Abstract
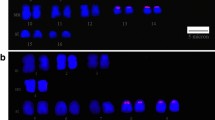
The family Mytilidae generally shows a genus-specific diploid number (2n) of chromosomes; however, one species from each genus, with the exception of Mytilus, is known to have a variable diploid number. Perna viridis is a cytogenetically significant species because it has a diploid chromosome (2n) number of 30, whereas the rest of species of genera Perna and Mytilus have a diploid number of 28. In the present study, we amplified the partial sequence of the 18S rRNA gene of Perna viridis, and the fluorescence (DIG-dUTP) labeled probe was hybridized to the interphase and metaphase chromosomes. The results localize the 18S rRNA gene clusters on the short arms of four chromosome pairs 1, 3, 7, and 11. This coincides with the position of the NORs by silver staining. The findings of the present study indicate a greater number of major rDNA clusters in Perna viridis than in closely related species. This is the first comprehensive molecular cytogenetic study carried out in Perna viridis.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adamkewicz, S. L., Harasewych, M. G., Blake, J. A., et al., A molecular phylogeny of bivalve mollusks, Mol. Biol. Evol., 1997, vol. 14, pp. 619–629.
Ahmed, M., Chromosomes of two species of the marine mussel Perna (Mytilidae:Pelecypoda), Bol. Inst. Oceanogr., Univ. Oriente, 1974, vol. 13, pp. 17–22.
Allen, J. A., The recent Bivalvia: Their form and evolution, in The Mollusca, Trueman, E.R. and Clarke, M.R., Eds., New York: Academic, 1985, vol. 10, pp. 337–403.
Canapa, A., Barucca, M., Merinelli, A., et al., A molecular phylogeny of Heterodonta (Bivalvia) based on small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2001, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 156–161.
Carrilho, J., Pérez-García, C., Leitão, A., et al., Cytogenetic characterization and mapping of rDNAs, core histone genes and telomeric sequences in Venerupis aurea and Tapes rhomboides (Bivalvia: Veneridae), Genetica, 2011, vol. 139, 823.
Charlesworth, B., Sniegowski, P., and Stephan, W., The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes, Nature, 1994, vol. 371, no. 6494, pp. 215–220.
Cornet, M. and Soulard, C., Chromosome number and karyotype of Donax trunculus L. (Mollusca, Bivalvia, Tellinacea), Genetica, 1990, vol. 82, pp. 93–97.
Cross, I., Díaz, E., Sánchez, I., and Rebordinos, L., Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of Crassostrea angulata chromosomes, Aquaculture, 2005, vol. 247, nos. 1–4, pp. 135–144.
Dalet, J.T., Saloma, C.P., Olivera, B.M., et al., Karyological analysis and FISH physical mapping of 18S rDNA genes, (GATA)n centromeric and (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequences in Conus magus Linnaeus, 1758, J. Molluscan Stud., 2015, vol. 81, no. 2, pp. 274–289.
Datson, P.M. and Murray, B.G., Ribosomal DNA locus evolution in Nemesia: Transposition rather than structural rearrangement as the key mechanism?, Chromosome Res., 2006, vol. 14, no. 8, pp. 845–857.
Drouin, G. and. De Sá, M.M., The concerted evolution of 5S ribosomal genes linked to the repeat units of other multigene families, Mol. Biol. Evol., 1995, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 481–493.
Fernández-Tajes, J., González-Tizón, A., Martínez-Lage, A., et al., Cytogenetics in the razor clam Solen marginatus (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Solenidae), Cytogenet. Genome Res., 2003, vol. 101, no. 1, pp. 43–46.
Fernández-Tajes, J., Martínez-Lage, A., Freire, R., Guerra, A., Mendez, J., González-Tizón, A., Genome sizes and karyotypes in the razor clams Ensis arcuatus (Jeffreys, 1865) and E. siliqua (Linnaeus, 1758), Cah. Biol. Mar., 2008, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 79–85.
Frischer, M., Danforth, J., Tyner, L., et al. Development of an Argopecten-specific 18S rRNA targeted genetic probe, Mar. Biotechnol., 2000, vol. 2, pp. 11–20.
Fuyun, Liu., Yuli, Li., Hongwei, Yu., et al., Mollusc DB: An integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca, Nucleic Acids Res., 2021, vol. 49, no. D1, pp. D988–D997.
Giribet, G. and Wheeler, W., On bivalve phylogeny: A high-level analysis of the Bivalvia (Mollusca) based on combined morphology and DNA sequence data, Invertebr. Biol., 2002, vol. 121, no. 4, pp. 271–324.
Gomes-dos-Santos, A., Lopes-Lima, M., Castro, L.F.C., et al., Molluscan genomics: The road so far and the way forward, Hydrobiologia, 2020, vol. 847, pp. 1705–1726.
González-Tizón, A., Martínez-Lage A., Rego I., et al., DNA content, karyotypes and chromosomal location of 18S–5.8S–28S ribosomal loci in some species of bivalve molluscs from the Pacific Canadian coast, Genome, 2000, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 1065–1072.
