Abstract
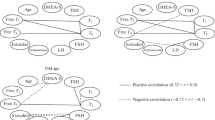
We measured blood concentration of active and non-active sex steroids, metabolites, and precursors and compared to changes in protein and peptide hormones controlling the reproductive axis (total 14 hormones and hormone-like substances) in male subjects aged 18 to 72 y.o. We found a significant decrease in serum concentration of precursors for active sex steroids (pregnenolone, progesterone, dehydroepiandrosterone, and DHEA-sulfate), free testosterone, androstenedione (non-active metabolite of testosterone) as well as 5α-dihydrotestone after the age of 35. However, the level of total testosterone and estradiol (another active testosterone metabolite) remained steady. The systems regulated production of active sex steroids resisted a higher load associated with age and caused the increase in luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones in hypophysis and activin in steroidogenic glands directly correlating with age; negative correlation for these hormones was confirmed with certain sex steroids explaining the negative feedback. Decrease in level of hypopheseal adrenocorticotropic hormone with age demonstrated a more substantial role for adrenal glands compared to that of testicles in reduction of blood concentration of active sex steroids. In general, despite the reduced activity of steroidogenic glands in 60-to 70-year old male subjects the level of testosterone and estradiol remained unchanged due to associated growth of level of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hypopheseal hormones as well as activin in steroidogenic glands that stimulated biosynthesis of sex steroids. Also androgen effects were inhibited due to the reduced level of free (unbound) testosterone and 5α-dihydrotestone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar, M., Kelly, S., and Kaderbhai, M., Cytochrome B5 Modulation of 17 Hydroxylase and 17–20 Lyase (CYP17) Activities in Steroidogenesis, J. Endocrinol., 2005, vol. 187, pp. 267–274.
Auchus, J. and Rainey, W., Adrenarche-Physiology, Biochemistry and Human Disease, Clin. Endocrinol., 2004, vol. 60, pp. 288–296.
Baquedano, M., Saraco, N., Berensztein, E., et al., Identification and Developmental Changes of Aromatase and Estrogen Receptor Expression in Prepubertal and Pubertal Human Adrenal Tissues, J. Clin. Endocrnol. Metab., 2007, vol. 92, pp. 2215–2222.
Belgorosky, A., Baquedano, M., Guercio, G., et al., Adrenarche: Postnatal Adrenal Zonation and Hormonal and Metabolic Regulation, Horm. Res., 2008, vol. 70, pp. 257–267.
Bernard, D., Both SMAD2 and SMED3 Mediate Activin-Stimulated Expression of the Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Beta Subunit in Mouse Gonadotrope Cells, Mol. Endocrinol., 2004, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 606–623.
Blouin, K., Nadeau, M., Mailloux, J., et al., Pathways of Adipose Tissue Androgen Metabolism in Women: Depot Differences and Modulation by Adipogenesis, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2009, vol. 296.
Carreau, S., Bourquiba, S., Lambard, S., et al., The Promoter(s) of Aromatase Gene in Male Testicular Cells, Reprod. Biol., 2004, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 23–34.
Chahal, H. and Drake, W., The Endocrine System and Aging, J. Pathol., 2007, vol. 211, no. 3, pp. 173–180.
Dolomie-Faqour, L., Gatta, B., Nguyen, T., et al., Bioavailable Estradiol in Men: Relationship with Age and Testosterone, Clin. Chim. Acta, 2008, vol. 398, no. 7, pp. 145–147.
Farnworth, P., Stanton, P., Wang, Y., et al., Inhibins Differentially Antagonize Activin and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Action in Mouse Adrenocortical Cell Line, Endocrinology, 2006, vol. 147, pp. 3462–3471.
Gennari, L., Nuti, R., and Bilezikian, J., Aromatase Activity and Bone Homeostasis in Men, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 2004, vol. 89, pp. 5898–6907.
Goncharov, N.P., Katsiya, G.V., and Nizhnik, F.N., Formula zhizni. Degidroepiandrosteron: svoistva, metabolizm, biologicheskoe znachenie (Life Formula. Dehydroepiandrosteron: Properties, Metabolism, and Biological Significance), Moscow: Adamant“, 2004.
