Abstract
Aim
The objective of this study is to evaluate the recovery of hearing function of auditory pathway after cochlear implantation by extracting the characterizations of electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses (EABR). The purpose of this study was to explore a reality and possible EABR test mode in clinical applications, rather than strict animal research.
Methods
53 patients received Nucleus 24 cochlear implant. The EABR tests were performed with a stimulus frequency of 100 Hz or less and a pulse width of 25, 50, and 75 µs/phase. The EABR signals were recorded from three electrodes (electrode 3, 10, and 20), simultaneously. The latency of the EABR wave III and V, the EABR threshold and the positive appearance rate of the EABR waves were measured.
Results
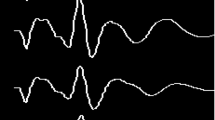
This study found that during EABR tests, the artifacts under the alternate polarity stimulus were smaller than those under the monopolarity stimulus. A similar result was found that the artifacts collected on the contra lateral side were smaller than that on the same lateral side. The latency of the EABR waves prolonged with the increase of the stimulus frequency. When the high cut-off frequency of the band-pass filter altered from 1.5 kHz to 3 kHz, the latency of the EABR wave V shortened, but the latency maintained constant from 3 kHz to 25 kHz. When the low cut-off frequency was changed from 100 Hz to 0.002 Hz, the latency of the EABR wave V maintained constant. In addition, it was found that the EABR threshold lowered with increasing the pulse width of the stimulus. This study indicated that the EABR threshold of the signals collected from the electrode 20 were significantly (p < 0.01) lower than those obtained from the electrode 3 and 10. However, no statistically significant difference in the EABR threshold existed between the signals collected from the electrode 3 and 10 (p > 0.05). Moreover, the latency of the EABR wave III and V at the electrode 3 was significantly (p < 0.01) longer than that at the electrode 10 and 20, and the latency of the wave III and V at the electrode 10 was significantly (p < 0.01) longer than that at the electrode 20. The positive appearance rate of the EABR waves was 96.22%.
Conclusion
The EABR tests with proper parameters were designed in this study. The characterizations of the EABR waves including amplitude, latency and threshold were extracted at different electrodes. The EABR test provides an effective method to evaluate the functions of the auditory pathway in patients after cochlear implantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. R. Kileny, T. A. Zwolan, A. Boerst, et al., Am. J. Otol. 18(6), 90 (1997).
C. J. Brown, Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck. Surg. 11, 383 (2003).
B. M. Clopton and F. A. Spelman, Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 191, 26 (2003).
E. H. Toh and W. M. Luxford, Otolaryngol. Clin. North. Am. 35, 325 (2002).
S. Burdo, S. Razza, F. di Berardino, et al., Acta Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Ital. 26(2), 69 (2006).
S. Mason, Int. J. Audiol. 43(Suppl.), S33 (2004).
P. R. Kileny and T. A. Zwolan, Int. J. Audiol. 43(Suppl.), S16 (2004).
K. A. Gordon, B. C. Papsin, and R. V. Harrison, Ear. Hear. 25, 447 (2004).
Yingfu Pan, J. Clin, Evoked Potentials (Press of Public Health, Beijing, 1999), pp. 320–321.
S. C. Jian and D. Gu, Clinical Audiology (Beijing Med. Univ., Peking Union Med. College, 1999), pp. 274–279.
E. Truy, S. Gallego, J. M. Chanal, et al., Laryngoscope 108, 554 (1998).
L. R. Aubert and G. P. Clarke, Brit. J. Audiology 28, 121 (1994).
T. Kubo, K. Yamamoto, Y. Iwaki, et al., Acta Otolaryngol. 121, 257 (2001).
P. A. Wackym, J. B. Firszt, W. Gaggl, et al., Laryngoscope 114, 71 (2004).
G. K. van Wermeskerken, A. F. van Olphen, and G. A. van Zanten, Int. J. Audiol. 45, 589 (2006).
P. Prado-Guitierrez, L. M. Fewster, J. M. Heasman, et al., Hear Res. 215, 47 (2006).
M. L. Hughes and P. J. Abbas, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 119, 1527 (2006).
M. J. Hay-McCutcheon, C. J. Brown, and P. J. Abbas, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 118, 2444 (2005).
M. Polak, A. Hodges, and T. Balkany, Otol. Neurotol. 26, 639 (2005).
J. H. Allum, J. K. Shallop, M. Hotz, et al., Scand. Audiol. 19, 263 (1990).
J. J. Briaire and J. H. Frijns, Hear Res. 205, 143 (2005).
M. D. Eisen and K. H. Franck, J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 6, 160 (2005).
D. Cafarelli Dees, N. Dillier, W. K. Lai, et al., Audiol. Neurootol. 10, 105 (2005).
K. A. Gordon, B. C. Papsin, and R. V. Harrison, Ear. Hear. 25, 447 (2004).
C. A. Miller, P. J. Abbas, M. J. Hay-McCutcheon, et al., Hear Res. 198, 75 (2004).
C. L. Runge-Samuelson, S. Drake, and P. A. Wackym, Otol. Neurotol. 29, 174 (2008).
A. H. Kim et al., Otol Neurotol. (2008).
M. Hey, I. Kevanishvili, H. von Specht, K. Begall, and Z. Kevanishvili, Georgian Med. News, 43–49 (2007).
C. A. Miller, P. J. Abbas, and J. T. Rubinstein, Hear Res. 135, 1 (1999).
N. Dillier, W. K. Lai, B. Almqvist, et al., Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 111, 407 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q. et al. Functional evaluation of auditory system in patients with cochlear implant using electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses. Acoust. Phys. 55, 857–865 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063771009060207
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063771009060207