Abstract
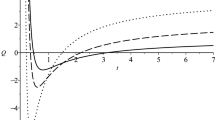
We study dynamics of induced gravity cosmological models with the sixth-degree polynomial potentials, that have been constructed using the superpotential method. We find conditions on the potential under which exact bounce solutions exist and study the stability of these solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. A. R. Ade et al. (Planck Collab.), “Planck 2015 results. XX. Constraints on inflation,” Astron. Astrophys. 594, A20 (2016); arXiv:1502.02114.
B. Boisseau, H. Giacomini, D. Polarski, and A. A. Starobinsky, “Bouncing universes in scalar-tensor gravity models admitting negative potentials,” J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1507, 002 (2015); arXiv:1504.07927.
B. Boisseau, H. Giacomini, and D. Polarski, “Bouncing universes in scalar-tensor gravity around conformal invariance,” J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1605, 048 (2016); arXiv:1603.06648.
A. Yu. Kamenshchik, E. O. Pozdeeva, A. Tronconi, G. Venturi, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Interdependence between integrable cosmological models with minimal and non-minimal coupling,” Classical Quantum Gravity 33, 015004 (2016); arXiv:1509.00590.
E. O. Pozdeeva, M. A. Skugoreva, A. V. Toporensky, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Possible evolution of a bouncing universe in cosmological models with non-minimally coupled scalar fields,” J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1612, 006 (2016); arXiv:1608.08214.
P. Fre, A. Sagnotti, and A. S. Sorin, “Integrable scalar cosmologies I. Foundations and links with string theory,” Nucl. Phys. B 877, 1028 (2013); arXiv:1307.1910; P. Fre, A. S. Sorin, and M. Trigiante, “Integrable scalar cosmologies II. Can they fit into gauged extended supergavity or be encoded in N = 1 superpotentials?,” Nucl. Phys. B 881, 91–180 (2014); arXiv:1310.5340.
A. Yu. Kamenshchik, E. O. Pozdeeva, A. Tronconi, G. Venturi, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Integrable cosmological models with non-minimally coupled scalar fields,” Classical Quantum Gravity 31, 105003 (2014); arXiv:1312.3540; A. Yu. Kamenshchik, E. O. Pozdeeva, A. Tronconi, G. Venturi, and S. Yu. Vernov, “General solutions of integrable cosmological models with non-minimal coupling,” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 14, 382 (2017); arXiv:1604.01959.
A. Yu. Kamenshchik, A. Tronconi, and G. Venturi, “Reconstruction of scalar potentials in induced gravity and cosmology,” Phys. Lett. B 702, 191 (2011); arXiv:1104.2125.
A. Yu. Kamenshchik, A. Tronconi, G. Venturi, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Reconstruction of scalar potentials in modified gravity models,” Phys. Rev. D 87, 063503 (2013); arXiv:1211.6272.
D. S. Salopek and J. R. Bond, “Nonlinear evolution of long-wavelength metric fluctuations in inflationary models,” Phys. Rev. D 42, 3936–3962 (1990);
A. G. Muslimov, “On the scalar field dynamics in a spatially flat Friedman universe,” Classical Quantum Gravity 7, 231–237 (1990).
V. M. Zhuravlev, V. M. Chervon, and V. M. Shchigolev, “New classes of exact solutions in inflationary cosmology,” J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 87, 223 (1998);
V. M. Chervon and I. V. Fomin, “On calculation of the cosmological parameters in exact models of inflation,” Gravity Cosmol. 14, 163 (2008); arXiv:1704.05378; A. V. Yurov, V. A. Yurov, V. M. Chervon, and M. Sami, “Total energy potential as a superpotential in integrable cosmological models,” Theor. Math. Phys. 166, 259–269 (2011).
