Abstract
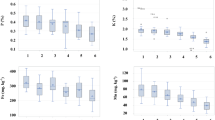
Plant and soil mechanisms of barley plant resistance to Cd toxicity as influenced by the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium P. fluorescens 21 were studied in a series of pot experiments on artificially Cd-contaminated gray forest soil. It has been established that the application of the bacterium improved the growth of plants and eliminated the toxicity of the heavy metal due to enhancing barrier functions of the plant root system and barrier functions of the soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Clemens, S., Molecular mechanisms of plant metal tolerance and homeostasis, Planta, 2001, vol. 212, no. 4, pp. 475–486.
Contamination of soils with heavy metals, in Neitralizatsiya zagryaznennykh pochv (Neutralization of Contaminated Soils), Mazhaiskii, Yu.A., Ed., Ryazan: Meshcherskii Fil. GNU VNIIGiM Rossel’khozakademii, 2008.
Kaznina, N.M. and Titov, A.F., Effect of cadmium on physiological processes and productivity of plants of the family Poaceae, Usp. Sovrem. Biol., 2013, vol. 133, no. 6, pp. 588–603.
Khan, M.S., Zaidi, A., Wani, P.A., and Oves, M., Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the remediation of metal contaminated soils, Environ. Chem. Lett., 2009, vol. 7, pp. 1–19.
Lebeau, T., Braud, A., and Jézéquel, K., Performance of bioaugmentation-assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review, Environ. Pollut., 2008, vol. 153, no. 3, pp. 497–522.
Loper, J.E. and Buyer, J.S., Siderophores in microbial interactions on plant surfaces, Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact., 1991, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 5–13.
Mal’tseva, A.N. and Shabaev, V.P., The effectiveness of growth-stimulating rhizosphere bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas in barley grown under conditions of lead contamination of gray forest soil, Agrokhimiya, 2010, no. 8, pp. 58–65.
Nazarov, A.V. and Ilarionov, S.A., The potential of using microbe–plant interaction for bioremediation, Biotekhnologiya, 2005, no. 5, pp. 54–62.
Shabaev, V.P., Microbiological nitrogen fixation and plant growth after introduction of rhizosphere microorganisms and mineral fertilizers, in Pochvennye protsessy i prostranstvenno-vremennaya organizatsiya pochv (Soil Processes and Spatiotemporal Organization of Soils), Moscow: Nauka, 2006, pp. 195–211.
Shabaev, V.P., Soil-agrochemical aspects of remediation of a gray forest soil polluted with Pb upon the application of growth-promoting rhizobacteria, Eurasian Soil Sci., 2012, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 539–550.
Smirnov, V.V. and Kiprianova, E.A., Bakterii roda Pseudomonas (Bacteria of the Genus Pseudomonas), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1990.
Sokolova, M.G., Belogolova, G.A., Gordeeva, O.N., and Akimova, G.P., Influence of rhizosphere bacteria on plant growth and accumulation of heavy metals in technogenically contaminated soils, Agrokhimiya, 2014, no. 2, pp. 73–80.
Sokolova, M.G., Belogolova, G.A., Akimova, G.P., and Vaishlya, O.B., Effect of inoculation with rhizosphere bacteria on plant growth and translocation of trace elements from contaminated soils, Agrokhimiya, 2016, no. 7, pp. 72–80.
Teoriya i praktika khimicheskogo analiza pochv (Theory and Practice of Chemical Analysis of Soils), Vorob’eva, L.A., Ed., Moscow: GEOS, 2006, pp. 295–296.
Titov, A.F., Talanova, V.V., Kaznina, N.M., and Laidinen, G.F., Ustoichivost’ rastenii k tyazhelym metallam (The Resistance of Plants to Heavy Metals), Petrozavodsk: Karel. Nauchn. Tsentr Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2007.
Vodyanitskii, Yu.N., Contamination of soils with heavy metals and metalloids and its ecological hazard (analytic review), Eurasian Soil Sci., 2013, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 793–801.
Zawadzka, A.M., Paszczynski, A.J., and Crawford, R.L., Transformations of toxic metals and metalloids by Pseudomonas stutzeri strain KC and its siderophore pyridine-2,6-bis (thiocarboxylic acid), in Advances in Applied Bioremediation (Soil Biology 17), Singh, A., Kuhad, R.C., and Ward, O.P., Eds., Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2009, pp. 221–238.
Funding
This study was conducted using the materials of research on the theme of state tasks nos. AAAA-A18-118013190180-9, AAAA-A17-117030110139-9 and AAAA-A18-118013190181-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by L. Solovyova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabayev, V.P., Bocharnikova, E.A. & Ostroumov, V.E. Plant and Soil Mechanisms of Plant Resistance to Cd Toxicity under Application of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacterium in Soil Contaminated with Heavy Metal. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 46, 381–386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359019040113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359019040113