Abstract
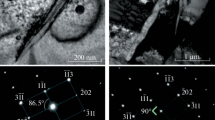
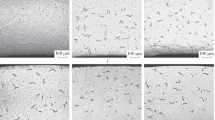
One of the factors capable of resulting in deconfinement of fuel element cladding upon long term storage of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) is reorientation of hydrides. This work estimates the extent of reorientation of hydrates in unirradiated gas filled specimens of fuel element claddings of VVER-1000 reactor (Zr‒1% Nb) under the conditions simulating conditions of dry storage. The specimens with the hydrogen content of 100 and 200 ppm were exposed to thermomechanical tests according to various scenarios at hoop stresses in cladding up to 100 MPa. It has been established that the extent of reorientation of hydrides and related decrease in plasticity of cladding material are insignificant. The most significant factor influencing the extent of reorientation is the level of hoop stresses.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. C. Billone et al., J. Nucl. Mater. 433, 431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.10.002
A. T. Motta et al., J. Nucl. Mater. 518, 440 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2019.02.042
Y. J. Kim et al., J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 52, 717 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2014.978829
Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Interim Staff Guidance (ISG)-11, Revision 3 (2003).
K. Kamimura, in Proceedings of the International Seminar on Spent Fuel Storage, Tokyo, 2010.
IAEA-TECDOC-1385 (Int. At. Energy Agency, Vienna, 2004).
Z. Wang et al., Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 532 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9866-0
R. A. Kurskiy et al., Phys. Met. Metallogr. 122, 861 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X21090076
L. Yegorova et al., NUREG/IA-0156 (U. S. Nucl. Regulatory Commission, 1999), Vol. 2.
D. Khatamian, J. Alloys Compd. 293, 893 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(99)00388-6
M. Kolesnik et al., J. Nucl. Mater. 508, 567 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.06.012
K. V. Mani Krishna et al., Acta Mater. 54, 4665 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.06.004
J. M. Lee et al., J. Nucl. Mater. 509, 285 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.07.005
Funding
This work was supported by TVEL Fuel Company using the experimental facilities of the Research Complex of Material Science Hot Cells, National Research Center Kurchatov Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by I. Moshkin
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The results of this work will be used in the model substantiating safety of long-term dry storage of SNF of VVER-1000 reactors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurskiy, R.A., Rozhkov, A.V., Zabusov, O.O. et al. Factors Influencing Reorientation of Hydrides in Unirradiated Cladding Tubes from E110 Alloy under Conditions of Long-Term Dry Storage of SNF. Phys. Atom. Nuclei 84, 1665–1671 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778821100203
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778821100203