Abstract
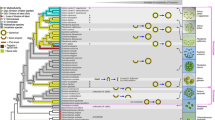
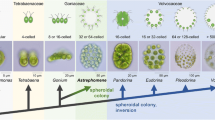
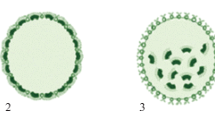
Recent literary data on inversion (turning inside out) in the embryos of flagellated algae of the genus Volvox are critically analyzed. In this process, active changes in the shape of embryonic cells and the displacement of intercellular cytoplasmic bridges play an important role. After inversion, the flagella appear on the outer side of the young colony and provide its motility. Within the genus Volvox, two main modes of embryo inversion have been recently established during the asexual developmental cycle—inversion of type A and inversion of type B—represented by the two species most thoroughly studied, respectively, Volvox carterif. nagariensis and V. globator. However, the published opinion that the inversion of V. aureus embryos is of the type B seems to be doubtful. Comparative and evolutionary aspects of embryonic inversion in Volvox are discussed with the use of data on other genera of colonial volvocine algae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darden, W.H., Sexual differentiation in Volvox aureus, J. Protozool., 1966, vol. 13, pp. 239–255.
Desnitskiy, A.G., Ontogenetic diversity of colonies and intercellular cytoplasmic bridges in the algae of the genus Volvox, Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2014, vol. 45, pp. 231–234.
Desnitskiy, A.G., Major ontogenetic transitions during Volvox (Chlorophyta) evolution: when and where might they have occurred?, Dev. Genes Evol., 2016, vol. 226, pp. 349–354.
Desnitskiy, A.G., Differentiation of reproductive structures and experimental sex change in Volvox (Chlorophyta, Volvocaceae), Int. J. Plant Reprod. Biol., 2017, vol. 9, pp. 63–68.
Dondua, A.K. and Kostyuchenko, R.P., Concerning one obsolete tradition: does gastrulation in sponges exist?, Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2013, vol. 44, pp. 267–272.
Ereskovsky, A.V., The Comparative Embryology of Sponges, Dordrecht (the Netherlands): Springer, 2010.
Ettl, H., Chlorophyta. 1. Phytomonadina, Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer, 1983.
Fortunato, S., Adamski, M., Bergum, B., et al., Genomewide analysis of the sox family in the calcareous sponge Sycon ciliatum: multiple genes with unique expression patterns, EvoDevo, 2012, vol. 3: 14. doi 10.1186/2041-9139-3-14
Fulton, A.B., Colonial development in Pandorina morum. II. Colony morphogenesis and formation of the extracellular matrix, Dev. Biol., 1978, vol. 64, pp. 236–251.
Haas, P.A. and Goldstein, R.E., Elasticity and glocality: initiation of embryonic inversion in Volvox, J. Roy. Soc. Interface, 2015, vol. 12: 20150671. doi 10.1098/rsif.2015.0671
Hallmann, A., Morphogenesis in the family Volvocaceae: different tactics for turning an embryo right-side out, Protist, 2006, vol. 157, pp. 445–461.
Herron, M.D. and Nedelcu, A.M., Volvocine algae: from simple to complex multicellularity, in Evolutionary Transitions to Multicellular Life, Ruiz-Trillo, I. and Nedelcu, A.M., Eds., Dordrecht (the Netherlands): Springer, 2015, pp. 129–152.
Herron, M.D., Desnitskiy, A.G., and Michod, R.E., Evolution of developmental programs in Volvox (Chlorophyta), J. Phycol., 2010, vol. 46, pp. 316–324.
Höhn, S. and Hallmann, A., There is more than one way to turn a spherical cellular monolayer inside out: type B embryo inversion in Volvox globator, BMC Biol., 2011, vol. 9: 89. doi 10.1186/1741-7007-9-89
Höhn, S. and Hallmann, A., Distinct shape-shifting regimes of bowl-shaped cell sheets—embryonic inversion in the multicellular green alga Pleodorina, BMC Dev. Biol., 2016, vol. 16: 35. doi 10.1186/s12861-016-0134-9
Höhn, S., Honerkamp-Smith, A.R., Haas, P.A., et al., Dynamics of a Volvox embryo turning itself inside out, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, vol. 114: 178101. doi 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.178101
Hoops, H.J., Nishii, I., and Kirk, D.L., Cytoplasmic bridges in Volvox and its relatives, in Cell–Cell Channels, Baluska, F., Volkmann, D., and Barlow, P., Eds., Georgetown (Texas): Landes Bioscience, 2006, pp. 65–84.
Iida, H., Nishii, I., and Inouye, I., Embryogenesis and cell positioning in Platydorina caudata (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta), Phycologia, 2011, vol. 50, pp. 530–540.
Iida, H., Ota, S., and Inouye, I., Cleavage, incomplete inversion, and cytoplasmic bridges in Gonium pectorale (Volvocales, Chlorophyta), J. Plant Res., 2013, vol. 126, pp. 699–707.
Ireland, G.W. and Hawkins, S.E., Inversion in Volvox tertius: the effects of conA, J. Cell Sci., 1981, vol. 48, pp. 355–366.
