Abstract
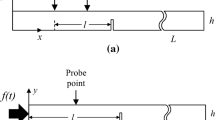
The asymmetric propagation of the first order antisymmetric (A1) Lamb wave in a tapered plate respectively carved with sharp bottom corner and round bottom corner is theoretically investigated. Through numerical simulation of A1 Lamb wave in time domain, we find that when the thickness of the waveguide abruptly decreases to below the cut-off thickness, about half of the A1 mode is converted into the fundamental symmetrical S0 and antisymmetrical A0 modes to pass through the defected region. Furthermore, the transmitted modes A0 and S0 are completely apart from each other and can be quantitatively evaluated. Conversely, when the thickness change is very smooth, most of the energy of A1 Lamb wave is reflected back. It is the unique mode conversion behavior that leads to great transmission difference value of A1 Lamb wave along the opposite directions. Finally, the influence of geometrical parameters on the transmission coefficient is also studied. The higher efficiency and proper working frequency range can be realized by adjusting the slope angle θ, height h 1 and h 2. The simple asymmetric systems will be potentially significant in applications of ultrasound diagnosis and therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. F. Li, X. Ni, L. Feng, M. H. Lu, C. He, and Y. F. Chen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106 (8), 084301 (2011).
Z. J. He, S. S. Peng, Y. T. Ye, Z. W. Dai, C. Y. Qiu, M. Z. Ke, and Z. Y. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 (8), 083505 (2011).
H. X. Sun, S. Y. Zhang, and X. J. Shui, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 (10), 103507 (2012).
Y. Li, B. Liang, Z. M. Gu, X. Y. Zou, and J. C. Chen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 (5), 053505 (2013).
H. Jia, M. Z. Ke, C. H. Li, C. Y. Qiu, and Z. Y. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 102 (15), 153508 (2013).
R. Krishnan, S. Shirrota, Y. Tanaka, and N. Nishiguchi, Solid State Commun. 144 (5–6), 194–197 (2007).
J. J. Chen, X. Han, and G. Y. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 113 (18), 184506 (2013).
X. F. Zhu, X. Y. Zou, B. Liang, and J. C. Cheng, J. Appl. Phys. 108 (12), 124909 (2010).
X. Y. Zou, B. Liang, Y. Yuan, X. F. Zhu, and J. C. Cheng, J. Appl. Phys. 114 (18), 164504 (2013).
H. X. Ding, L. L. Dai, Z. H. Shen, L. Yuan, and X. W. Ni, Acoust. Phys. 60 (1), 110–114 (2014).
Y. Li, J. Tu, B. Liang, X. S. Guo, D. Zhang, and J. C. Cheng, J. Appl. Phys. 112 (6), 064504 (2012).
C. H. Li, M. Z. Ke, Y. T. Ye, S. J. Xu, C. Y. Qiu, and Z. Y. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 105 (2), 023511 (2014).
A. D. Lapin, Acoust. Phys. 59 (3), 267–271 (2013).
W. Lin, X. H. Deng, and X. Li, Appl. Acoust. 74 (8), 1018–1021 (2013).
Z. Chen, L. Fan, S. Y. Zhang, and H. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys. 115 (20), 204513 (2014).
W. Lin, L. Fan. C. M. Gan, Z. M. Zhu, and X. B. Wang, Appl. Acoust. 70 (11–12), 1446–1448 (2009).
Y. W. Yao, Z. L. Hou, Y. J. Cao, and Y. Y. Liu, Physica B: Condens. Matter 388 (1–2), 75–81 (2007).
P. Hora and O. Cervená, Appl. Comput. Mech. 6 (1), 5–16 (2012).
V. Giurgiutiu, J. Bao, and W. Zhao, Exp. Mech. 43 (4), 428–449 (2003).
K. L. Xu. D. Ta, Z. Q. Su, and W. Q. Wang, Ultrasonics. 54 (1), 395–401 (2014).
O. A. Sapozhnikov and M. A. Smagin, Acoust. Phys. 61 (2), 181–187 (2015).
J. Gao, J. Yang. L. J. Cui, J. C. Cheng, and M. L. Qian, Ultrasonics. 44 (1), e985–e989 (2006).
Z. Hamitouche, M. E.-C. EI-Kettani, J.-L. Izbicki, and H. Djelouah, Acta Acoust. United Acoust. 95 (5), 789–794 (2009).
M. El Allami, H. Rhimini, A. Nassim, and M. Sidki, Electron. J. Tech. Acoust. Art. 8 (2010).
J. L. Rose, Ultrasonic Guided Waves in Solid Media (Cambridge University Press, 2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, SY., Chen, JJ., Song, GH. et al. Asymmetric propagation of the first order antisymmetric lamb wave in a tapered plate based on time domain analysis. Acoust. Phys. 63, 393–401 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063771017040054
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063771017040054