Abstract
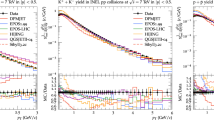
Double differential yield of π±, K±, protons, and antiprotons as a function of laboratory momentum is presented using hadron production models. This study is done in several polar angle intervals from 0 < θ < 420 mrad for π± mesons and 0 < θ < 360 mrad for K± mesons, protons, and antiprotons. The study is carried out for p + C interactions at 120 GeV/c. For simulation, three hadron-production models: EPOS-LHC, EPOS 1.99, and QGSJETII-04 are used. Since no experimental data at 120 GeV/c is available yet, therefore, the models’ predictions are compared with the measurements of NA61/SHINE experiments at 31 GeV/c. It is found that the QGSJETII-04 model gives high peak value, for π± mesons, in the polar angle interval of 20–40 mrad, while in the range of 40–240 mrad, EPOS-LHC shows higher yield than EPOS 1.99 and QGSJETII-04 models, whereas all show higher yield than the experimental data. For π± mesons, in all angular intervals, at high momentum values, all the three models are consistent and surprisingly give the same yield as that of the experimental data. For K± mesons, QGSJETII-04 shows higher peak values at all polar angles ranging from 0 to 360 mrad as compared to that of EPOS 1.99 and EPOS-LHC models, whereas all models give higher yield at low angular intervals than the experimental data and the same yield at high angular intervals. The models demonstrate similar yields for protons at all angles but underestimate the experimental data at low angular intervals and provide the same yield at high angular intervals. The QGSJETII-04 model presents higher yields of antiprotons in comparison to the EPOS 1.99 and EPOS-LHC models, for almost all angular intervals. Generally, at higher angular range, i.e., from 240 to 420 mrad, particularly at high momentum, all the three models show similar results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. E. Kopp, Phys. Rept. 439, 101 (2007).
C. Patrignani et al. (Particle Data Group), Chin. Phys. C 40, 100001 (2016).
K. Abe et al. (T2K Collab.), Phys. Rev. D 87, 019902 (2013).
A. E. Hervé (for the NA61/SHINE Collab.), PoS(ICRC2015) 330 (2016).
T. Pierog and K. Werner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 171101 (2008).
M. G. Catanesi et al. (HARP Collab.), CERN-SPSC/99-35, 15 November 1999.
R. Raja, Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 175–176, 17 (2008).
S. Afanasiev, T. Alber, H. Appelshäuser, J. Bächler, D. Barna, L. S. Barnby, J. Bartke, R. A. Barton, L. Betev, H. Bialkowska, F. Bieser, A. Billmeier, C. O. Blyth, R. Bock, C. Bormann, J. Bracinik, et al., Nucl.Instrum.Methods A 430, 210 (1999).
B. A. Popov, Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 235–236, 135 (2013).
B. A. Popov, EPJ Web Conf. 99, 020022 (2015).
N. Abgrall et al. (for the benefit of the NA61/SHINE Collab.), JINST 9, P06005 (2014).
http://home.cern/about/accelerators/super-proton-synchrotron.
N. Abgrall et al. (The NA61/SHINE Collab.), Phys. Rev. C 84, 034604 (2011).
N. Abgrall et al. (The NA61/SHINE Collab.), Phys. Rev. C 85, 035210 (2012).
N. Abgrall et al. (The NA61/SHINE Collab.), Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 701, 99 (2013).
N. Abgrall, CERN-THESIS-2011-165 (Université de Genève, 2011).
L. Zambelli CERN-THESIS-2013-290 (Université Paris Diderot, 2013).
N. Abgrall et al. (The NA61/SHINE Collab.), Eur. Phys. J. C 76, 84 (2016).
N. Abgrall et al. (The NA61/SHINE Collab.), Eur. Phys. J. C 76, 617 (2016).
A. Hasler, CERN-THESIS-2015-103 (Université de Genève, 2015).
M. Pavin, CERN-THESIS-2017-233 (University of Paris VI, 2017).
N. Abgrall et al. (The NA61/SHINE Collab.), Report from the NA61/SHINE Experiment at the CERN SPS, Status Report to the Proposal SPSC-P-330, 10 October, 2013.
S. Ullah, Y. Ali, M. Ajaz, U. Tabassam, and Q. Ali, Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 33, 1850108 (2018); S. Ullah, M. Ajaz, and Y. Ali, EPL 123, 31001 (2018).
M. Ajaz, S. Ullah, Y. Ali, and H. Younis, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 33, 1850038 (2018).
M. Ajaz, Y. Ali, S. Ullah, Q. Ali, and U. Tabassam, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 33, 1850079 (2018).
K. Werner, F-.M. Liu, and T. Pierog, Phys. Rev. C 74, 044902 (2006).
T. Pierog, Iu. Karpenko, J. M. Katzy, E. Yatsenko, and K. Werner, Phys. Rev. C 92, 034906 (2015).
S. Ostapchenko, Phys. Rev. D 83, 014018 (2011).
M. Ajaz, M. K. Suleymanov, K. H. Khan, and A. Zaman, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 21, 1250095 (2012).
M. Ajaz, M. K. Suleymanov, K. H. Khan, A. Zaman, H. Younis, and A. Rahman, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 28, 1350175 (2013).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Abdul Wali Khan University Mardan, and COMSATS University, Park Road, Islamabad Pakistan as they provide us suitable platform and all possible facilities to perform the simulations and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajaz, M., Ali, Y., Ullah, S. et al. Study of Hadrons Produced in Proton—Carbon Interactions at 120 GeV/c Using Hadron-Production Models. Phys. Atom. Nuclei 82, 291–298 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778819030037
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778819030037