González-Tizón, A., Rojo, V., Vierna, J., et al., Cytogenetic characterisation of the razor shells Ensis directus (Conrad, 1843) and E. minor (Chenu, 1843) (Mollusca: Bivalvia), Helgol. Mar. Res., 2013, vol. 67, pp. 73–82.
Hills, D.M. and Dixon, M.T., Ribosomal DNA: Molecular evolution and phylogenetic interference, Q. Rev. Biol., 1991, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 411–453.
Hurtado, N.S. and Pasantes, J.J., Surface spreading of synaptonemal complexes in the clam Dosinia exoleta (Mollusca, Bivalvia), Chromosome Res., 2005, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 575–580.
Insua, A., Freire, R., and Méndez, J., The 5S rDNA of the bivalve Cerastoderma edule: Nucleotide sequence of the repeat unit and chromosomal location relative to 18S-28S rDNA, Genet., Sel., Evol., 1999, vol. 31, 509.
Insua., A., Freire, R., Ríos, J., and Méndez, J., The 5S rDNA of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. edulis: Sequence variation and chromosomal location, Chromosome Res., 2001, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 495–505.
Insua, A., Labat, J.P., and Thiriotquievreux, C., Comparative analysis of karyotypes and nucleolar organizer regions in different populations of Mytilus trossulus, Mytilus edulis and Mytilus galloprovincialis, J. Molluscan Stud., 1994, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 359–370.
Insua, A., Lopez-Pinon, M.J., Freire, R., et al., Karyotype and chromosomal location of 18S-28S and 5S ribosomal DNA in the scallops Pecten maximus and Mimachlamys varia (Bivalvia: Pectinidae), Genetica, 2006, vol. 126, pp. 291–301.
Insua, A. and Méndez, J., Physical mapping and activity of ribosomal RNA genes in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis, Hereditas, 1998, vol. 128, no. 3, pp. 189–194.
Insua, A., Lopez-Pinon, M. J., and Méndez, J., Characterization of Aequipecten opercularis (Bivalvia: Pectinidae) chromosomes by different staining techniques and fluorescent in situ hybridization, Genes Genet. Syst., 1998, vol. 73, pp. 193–200.
Justo, C.C., Murofushi, M., Aida, K., and Hanyu, I., Karyological studies on the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii, Aquaculture, 1991, vol. 97, no. 4, pp. 327–334.
Kartavtsev, Y.P., Sharina, S.N., Chichvarkhin, A.Y., et al., Genetic divergence of mussels (Mollusca, Mytilidae) based on the 28S rRNA, 18S rRNA, and H3 nuclear gene sequences, Russ. J. Genet., 2018, vol. 54, pp. 652–669.
Kenchington, E.L.R., Landry, D., and Bird, C.J., Comparison of taxa of the mussel Mytilus (Bivalvia) by analysis of the nuclear small-subunit rRNA gene sequence, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 1995, vol. 52, no. 12, pp. 2613–2620.
Kocot, K.M., Poustka, A.J., Stöger, I., et al., New data from Monoplacophora and a carefully-curated dataset resolve molluscan relationships, Sci. Rep., 2020, vol. 10, 101.
Levan, A., Fredga, K., and Sandberg, A.A., Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes, Hereditas, 1964, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 201–220.
López-Piñón, M.J., Insua, A., and Méndez, J., Chromosome analysis and mapping of ribosomal genes by one- and two-color fluorescent in situ hybridization in Hinnites distortus (Bivalvia: Pectinidae), J. Hered., 2005, vol. 96, no. 1, pp. 52–58.
Martínez-Lage, A., Mariñas, L., González-Tizón, A., et al., Cytogenetic characterization of Donax trunculus (Bivalvia: Donacidae) by means of karyotyping, fluorochrome banding and fluorescent in situ hybridization, J. Molluscan Stud., 2002, vol. 68, pp. 393–396.
Martínez-Lage, A., González-Tizón, A., Ausió, J., et al., Karyotype and Ag-NORs of the mussels Mytilus californianus and M. trossulus from the Pacific Canadian coast, Aquaculture, 1997, vol. 153, pp. 239–249.
Martínez-Lage, A., González-Tizón, and Méndez, J., Characterization of different chromatin types in Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. after C–banding, fluorochrome and restriction endonuclease treatments, Heredity, 1994, vol. 72, pp. 242–249.
Martínez-Lage, A., González-Tizón, and Méndez, J., Chromosomal markers in three species of the genus Mytilus (Mollusca: Bivalvia), Heredity, 1995, vol. 74, no. 4, pp. 369–375.
Moritz, C., Hills, D.M., and Marble, B., Molecular systematics: Context and controversies, in Molecular Systematics, Sunderland: Sinauer Associates, 1997, pp. 1–13.
Muhammed Zafar Iqbal, A.N., Khan, M.S., and Goswami, U., Cytogenetic studies in green mussel, Perna viridis (Mytiloida: Pteriomorphia), from West Coast of India, Mar. Biol., 2008, vol. 153, no. 5, pp. 987–993.