Ivanov, A.V., On the reasons of excurvation of the embryo in the colonial Phytomonadina and calcareous sponges, Monitore Zool. Ital., 1971, vol. 5, pp. 1–10.
Janet, C., Le Volvox. Troisième mémoire. Ontogénèse de la blastéa volvocéenne, Mâcon (France): Protat Frères, 1923.
Kelland, J.L., Inversion in Volvox (Chlorophyceae), J. Phycol., 1977, vol. 13, pp. 373–378.
Keller, R. and Shook, D., The bending of cell sheets—from folding to rolling, BMC Biol., 2011, vol. 9: 90. doi 10.1186/1741-7007-9-90
Kirk, D.L., Volvox: Molecular-Genetic Origins of Multicellularity and Cellular Differentiation, New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1998.
Kirk, D.L. and Nishii, I., Volvox carteri as a model for studying the genetic and cytological control of morphogenesis, Dev. Growth Differ., 2001, vol. 43, pp. 621–631.
Kuschakewitsch, S., Zur Kenntnis der Entwicklungsgeschichte von Volvox, Arch. Protistenkd., 1931, vol. 73, pp. 323–330.
Lanna, E. and Klautau, M., Embryogenesis and larval ultrastructure in Paraleucilla magna (Calcarea, Calcaronea), with remarks on the epilarval trophocyte epithelium (“placental membrane”), Zoomorphology, 2012, vol. 131, pp. 277–292.
Marchant, H.J., Colony formation and inversion in the green alga Eudorina elegans, Protoplasma, 1977, vol. 93, pp. 325–339.
Matt, G. and Umen, J., Volvox: a simple algal model for embryogenesis, morphogenesis and cellular differentiation, Dev. Biol., 2016, vol. 419, pp. 99–113.
McCracken, M.D. and Starr, R.C., Induction and development of reproductive cells in the K-32 strains of Volvox rousseletii, Arch. Protistenkd., 1970, vol. 112, pp. 262–282.
Nishii, I. and Ogihara, S., Actomyosin contraction of the posterior hemisphere is required for inversion of the Volvox embryo, Development, 1999, vol. 126, pp. 2117–2127.
Nishii, I., Ogihara, S., and Kirk, D.L., A kinesin, invA, plays an essential role in Volvox morphogenesis, Cell, 2003, vol. 113, pp. 743–753.
Nozaki, H., Matsuzaki, R., Yamamoto, K., et al., Delineating a new heterothallic species of Volvox (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyceae) using new strains of “Volvox africanus,” PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10 (11): e0142632. doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0142632
Okamura, B. and Gruhl, A., Myxozoa + Polypodium: a common route to endoparasitism, Trends Parasitol., 2016, vol. 32, pp. 268–271.
Pickett-Heaps, J.D., Some ultrastructural features of Volvox, with particular reference to the phenomenon of inversion, Planta, 1970, vol. 90, pp. 174–190.
Pocock, M.A., Volvox and associated algae from Kimberley, Ann. South Afr. Mus., 1933a, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 473–521.
Pocock, M.A., Volvox in South Africa, Ann. South Afr. Mus., 1933b, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 523–646.
Powers, J.H., Further studies in Volvox, with descriptions of three new species, Trans. Amer. Microsc. Soc., 1908, vol. 28, pp. 141–175.
Raikova, E.V., Life cycle, cytology, and morphology of Polypodium hydriforme, a coelenterate parasite of the eggs of acipenseriform fishes, J. Parasitol., 1994, vol. 80, pp. 1–22.
Shelton, D.E., Desnitskiy, A.G., and Michod, R.E., Distribution of reproductive and somatic cell numbers in diverse Volvox (Chlorophyta) species, Evol. Ecol. Res., 2012, vol. 14, pp. 707–721.
Ueki, N. and Nishii, I., Controlled enlargement of the glycoprotein vesicle surrounding a Volvox embryo requires the InvB nucleotide-sugar transporter and is required for normal morphogenesis, Plant Cell, 2009, vol. 21, pp. 1166–1181.
Umen, J.G. and Olson, B.J., Genomics of volvocine algae, Adv. Bot. Res., 2012, vol. 64, pp. 185–243.
Viamontes, G.I. and Kirk, D.L., Cell shape changes and the mechanism of inversion in Volvox, J. Cell Biol., 1977, vol. 75, pp. 719–730.
Yamashita, S., Arakaki, Y., Kawai-Toyooka, H., et al., Alternative evolution of a spheroidal colony in volvocine algae: developmental analysis of embryogenesis in Astrephomene (Volvocales, Chlorophyta), BMC Evol. Biol., 2016, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 243. doi 10.1186/s12862-016-0794-x
Zimmermann, W., Die ungeschlechtliche Entwicklung von Volvox, Naturwissenschaften, 1925, vol. 19, pp. 397–402.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.G. Desnitskiy, 2018, published in Ontogenez, 2018, Vol. 49, No. 3.
The article was translated by the author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desnitskiy, A.G. Comparative Analysis of Embryonic Inversion in Algae of the Genus Volvox (Volvocales, Chlorophyta). Russ J Dev Biol 49, 129–133 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360418030025
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360418030025