Gooren, L., Saad, F., Haide, A., and Yassin, A., Decline of Plasma 5α-Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Levels upon Testosterone Administration to Elderly Men with Subnormal Plasma Testosterone and High DHT Levels, Andrologia, 2008, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 298–302.
Hamden, K., Silandre, D., Delalande, C., et al., Age-Related Decrease in Aromatase and Estrogen Receptor (ER and ER) Expression in Rat Testis: Prospective Effect of Low Caloric Diets, Asian J. Androl., 2008, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 177–187.
Hammer, F., Drescher, D., Schneider, S., et al., Sex Steroid Metabolism in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Changes with Aging, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 2005, vol. 90, pp. 6283–6289.
Hayashi, T. and Yamada, T., Association of Bioavailable Estradiol Levels and Testosterone Levels with Serum Albumin Levels in Elderly Men, Aging Male, 2008, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 63–70.
Hirai, S., Yamanaka, M., Kawachi, H., et al., Activin A Inhibits Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte, Mol. Cell Endocrinol., 2005, vol. 232, pp. 21–26.
Kogame, M., Matsuo, S., Nakatani, M., et al., ALK7 is a Novel Marker for Adipocyte Differentiation, J. Med. Invest., 2006, vol. 53, pp. 238–245.
Lunenfeld, B., Endocrinology of Aging Male, Minerva Ginecol., 2006, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 153–170.
Luo, L., Chen, H., and Zirkin, B., Temporal Relationships among Testosterone Production, Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR), and P450 Side-Chain Cleavage Enzyme (P450scc) during Leidig Cell Aging, J. Androl., 2005, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 25–31.
Miwa, Y., Kaneda, T., and Yokoyama, O., Correlation between the Aging Males Symptoms Scale and Sex Steroids, Gonadotropins, Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate and Growth Hormone Levels in Ambulatory Men, J. Sex. Med., 2006, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 723–726.
Mukasa, C., Nomura, M., Tanaka, T., et al., Activin Signalling through Type IB Activin Receptor Stimulates Aromatase Activity in the Ovarian Granulose Cell-Like Human Granulose (KGN) Cells, Endocrinology, 2003, vol. 144, pp. 1603–1611.
Payne, A. and Hales, D., Overview of Steroidogenic Enzymes in the Pathway from Cholesterol to Active Steroid Hormones, Endocrine Rev., 2004, vol. 25, pp. 947–970.
Simpson, E. and Davis, S., Aromatase and the Regulation of Estrogen Biosynthesis-Some New Perspectives, Endocrinology, 2001, vol. 142, pp. 4589–4594.
Suzuki, J., Otsuka, F., Inagi, K., et al., Novel Action of Activin and Bone Morphogenetic Protein in Regulating Aldosterone Production by Human Adrenocortical Cells, J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. Chromatogr. Commun., 2004, vol. 145, pp. 639–649.
Vanttinen, T., Liu, J., Kuulasmaa, T., et al., Expression of Activin/Inhibin Signaling Components in the Human Adrenal Gland and the Effects of Activins and Inhibins on Adrenocortical Steroidogenesis and Apoptosis, J. Endocrinol., 2003, vol. 178, no. 3, pp. 479–489.
Vermeulen, A., Kaufman, J., Goemaere, S., et al., Estradiol in Elderly Men, Aging Male, 2002, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 98–102.
Wu, F., Tajar, A., Pye, S., et al., Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis Disruptions in Older Men are Differentially Linked to Age and Modifiable Risk Factors: The European Male Aging Study, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 2008, vol. 93, pp. 2737–2745.
Yavus, B., Ozakayar, N., Halil, M., et al., Free Testosterone Levels and Implications on Clinical Outcomes in Elderly Men, Aging Clin. Exp. Res., 2008, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 201–206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.V. Petrov, I.N. Kuzina, V.V. Kilikovsky, O.V. Smirnova, 2009, published in Ontogenez, 2009, Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 456–465.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrov, R.V., Kuzina, I.N., Kilikovsky, V.V. et al. Age-dependent changes in the concentration of active sex steroids, precursors, metabolites, and regulatory agents in blood serum of male subjects. Russ J Dev Biol 40, 373–381 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360409060071
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360409060071