I. Ya. Aref’eva, S. Yu. Vernov, and A. S. Koshelev, “Exact solution in a string cosmological model,” Theor. Math. Phys. 148, 895–909 (2006), astro-ph/0412619; I. Ya. Aref’eva, A. S. Koshelev, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Crossing the \(w = - 1\) barrier in the D3-brane dark energy model,” Phys. Rev. D 72, 064017 (2005); arXiv:astro-ph/0507067; S. Yu. Vernov, “Construction of exact solutions in two-field cosmological models,” Theor. Math. Phys. 155, 544 (2008); arXiv:astro-ph/0612487; I. Ya. Aref’eva, N. V. Bulatov, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Stable exact solutions in cosmological models with two scalar fields,” Theor. Math. Phys. 163, 788 (2010); arXiv:0911.5105.
K. Skenderis and P. K. Townsend, “Hamilton–Jacobi method for domain walls and cosmologies,” Phys. Rev. D 74, 125008 (2006); arXiv:hep-th/0609056; P. K. Townsend, “Hamilton–Jacobi mechanics from pseudo-supersymmetry,” Classical Quantum Gravity 25, 045017 (2008); arXiv:0710.5178.
D. Bazeia, C. B. Gomes, L. Losano, and R. Menezes, “First-order formalism and dark energy,” Phys. Lett. B 633, 415–419 (2006); arXiv:astro-ph/0512197; D. Bazeia, L. Losano, and R. Rosenfeld, “First-order formalism for dust,” Eur. Phys. J. C 55, 113–117 (2008); arXiv:astro-ph/0611770.
A. A. Andrianov, F. Cannata, A. Yu. Kamenshchik, and A. Yu. Regoli, “Reconstruction of scalar potentials in two-field cosmological models,” J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 0802, 015 (2008); arXiv:0711.4300; A. Yu. Kamenshchik and S. Manti, “Scalar field potentials for closed and open cosmological models,” Gen. Relativ. Gravitation 44, 2205–2214 (2012); arXiv:1111.5183.
T. Harko, F. S. N. Lobo, and M. K. Mak, “Arbitrary scalar field and quintessence cosmological models,” Eur. Phys. J. C 74, 2784 (2013); arXiv:1310.7167.
E. O. Pozdeeva and S. Yu. Vernov, “Stable exact cosmological solutions in induced gravity models,” AIP Conf. Proc. 1606, 48–58 (2014); arXiv:1401.7550.
A. D. Sakharov, “Vacuum quantum fluctuations in curved space and the theory of gravitation,” Sov. Phys. – Dokl. 12, 1040 (1968);
Gen. Relativ. Gravitation 32, 365 (2000).
F. Cooper and G. Venturi, “Cosmology and broken scale invariance,” Phys. Rev. D 24, 3338 (1981);
A. Cerioni, F. Finelli, A. Tronconi, and G. Venturi, “Inflation and reheating in induced gravity,” Phys. Lett. B 681, 383 (2009); arXiv:0906.1902; A. Yu. Kamenshchik, A. Tronconi, and G. Venturi, “Dynamical dark energy and spontaneously generated gravity,” Phys. Lett. B 713, 358 (2012); arXiv:1204.2625.
J. L. Cervantes-Cota and H. Dehnen, “Induced gravity inflation in the standard model of particle physics,” Nucl. Phys. B 442, 391 (1995); arXiv:astro-ph/9505069; J. L. Cervantes-Cota, R. de Putter, and E. V. Linder, “Induced gravity and the attractor dynamics of dark energy/dark matter,” J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 1012, 019 (2010); arXiv:1010.2237.
I. Ya. Aref’eva, N. V. Bulatov, R. V. Gorbachev, and S. Yu. Vernov, “Non-minimally coupled cosmological models with the Higgs-like potentials and negative cosmological constant,” Classical Quantum Gravity 31, 065007 (2014); arXiv:1206.2801.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partially supported by grant NSh‑7989.2016.2 of the President of Russian Federation. Research of E.P. is supported in part by grant MK-7835.2016.2 of the President of Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
1The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pozdeeva, E.O., Vernov, S.Y. Induced Gravity Models with Exact Bounce Solutions. Phys. Part. Nuclei 49, 914–917 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063779618050337
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063779618050337