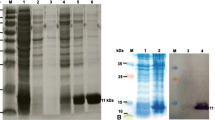
Abstract
Sweet tasting and taste modifying proteins are the natural alternative to flavor enhancers and artificial sweeteners. Curculin is a unique protein, which has both sweet tasting and taste modifying properties. In this study, pinII Ti plasmid vector was constructed with curculin gene, where the gene encoding curculin protein was placed under the control of the duel cauliflower mosaic virus 35S (2× CaMV 35S) promoter into rice (Oryza sativa L. var. Japonica cv. Dongjinbyeo) by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation to generate transgenic plants. Here, twenty-six plant lines were regenerated and the transgenic rice plant lines were confirmed by different molecular analysis. The genomic PCR result revealed that all of the plant lines were transgenic. The single copied and intergenic plant lines were selected by Taqman PCR analysis and FST analysis, respectively. Expression of curculin gene in transgenic rice resulted in the accumulation of curculin protein in the leave. The transgenic lines obtained in next generation, where curculin protein was also accumulated in the plant leave. Sensory analysis result suggested that the curculin protein expressing transgenic lines exerted both sweet and taste modifying activities. These results demonstrated that curculin was expressed in transgenic rice plants.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akter, S., Huq, M.A., Jung, Y.J., Cho, Y.G., and Kang, K.K., Application of sweet and taste modifying genes for development in plants: current status and prospects, J. Plant Biotechnol., 2016, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 397–404.
Assadi-Porter, F.M., Aceti, D., and Markley, J.L., Sweetness determinant sites of brazzein, a small, heat-stable, sweet-tasting protein, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2000, vol. 376, no. 2, pp. 259–265.
Bernard, F.G., Alli, I., and Mulligan, C., Sweet and taste-modifying proteins: a review, Nutr. Res., 1996, vol. 16, no. 9, pp. 1619–1630.
Bradford, M.M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, nos. 1–2, pp. 248–254.
Colinas, J., Schmidler, S.C., Bohrer, G., Iordanov, B., and Benfey, P.N., Intergenic and genic sequence lengths have opposite relationships with respect to gene expression, PLoS One, 2008, vol. 3, no. 11. e3670.
Daniell, H., Streatfield, S.J., and Wycoff, K., Medical molecular farming: production of antibodies, biopharmaceuticals and edible vaccines in plants, Trends Plant Sci., 2001, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 219–226.
Faus, I., Recent developments in the characterization and biotechnological production of sweet-tasting proteins, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2000, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 145–151.
Hood, E.E. and Jilka, J.M., Plant-based production of xenogenic proteins, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 1999, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 382–386.
Hood, E.E., Woodard, S.L., and Horn, M.E., Monoclonal antibody manufacturing on transgenic plants—myths and realities, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2002, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 630–635.
Horn, M.E., Woodard, S.L., and Howard, J.A., Plant molecular farming: systems and products, Plant Cell Rep., 2004, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 711–720.
Howard, J.A. and Hood, E., Bioindustrial and biopharmaceutical products produced in plants, Adv. Agro., 2005, vol. 85, pp. 91–124.
Kant, R., Sweet proteins, potential replacement for artificial low calorie sweeteners, Nutr. J., 2005, vol. 4, p. 5.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 1970, vol. 227, pp. 680–685.
Lamphear, B.J., Barker, D.K., Brooks, C.A., Delaney, D.E., Lane, J.R., Beifuss, K., Love, R., Thompson, K., Mayor, J., Clough, R., Harkey, R., Poage, M., Drees, C., Horn, M.E., Streatfield, S.J., Nikolov, Z., Woodard, S.L., Hood, E.E., Jilka, J.M., and Howard, J.A., Expression of the sweet protein brazzein in maize for production of a new commercial sweetener, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2005, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 103–114.
Ming, D. and Hellekant, G., Brazzein, a new high-potency thermostable sweet protein from Pentadiplandra brazzeana B., FEBS Lett., 1994, vol. 355, no. 1, pp. 106–108.
Price, J.M., Biava, C.G., Oser, B.L., Vogin, E.E., Steinfield, J., and Ley, H.L., Bladder tumors in rats fed cyclohexylamine or high doses of a mixture of cyclamate and saccharin, Science, 1970, vol. 167, no. 3921, pp. 1131–1132.
Streatfield, S.J., Approaches to achieve high-level heterologous protein production in plants, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2007, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 2–15.
Streatfield, S.J. and Howard, J.A., Plant-based vaccines, Int. J. Parasitol., 2003, vol. 33, no. 5–6, pp. 479–493.
Sun, H.J., Cui, M.L., Ma, B., and Ezura, H., Functional expression of the taste-modifying protein, miraculin, in transgenic lettuce, FEBS Lett., 2006, vol. 580, no. 2, pp. 620–626.
Sun, H.J., Kataoka, H., Yano, M., and Ezura, H., Genetically stable expression of functional miraculin, a new type of alternative sweetener, in transgenic tomato plants, Plant Biotechnol. J., 2007, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 768–777.
Suzuki, M., Kurimoto, E., Nirasawa, S., Masuda, Y., Hori, K., Kurihara, Y., Shimba, N., Kawai, M., Suzuki, E., and Kato, K., Recombinant curculin heterodimer exhibits taste-modifying and sweet-tasting activities, FEBS Lett., 2004, vol. 573, nos. 1–3, pp. 135–138.
Thole, V., Alves, S.C., Worland, B., Bevan, M.W., and Vain, P., A protocol for efficiently retrieving and characterizing flanking sequence tags (FSTs) in Brachypodium distachyon T-DNA insertional mutants, Nat. Protoc., 2009, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 650–661.
Wang, X., Jiang, D., and Yang, D., Fast-tracking determination of homozygous transgenic lines and transgene stacking using a reliable quantitative real-time PCR assay, Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 2015, vol. 175, no. 2, pp. 996–1006.
Witty, M. and Higginbotham, J.D., Thaumatin, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1994.
Yamashita, H., Akabane, T., and Kurihara, Y., Activity and stability of a new sweet protein with taste-modifying action, curculin, Chem. Senses, 1995, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 239–243.
Yamashita, H., Theeraship, A., Nakaya, T., Nakamura, Y., and Kurihara, Y., Purification and complete amino acid sequence of a new type of sweet protein with taste-modifying activity, curculin, J. Biol. Chem., 1990, vol. 265, no. 26, pp. 15770–15775.
Yoshida, K. and Shinmyo, A., Transgenic expression systems in plants, a natural bioreactor, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2000, vol. 90, no. 4, pp. 353–362.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (project no. PJ01368902), Rural Development Administration, and by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2017R1C1B5017833), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Shahina Akter and Md. Amdadul Huq contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahina Akter, Huq, M.A., Jung, YJ. et al. Expression of Curculin, a New Type of Alternative Sweetener in Transgenic Rice. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 47, 7–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359020010112
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359020010112