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063780X18010014
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063780X18010014