Abstract
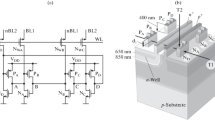
TCAD simulation of single event effects in memory cells with transistors spaced into two groups (spaced transistor groups—STG DICE) is carried out on the set of test tracks passing through the drains of mutually sensitive CMOS transistors from one group and between the two groups at depths of 50–850 nm from the chip surface. When the charge from the track affects only one group of transistors, no upsets occur; in this case, the duration of the unsteady state is described by a linear function with a coefficient of 1.3–2.4 ps/(MeV cm2/mg) for tracks 50–350 nm deep and a coefficient of 11–12 ps/(MeV cm2/mg) for tracks 450–850 nm deep, with the linear energy transfer on the tracks ranging from 1 to 60 MeV cm2/mg in both cases. An upset of the logical state of the STG DICE cell can occur when the particle tracks follow the line connecting the two groups of transistors and when angular deviations from it are in the range of 40°. With the track normal to the chip surface, an upset can occur when the linear energy transfer exceeds 50–60 MeV cm2/mg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katunin, Yu.V., Stenin, V.Ya., Stepanov, P.V., Modeling the characteristics of trigger elements of two-phase CMOS logic, taking into account the charge sharing effect under exposure to single nuclear particles, Russ. Microelectron., 2014, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 112–124.
Stenin, V.Ya., Simulation of the characteristics of the DICE 28-nm CMOS cells in unsteady states caused by the effect of single nuclear particles, Russ. Microelectron., 2015, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 324–334.
Calin, T., Nicolaidis, M., and Velazco, R., Upset hardened memory design for submicron CMOS technology, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 1996, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 2874–2878.
Stenin, V.Ya. and Stepanov, P.V., Basic memory elements using DICE cells for fault-tolerant 28 nm CMOS RAM, Russ. Microelectron., 2015, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 368–379.
Stenin, V.Ya., Katunin, Yu.V., Stepanov, P.V., Upsetresilient RAM on STG DICE memory elements with the spaced transistors into two groups, Russ. Microelectron., 2016, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 419–432.
Seifert, N., Gill, B., Foley, K., and Relangi, P., Multicell upset probabilities of 45 nm high-k + metal gate SRAM devices in terrestrial and space environments, in Proceedings of IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, 2008, pp. 181–186.
Loveless, T.D., Jagannathan, S., Reece, T., Chetia, J., Bhuva, B.L., McCurdy, M.W., Massengill, L.W., Wen, S.-J., Wong, R., and Rennie, D., Neutron-and proton-induced single event upsets for D-and DICEflip/flop designs at a 40 nm technology node, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2011, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 1008–1014.
Gaspard, N., Jagannathan, S., Diggins, Z., McCurdy, M., Loveless, T.D., Bhuva, B.L., Massengill, L.W., Holman, W.T., Oates, T.S., Fang, Y.-P., Wen, S.-J., Wong, R., Lilja, K., and Bounasser, M., Estimation of hardened flip-flop neutron soft error rates using SRAM multiplecell upset data in bulk CMOS, in Proceedings of IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, 2013, pp. SE.6.1–SE.6.5.
Wang, T., Xiao, L., and Huang, Q., Simulation study of single event effect for different N-well and deep-N-well doping in 65nm triple-well CMOS devices, in Proceedings of International Conference on Optoelectronics and Microelectronics, 2012, pp. 505–509.
Giot, D., Roche, P., Gasiot, G., Autran, J-L., and Harboe-Sørensen, R., Heavy ion testing and 3D simulations of multiple cell upset in 65nm standard SRAMs, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2008, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 2048–2054.
Uznanski, S., Gasiot, G., Roche, P., Tavernier, C., and Autran, J.-L., Single event upset and multiple cell upset modeling in commercial bulk 65-nm CMOS SRAMs and flip-flops, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2010, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 1876–1883.
Katunin, Yu.V. and Stenin, V.Ya., The multiport CMOS memory cell based on the DICE trigger with two spaced transistor groups for hardened 65-nm CMOS SRAM, in Proceedings of International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications, Moscow, 2016, pp. 1–5.
Stenin, V.Ya. and Antonyuk, A.A., Design of the 65-nm CMOS comparison element for a content-addressable memory and simulation of single-event transients, in Proceedings of 24th Telecommunications Forum, Belgrade, 2016, pp. 413–416.
Antonyuk, A.A., Katunin, Yu.V., Stepanov, P.E., Design of logical elements for the 65-nm CMOS translation lookaside buffer with compensation of single events effects, in Proceedings of International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications, Astana, 2017, pp. 1–6.
Baze, M.P., Hughlock, B., Wert, J., Tostenrude, J., Massengill, L., Amusan, O., Lacoe, R., Lilja, K., and Johnson, M., Angular dependence of single-event sensitivity in hardened flip/flop design, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2008, vol. 55, no. 6, pp. 3295–3301.
Warren, K., Sternberg, A., Black, J., Weller, R., Reed, R., Mendenhall, M., Schrimpf, R., and Massengill, L., Heavy ion testing and single-event upset rate prediction considerations for a DICE flip-flop, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2009, vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 3130–3137.
Lilja, K., Bounasser, M., Wen, S., Wong, R., Holst, J., Gaspard, N., Jagannathan, S., Loveless, D., and Bhuva, B., Single event performance and layout optimization of flip-flops in a 28-nm bulk technology, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2013, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 2782–2788.
Dodd, P.E. and Massengill, L.W., Basic mechanisms and modeling of single-event upset in digital microelectronics, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2003, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 583–602.
Ferlet-Cavrois, V., Paillet, P., Gaillardin, M., Lambert, D., Baggio, J., Schwank, R., Vizkelethy, G., Shaneyfelt, M.R., Hirose, K., Blackmore, E.W., Faynot, O., Jahan, C., and Tosti, L., Statistical analysis of the charge collected in SOI and bulk devices under heavy ion and proton irradiation—implications for digital SETs, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2006, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 3242–3252.
Mavis, D.G. and Eaton, P.H., SEU and SET modeling and mitigation in deep submicron technologies, in Proceedings of IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, 2007, pp. 293–305.
Walstra, S.V. and Dai, C., Circuit-level modeling of soft errors in integrated circuits, IEEE Trans. Dev. Mater. Reliab., 2005, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 358–364.
Nicolaidis, M., Soft Errors in Modern Electronic Systems, New York: Springer, 2011, pp. 35–37.
Garg, R. and Khatri, S.P., Analysis and Design of Resilient VLSI Circuits: Mitigating Soft Errors and Process Variations, New York: Springer, 2010, pp. 194–205.
Sentaurus Device User Guide, Version I-2013.12, Synopsys Inc., 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Yu.V. Katunin, V.Ya. Stenin, 2018, published in Mikroelektronika, 2018, Vol. 47, No. 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katunin, Y.V., Stenin, V.Y. Simulation of Single Event Effects in STG DICE Memory Cells. Russ Microelectron 47, 20–33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739718010031
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739718010031