Abstract
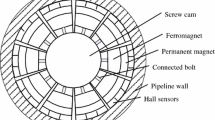
The magnetic flux leakage (MFL) method has established itself as the most widely used inline inspection technique for the evaluation of pipelines. The MFL signal is usually contaminated by various noise sources This paper presents the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) for enhancing signal-to-noise ratio. Experiments are conducted on the pipeline steel samples with different depth artificial defects. The MFL signal is decomposed into several intrinsic mode functions by EMD. Some modes are selected to reconstruct a new signal considering their frequencies and energy. The reconstructed signal has a better signal-to-noise ration. The results show that EMD technology is efficient in eliminating noise in the MFL signal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Udpa, L., Mandayam, S., and Udpal, S.S., Developments in Gas Pipeline Inspection Technology, Materials Evaluation, 1996, vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 467–472.
Jin Tao, Que Peiwen, Chen Liang, et al., Research on a Recognition Algorithm of Offshore-Pipeline Defect during Magnetic-Flux Inspection, Russian Journal of Nondestructive Testing, 2005, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 34–43.
Huang Zuoying, Que Peiwen, and Chen Liang, 3D FEM Analysis in Magnetic Flux Leakage Method, NDT&E International, 2006, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 61–66.
Afzal, M. and Udpa, S., Advanced Signal Processing of Magnetic Flux Leakage Data Obtained from Seamless Gas Pipeline, NDT & E International, 2002, vol. 35, no. 7, pp. 449–457.
Afzal, M., Polikar, R., Udpa, L., and Udpa, S., Adaptive Noise Cancellation Schemes for Magnetic Flux Leakage Signals Obtained from Gas Pipeline Inspection, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing — Proceedings, 2001, no. 6, pp. 3389–3392.
Liang Wei, Que Peiwen, Zhang Qi, et al., Ultrasonic Defect Detection of a Petroleum Pipeline in a Viscoelastic Medium, Russian Journal of Nondestructive Testing, 2006, vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 692–699.
Chen Tianlu, Que Peiwen, Zhang Qi, et al., Ultrasonic Nondestructive Testing Accurate Sizing and Locating Technique Based on Time-of-flight-diffraction Method, Russian Journal of Nondestructive Testing, 2005, vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 594–601.
Zhang Qi, Que Pei-Wen, Liu Qing-Kun et al., Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition to Ultrasonic Signal, Proceedings—IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, 2005, vol. 3, pp. 1789–1792.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Published in Russian in Defektoskopiya, 2008, Vol. 44, No. 12, pp. 72–79.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Li, X., Qin, G. et al. Signal processing of magnetic flux leakage surface flaw inspect in pipeline steel. Russ J Nondestruct Test 44, 859–867 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061830908120097
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061830908120097