Abstract
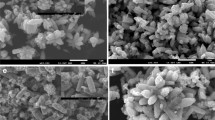
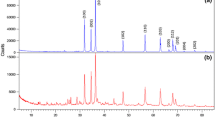
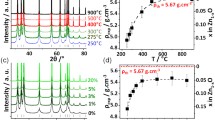
Zinc oxide low-dimensional hollow structures in the form of hexagonal plates with holes at the center of the {0001} facets are synthesized in the course of the low-temperature interaction of ZnO precursors with aqueous solutions of potassium fluoride under hydrothermal conditions. Crystals have the shape of single-walled or multiwalled “nuts.” The high optical quality of the structures is confirmed by cathodoluminescence data at room temperature. The mechanism of the formation of ZnO “nanonuts” and products of the interaction of the ZnO precursors with KF is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, Nature (London) 354, 56 (1991).
H. P. Liang, L. J. Wan, C. L. Bai, and L. Jiang, J. Phys. Chem. B 109(16), 7795 (2005).
Y. Zhang, S. Wang, X. Wang, et al., J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 6(5), 1423 (2006).
L. Shi, Y. M. Xu, and Q. Li, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 6(1), 185 (2006).
A. Ghicov, J. M. Macak, H. Tsuchiya, et al., Nano Lett. 6(5), 1080 (2006).
G. Xi, Y. Peng, L. Xu, et al., Inorg. Chem. Commun. 7(5), 607 (2004).
Y. Wu, Z. Xi, G. Zhang, et al., J. Cryst. Growth 292, 143 (2006).
G. Zhang, C. Li, C. Fangyi, and J. Chen, Sens. Actuators, B 120(2), 403 (2007).
Y. J. Li, M. Y. Lu, C. W. Wang, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 143102 (2006).
H. Zhu, K. Yao, H. Zhang, and D. Yang, J. Phys. Chem. B 109(44), 20676 (2005).
P. Zhao, J. Wang, G. Cheng, and K. Huang, J. Phys. Chem. B 110(45), 22400 (2006).
Z. Hu, L. Li, X. Zhou, et al., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 294(2), 328 (2006).
H. Song, D. Wang, X. Ma, et al., Solid State Commun. 139(8), 430 (2006).
Z. Y. Wang, X. S. Fang, Q. F. Lu, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 083102 (2006).
Y. Cheng, Y. Wang, C. Jia, and F. Bao, J. Phys. Chem. B 110(48), 24399 (2006).
X.-P. Shen, G. Yin, W.-L. Zhan, and Z. Xu, Solid State Commun. 140(3–4), 116 (2006).
W.-S. Wang, L. Zhen, C.-Y. Xu, et al., J. Phys. Chem. B 110(46), 23154 (2006).
C. Yan and D. Xue, J. Phys. Chem. B 110(23), 11076 (2006).
P. X. Gao and Z. L. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(37), 11299 (2003).
H. J. Fan, R. Scholz, F. M. Kolb, et al., Solid State Commun. 130(8), 517 (2004).
A. Umar, S. H. Kim, Y. H. Im, and Y. B. Hahn, Superlattices Microstruct. 39(1–4), 238 (2006).
J. Duan, X. Huang, E. Wang, and H. Ai, Nanotechnology 17, 1786 (2006).
G. Shen, Y. Bando, and C.-J. Lee, J. Phys. Chem. B 109(21), 10578 (2005).
Z. L. Wang, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process. 88(1), 7 (2007).
R.-C. Wang, C.-P. Liu, J.-L. Huang, and S.-J. Chen, Nanotechnology 17, 753 (2006).
G. Shen, Y. Bando, and C.-J. Lee, J. Phys. Chem. B 109(21), 10578 (2005).
Q. P. Ding, Q. Q. Cao, H. B. Huang, et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 39, 46 (2006).
D. Wu, L. Huang, Q. Wang, et al., Mater. Chem. Phys. 96(1), 51 (2006).
A. Yang and Z. Cui, Mater. Lett. 60(19), 2403 (2006).
A. Wei, X. W. Sun, C. X. Xu, et al., Nanotechnology 17, 1740 (2006).
Y. S. Han, L. W. Lin, M. Fuji, and M. Takahashi, Chem. Lett. 36(8), 1002 (2007).
J. Zhang, L. Sun, C. Liao, and C. Yan, Chem. Commun. (Cambridge, UK), No. 3, 262 (2002).
J. Liu and X. Huang, J. Solid State Chem. 179(3), 843 (2006).
A. Eftekhari, F. Molaei, and H. Arami, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 437(2), 446 (2006).
M. Yang, G. Pang, L. Jiang, and S. Feng, Nanotechnology 17, 206 (2006).
H. Hou, Y. Xie, and Q. Li, Solid State Sci. 7(1), 45 (2005).
A. Yang and Z. Cui, Mater. Lett. 60(19), 2403 (2006).
Y. Sun, D. J. Riley, and M. N. Ashfold, J. Phys. Chem. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Surf. Interfaces Biophys. 110(31), 15186 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.N. Dem’yanets, V.V. Artemov, L.E. Li, Yu.M. Mininzon, T.G. Uvarova, 2008, published in Kristallografiya, 2008, Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 937–942.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dem’yanets, L.N., Artemov, V.V., Li, L.E. et al. Zinc oxide hollow microstructures and nanostructures formed under hydrothermal conditions. Crystallogr. Rep. 53, 888–893 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774508050258
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774508050258