Abstract
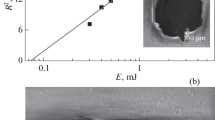
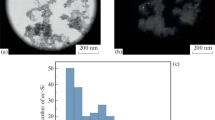
The dependence of acoustic cavitation thresholds in aqueous suspensions of porous silicon nanoparticles (pSiNPs) on the degree of hydrophobicity of their surface has been studied. Nanoparticles with an average size of 100 nm were prepared by mechanical grinding of porous silicon (pSi) films in ethanol. According to IR spectroscopy data, such pSiNPs are initially characterized by a hydrophilic surface. To obtain amphiphilic (hydrophobic–hydrophilic) nanoparticles, pSi films were hydrophobized before grinding by surface modification with octadecylsilane. When hydrophobic pSi films are ground in ethanol to nanoparticles, silicon–silicon bonds are broken, followed by their oxidation, due to which the surface is partially hydrophilized. It has been shown that the threshold of acoustic cavitation in suspensions of amphiphilic pSiNPs is significantly reduced compared to that of hydrophilic pSiNPs. The threshold value of acoustic cavitation in a suspension of amphiphilic nanoparticles at a concentration of 1 mg/mL remained almost constant for 5 days. The results obtained are important for the development of methods for sonodynamic therapy of cancer using pSiNPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. J. Anglin, L. Cheng, W. R. Freeman, and M. J. Sailor, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 60 (11), 1266 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.03.017
P. V. Maximchik, K. Tamarov, E. V. Sheval, E. Tolstik, T. Kirchberger-Tolstik, Z. Yang, V. Sivakov, B. Zhivotovsky, and L. A. Osminkina, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 5 (11), 6063 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01292
L. A. Osminkina, A. L. Nikolaev, A. P. Sviridov, N. V. Andronova, K. P. Tamarov, M. B. Gongalsky, A. A. Kudryavtsev, H. M. Treshalina, and V. Y. Timoshenko, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 210, 169 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.02.037
K. Tamarov, A. Sviridov, W. Xu, M. Malo, V. Andreev, V. Timoshenko, and V.-P. Lehto, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9 (40), 35234 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b11007
A. Sviridov, K. Tamarov, I. Fesenko, W. Xu, V. Andreev, V. Timoshenko, and V.-P. Lehto, Front. Chem. 7, 393 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00393
M. J. Montoya, L. Wu, S. Sabuncu, A. Sapre, F. Civitci, S. Ibsen, S. Esener, and A. Yildirim, ACS Omega 5 (38), 24762 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03377
M. B. Gongalsky, N. V. Pervushin, D. E. Maksutova, U. A. Tsurikova, P. P. Putintsev, O. D. Gyuppenen, Y. V. Evstratova, O. A. Shalygina, G. S. Kopeina, A. A. Kudryavtsev, B. Zhivotovsky, and L. A. Osminkina, Nanomaterials 11 (9), 2167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092167
A. A. Atchley and A. Prosperetti, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 86 (3), 1065 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.398098
A. Giacomello and R. Roth, Adv. Phys.: X 5 (1), 1817780 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/23746149.2020.1817780
B. M. Borkent, S. Gekle, A. Prosperetti, and D. Lohse, Phys. Fluids 21 (10), 102003 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3249602
J. C. Simon, O. A. Sapozhnikov, W. Kreider, M. Breshock, J. C. Williams, and M. R. Bailey, Phys. Med. Biol. 63 (2), 025011 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/aa9a2f
D. V. Leonov, N. S. Kulberg, A. I. Gromov, S. P. Morozov, and S. Yu. Kim, Acoust. Phys. 64 (1), 105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063771018010128
V. A. Akulichev and V. I. Il’ichev, Acoust. Phys. 51 (2), 128 (2005).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was carried out within the framework of the Development Program of the Interdisciplinary Scientific and Educational School of Moscow University “Photonic and Quantum Technologies. Digital Medicine.”
Funding
The study was funded through a grant from the Russian Science Foundation, no. 22-75-10107 https://rscf.ru/project/22-75-10107/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Egoshina, V.D., Gongalsky, M.B., Tsurikova, U.A. et al. The Cavitation Activity of Aqueous Suspensions of Porous Silicon Nanoparticles with Different Degrees of Surface Hydrophobicity. Acoust. Phys. 68, 649–656 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106377102206015X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106377102206015X