Abstract
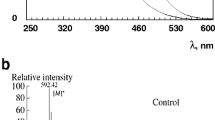
Fluorescence and chromatographic analysis of bisretinoids from the retina and retinal pigment epithelium of mouse eyes was carried out before and after exposure to accelerated protons in the Bragg peak. It has been shown that ionizing radiation at doses of 1–4 Gy leads to a shift in the short-wave region of the maximum of the fluorescence spectrum in the chloroform extract obtained from both the retinal pigment epithelium and the retina. Chromatographic analysis of these extracts has shown a change in the relative content of individual bisretinoids. The obtained spectral and chromatographic data indicate that the exposure of mice to accelerated protons in the Bragg peak at doses of 1–4 Gy leads to radiation oxidation of bisretinoids in eye tissues.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Grigorev, A.I., Krasavin, E.A., and Ostrovsky, M.A., Galactic heavy charged particles damaging effect on biological structures, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2013, vol. 99, no. 3, pp. 273–280.
Tommasino, F. and Durante, M., Proton radiobiology, Proton Radiobiol. Cancers, 2015, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 353–381.
Liu, C.Y., Francis, J.H., Brodie, S.E., et al., Retinal toxicities of cancer therapy drugs, Retina, 2014, vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 1261–1280.
Worgul, B.V., Accelerated heavy particles and the lens, Ophthal. Res., 1988, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 143–148.
Jung, T., Bader, N., and Grune, T., Lipofuscin: formation, distribution, and metabolic consequences, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2007, vol. 1119, pp. 97–111.
Geng, L., Wihlmark, U., and Algvere, P.V., Lipofuscin accumulation in iris pigment epithelial cells exposed to photoreceptor outer segments, Exp. Eye Res., 1999, vol. 69, pp. 539–546.
Sparrow, J.R. and Boulton, M.E., RPE lipofuscin and its role in retinal photobiology, Exp. Eye Res., 2005, vol. 80, pp. 595–606.
Holz, F.G., Pauleikhoff, D., Klein, R., and Bird, A.C., Pathogenesis of lesions in late age-related macular disease, Am. J. Ophthalmol., 2004, vol. 137, pp. 504–510.
Ostrovsky, M.A., Dontsov, A.E., Sakina, N.L., Boulton, M., and Jarvis-Evans, J., The ability of lipofuscin granules from lipids under exposure to visible light, Sensor. Sistemy, 1992, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 51–54.
Boulton, M., Dontsov, A., Jarvis-Evans, J., Ostrovsky, M., and Svistunenko, D., Lipofuscin is a photoinducible free radical generator, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 1993, vol. 19, pp. 201–204.
Von Ruckmann, A., Fitzke, F.W., and Bird, A.C., In vivo fundus autofluorescence in macular dystrophies, Arch. Ophthalmol., 1997, vol. 115, pp. 609–615.
Feldman, T.B., Yakovleva, M.A., Arbukhanova, P.M., et al., Changes in spectral properties and composition of lipofuscin fluorophores from human-retinal-pigment epithelium with age and pathology, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2015, vol. 407, no. 4, pp. 1075–1088.
Wu, Y., Fishkin, N.E., Pande, A., et al., Novel lipofuscin bis-retinoids prominent in human retina and in a model of recessive Stargardt disease, J. Biol. Chem., 2009, vol. 284, pp. 20155–20166.
Sparrow, J.R., Zhou, J., and Cai, B., DNA is a target of the photodynamic effects elicited in A2E-laden RPE by blue-light illumination, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci., 2003, vol. 44, pp. 2245–2251.
Feldman, T.B., Yakovleva, M.A., Larichev, A.V., et al., Spectral analysis of fundus autofluorescence pattern as a tool to detect early stages of degeneration in the retina and retinal pigment epithelium, Eye, 2018, vol. 32, no. 9, pp. 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-018-0109-0
Chien, T., Tseng, T.L., Wang, J.Y., et al., Candida albicans DBF4 gene inducibly duplicated by the mini-Ura-blaster is involved in hypha-suppression, Mutat. Res., 2015, vol. 779, pp. 78–85.
Saha, A.K., Kappes, F., Mundade, A., et al., Intercellular trafficking of the nuclear oncoprotein DEK, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, vol. 110, no. 17, pp. 6847–6852.
Kobashigawa, S., Suzuki, K., and Yamashita, S., Ionizing radiation accelerates Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission, which involves delayed mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production in normal human fibroblast-like cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2011, vol. 414, no. 4, pp. 795–800.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Stanley, G.H.S., A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues, J. Biol. Chem., 1957, vol. 226, pp. 497–509.
Parish, C.A., Hashimoto, M., Nakanishi, K., et al., Isolation and one-step preparation of A2E and iso-A2E, fluorophores from human retinal pigment epithelium, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1998, vol. 95, no. 25, pp. 14609–14613.
Feldman, T.B., Yakovleva, M.A., Dontsov, A.E., and Ostrovsky, M.A., Fluorescence and excitation spectra of fluorophores of lipofuscin granules obtained from the retinal pigment epithelium of human cadaver eye, Izv. Akad. Nauk. Ser. Khim., 2010, no. 1, pp. 269–276.
Kim, S.R., Jang, Y.P., Jockusch, S., et al., The all-trans-retinal dimer series of lipofuscin pigments in retinal pigment epithelial cells in a recessive Stargardt disease model, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2007, vol. 104, pp. 19273–19278.
Sparrow, J.R., Wu, Y., Nagasaki, T., et al., Fundus autofluorescence and the bis-retinoids of retina, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2010, vol. 9, pp. 1480–1489.
Radu, R.A., Mata, N.L., Bagla, A., and Travis, G.H., Light exposure stimulates formation of A2E oxiranes in a mouse model of Stargardt’s macular degeneration, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, vol. 101, no. 16, pp. 5928–5933.
Sparrow, J.R., Wu, Y., Kim, C.Y., and Zhou, J., Phospholipid meets all-trans-retinal: the making of RPE bis-retinoids, Lipid Res., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 247–261.
Feldman, T.B., Ostrovsky, M.A., Yakovleva, M.A., et al., A method for the early detection of age-related macular retinal dystrophy, RF Patent No. 2651126, 2018.
Larichev, A.V., Panchenko, V.Ya., Ostrovsky, M.A., and Feldman, T.B., An optical device for studying the fundus to identify age-related macular degeneration of the retina: a utility model, RF Patent No. 176795, 2018.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 17-29-01028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Translated by E. Makeeva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakovleva, M.A., Lyakhova, K.N., Utina, D.M. et al. Changes in the Composition and Fluorescent Properties of Bisretinoids in the Retina and the Retinal Pigment Epithelium of the Mouse Eye under Exposure to Ionizing Radiation. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 46, 1641–1645 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359019120094
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359019120094