Abstract
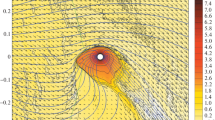
As a rule, the orbital velocities of “hot Jupiters,” i.e., exoplanets with masses comparable to the mass of Jupiter and orbital semi-major axes less than 0.1 AU, are supersonic relative to the stellar wind, resulting in the formation of a bow shock. Gas-dynamical modeling shows that the gaseous envelopes around hot Jupiters can belong to two classes, depending on the position of the collision point. if the collision point is inside the Roche lobe of the planet, the envelopes have the almost spherical shapes of classical atmospheres, slightly distorted by the influence of the star and interactions with the stellar-wind gas; if the collision point is located outside the Roche lobe, outflows from the vicinity of the Lagrangian points L1 and L2 arise, and the envelope becomes substantially asymmetrical. The latter class of objects can also be divided into two types. If the dynamical pressure of the stellar-wind gas is high enough to stop the most powerful outflow from the vicinity of the inner Lagrangian point L1, a closed quasi-spherical envelope with a complex shape forms in the system. If the wind is unable to stop the outflow from L1, an open aspherical envelope forms. The possible existence of atmospheres of these three types is confirmed by 3D numerical modeling. Using the typical hot Jupiter HD 209458b as an example, it is shown that all three types of atmospheres could exist within the range of estimated parameters of this planet. Since different types of envelopes have different observational manifestations, determining the type of envelope in HD 209458b could apply additional constrains on the parameters of this exoplanet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. A. Murray-Clay, E. I. Chiang, and N. Murray, Astrophys. J. 693, 23 (2009).
M. Mayor and D. Queloz, Nature 378, 355 (1995).
D. Charbonneau, T. M. Brown, D. W. Latham, and M. Mayor, Astrophys. J. Lett. 529, L45 (2000).
A. Vidal-Madjar, A. Lecavelier des Etangs, J.-M. Désert, et al., Nature 422, 143 (2003).
A. Vidal-Madjar, A. Lecavelier des Etangs, J.-M. Désert, et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 676, L57 (2008).
L. Ben-Jaffel, Astrophys. J. Lett. 671, L61 (2007).
A. Vidal-Madjar, J.-M. Désert, A. Lecavelier des Etangs, et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 604, L69 (2004).
L. Ben-Jaffel and S. Sona Hosseini, Astrophys. J. 709, 1284 (2010).
J. L. Linsky, H. Yang, K. France, et al., Astrophys. J. 717, 1291 (2010).
R. V. Yelle, Icarus 170, 167 (2004).
A. García Muñoz, Planet. and Space Sci. 55, 1426 (2007).
T. T. Koskinen, M. J. Harris, R. V. Yelle, and P. Lavvas, Icarus (2013, in press); arXiv:1210.1536 [astro-ph] (2012).
H. Lammer, K. G. Kislyakova, M. Holmström, et al., Astrophys. Space Sci. 335, 9 (2011).
A. Lecavelier Des Etangs, D. Ehrenreich, A. Vidal-Madjar, et al., Astron. Astrophys. 514, A72 (2010).
L. Fossati, C. A. Haswell, C. S. Froning, et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 714, L222 (2010).
L. Fossati, S. Bagnulo, A. Elmasli, et al., Astrophys. J. 720, 872 (2010).
D. Lai, C. Helling, and E. P. J. van den Heuvel, Astrophys. J. 721, 923 (2010).
S.-L. Li, N. Miller, D. N. C. Lin, and J. J. Fortney, Nature 463, 1054 (2010).
A. A. Vidotto, M. Jardine, and C. Helling, Astrophys. J. Lett. 722, L168 (2010).
A. A. Vidotto, M. Jardine, and C. Helling, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 411, L46 (2011).
A. A. Vidotto, M. Jardine, and C. Helling, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 414, 1573 (2011).
D. Bisikalo, P. Kaygorodov, D. Ionov, et al., Astrophys. J. 764, 19 (2013).
A. Lecavelier des Etangs, V. Bourrier, P. J. Wheatley, et al., Astron. Astrophys. 543, L4 (2012).
T. T. Koskinen, R. V. Yelle, P. Lavvas, and N. K. Lewis, Astrophys. J. 723, 116 (2010).
L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshits, Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol. 6: Fluid Mechanics (Nauka, Moscow, 1986; Pergamon, New York, 1987).
V. B. Baranov and K. V. Krasnobaev, Hydrodynamical Theory of Cosmic Plasma (Nauka, Moscow, 1977) [in Russian].
G. L. Withbroe, Astrophys. J. 325, 442 (1988).
S. H. Lubow and F. H. Shu, Astrophys. J. 198, 383 (1975).
A. A. Boyarchuk, D. V. Bisikalo, O. A. Kuznetsov, and V. M. Chechetkin, Mass Transfer in Close Binary Stars (Taylor and Francis, London, 2002).
D. V. Bisikalo, A. A. Boyarchuk, P. V. Kaigorodov, and O. A. Kuznetsov, Astron. Rep. 47, 809 (2003).
J. I. Moses, C. Visscher, J. J. Fortney, et al., Astrophys. J. 737, 15 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.V. Bisikalo, P.V. Kaigorodov, D.E. Ionov, V.I. Shematovich, 2013, published in Astronomicheskii Zhurnal, 2013, Vol. 90, No. 10, pp. 779–790.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bisikalo, D.V., Kaigorodov, P.V., Ionov, D.E. et al. Types of gaseous envelopes of “hot Jupiter” exoplanets. Astron. Rep. 57, 715–725 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772913100016
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772913100016