Pasantes, J.J., Martínez-Expósito, M.J., Martínez-Lage, A., et al., Chromosomes of Galician mussels, J. Molluscan Stud., 1990, vol. 56 pp. 123–126.
Pérez-García, C., Guerra-Varela, J., Morán, P., et al., Chromosomal mapping of rDNAs, core histone genes and telomeric sequences in Perumytilus purpuratus (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2010, vol. 395, nos. 1–2, pp. 199–205.
Pérez-García, C., Guerra-Varela, J., Morán, P., et al., Chromosomal mapping of rRNA genes, core histone genes and telomeric sequences in Brachidontes puniceus and Brachidontes rodriguezi (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), BMC Genet., 2010, vol. 11, 109.
Pérez-García, C., Guerra-Varela, J., Morán, P., et al., Cytogenetic characterization of the invasive mussel species Xenostrobus securis Lmk. (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), Genome, 2011, vol. 54, no. 9, pp. 771–778.
Pérez-García, C., Hurtado, N.S., Morán, P., et al., Evolutionary dynamics of rDNA clusters in chromosomes of five clam species belonging to the family Veneridae (Mollusca, Bivalvia), BioMed Res. Int., 2014, vol. 2014, 754012.
Pochon, X., Bott, N.J., Smith, K.F., et al., Evaluating detection limits of next-generation sequencing for the surveillance and monitoring of international marine pests, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 9, e73935.
Roy, V., Monti-Dedieu, L., Chaminade, N., et al., Evolution of the chromosomal location of rDNA genes in two Drosophila species subgroups: ananassae and melanogaster, Heredity, 2005, vol. 94, no. 4, pp. 388–395.
Sambrook, J.F., and Russel, D.W., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor, 2000.
Siddall, S.E. and Scott, E., A clarification of the genus Perna (Mytilidae), Bull. Mar. Sci., 1980, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 858—870.
Thiriot-Quievreux, C., Chromosome analysis of three species of Mytilus (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), Mar. Biol. Lett., 1984, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 265–273.
Thiriot-Quievreux, C., Advances in cytogenetics of aquatic organisms, in Genetics and Evolution of Aquatic Organisms, Beaumont, A.R., Ed., London: Chapman and Hall, 1994, pp. 369–388.
Thiriot-Quievreux, C., Review of the literature on bivalve cytogenetics in the last ten years, Cah. Biol. Mar., 2002, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 17–26.
Torreiro, A., Martínez-Expósito, M.J., Trucco, M.I., et al., Cytogenetics in Brachidontes rodriguezi d’Orb (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), Chromosome Res., 1999, vol. 7, no. 1, 49.
Vitturi, R., Gianguzza, P., Colomba, M. S., Jensen, K. R., and Riggio, S., Cytogenetics in the sacoglossan Oxynoe olivacea (Mollusca: Opisthobranchia): Karyotype, chromosome banding and fluorescent in situ hybridization, Mar. Biol., 2000, vol. 137, no. 4, pp. 577–582.
Vitturi, R., Gianguzza, P., Colomba, M.S., et al., Cytogenetic characterization of Brachidontes pharaonis (Fisher P., 1870): Karyotype, banding and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Mytilidae), Ophelia, 2000, vol. 52, no. 3, рр. 213–220.
Vonnemann, V., Schrödl, M., Klussmann-Kolb, A., et al., Reconstruction of the phylogeny of the Opisthobranchia (Mollusca: Gastropoda) by means of 18s and 28s rRNA gene sequences, J. Molluscan Stud., 2005, vol. 71, no. 2, pp. 113–125.
Wang, Y. and Guo, X., Chromosomal rearrangement in Pectinidae revealed by rRNA loci and implications for bivalve evolution, Biol. Bull., 2004, vol. 207, no. 3, pp. 247–256.
Wang, Y. and Guo, X., Chromosomal mapping of major ribosomal rRNA genes in the hard clam (Mercenaria mercenaria) using fluorescence in situ hybridization, Mar. Biol., 2007, vol. 150, pp. 1183–1189.
Wang, Y. and Guo, X., Chromosomal mapping of the major ribosomal RNA genes in the Dwarf Surfclam (Mulinia lateralis Say), J. Shellfish Res., 2008, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 307–311.
Wanninger, A. and Wollesen, T., The evolution of molluscs, Biol. Rev. Cambridge Philos. Soc., 2019, vol. 94, no. 1, pp. 102–115.
Wicke, S., Costa, A., Muñoz, J., and Quandt, D., Restless 5S: The re-arrangement(s) and evolution of the nuclear ribosomal DNA in land plants, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 2011, vol. 61, no. 2, pp. 321–332.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Director, CSIR-National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula Goa for providing necessary facilities to carry out the present research work. This is a National Institute of Oceanography’s contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhammed Zafar Iqbal, A.N., Khan, M.S., Navalgund, M.A. et al. Physical Mapping of 18S rRNA Gene in Green Mussel Perna viridis – An Indication of Higher Major rRNA Gene Clusters. Russ J Mar Biol 48, 195–201 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074022030038
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074022030038