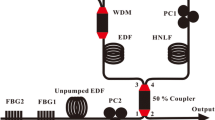
Abstract
An L-band tunable multiwavelength source is newly proposed and demonstrated employing an unpumped polarization maintaining an erbium-ytterbium codoped double-clad fiber (PM-EYDF) loop mirror in a semiconductor optical amplifier-based fiber-ring laser. This is achieved by only adjusting the polarization controller in the loop mirror for the birefringence of the PM-EYDF, which is polarization dependent, and which originates from the fact that the traversing signal with a different polarization state absorbed by the PM-EYDF changes its effective birefringence. A similar behavior also happens when the traversing signal power is varied. The multiwavelength operation with the tunable range as large as the comb spacing of the transmission spectrum of the PM-EYDF loop mirror is successfully accomplished.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. X. Zhang, Z. Q. Ye, M. H. Sang, and Y. Y. Nie, “Passively Mode-Locked Fiber Laser Based on Symmetrical Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror,” Laser Phys. Lett. 5, 364 (2008).
Z. X. Zhang, K. Xu, J. Wu, et al., “Multiwavelength Figure-of-Eight Fiber Laser With a Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror,” Laser Phys. Lett. 5, 213 (2008).
G. A. Pavlath and H. J. Shaw, “Birefringence and Polarization Effects in Fiber Gyroscopes,” Appl. Opt. 21, 1752 (1982).
D.-M. Liang, X.-F. Xu, Y. Li, et al., “Multiwavelength Fiber Laser Based on a High Birefringence Fiber Loop Mirror,” Laser Phys. Lett. 4, 57 (2007).
S. W. Harun, F. A. Rahman, K. Dimyati and H. Ahmad, “An Efficient Multiwavelength Light Source Based on ASE Slicing,” Laser Phys. Lett. 3, 495 (2006).
D. S. Moon, B. H. Kim, A. Lin, et al., “Tunable Multi-Wavelength SOA Fiber Laser Based on a Sagnac Loop Mirror Using an Elliptical Core Side-Hole Fiber,” Opt. Express 15, 8371 (2007).
L. R. Chen, “Tunable Multiwavelength Fiber Ring Lasers Using a Programmable High-Birefringence Fiber Loop Mirror,” IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16, 410 (2004).
M. P. Fok, K. Lee, and C. Shu, “Waveband-Switchable SOA Ring Laser Constructed with a Phase Modulator Loop Mirror Filter,” IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 17, 1393 (2005).
K. L. Lee, M. P. Fok, S. M. Wan, and C. Shu, “Optically Controlled Sagnac Loop Comb Filter,” Opt. Express 12, 6335 (2004).
G. Das and J. W. Y. Lit, “L-Band Multiwavelength Fiber Laser Using an Elliptical Fiber,” IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 14, 606 (2002).
D. Liu, N. Q. Ngo, X. Y. Dong, et al., “A Tunable Multiwavelength Fiber Laser Source with an Elliptical Core Fiber Sagnac Loop Filter,” SPIE Passive Components and Fiber-Based Devices, 910 (2005).
X. Fan, Z. He, and K. Hotate, “Novel Strain-and Temperature-Sensing Mechanism Based on Dynamic Grating in Polarization-Maintaining Erbium-Doped Fiber,” Opt. Express 14, 556 (2006).
J. L. Wagener, D. G. Falquier, M. J. F. Digonnet, and H. J. Shaw, “A Mueller Matrix Formalism for Modeling Polarization Effects in Erbium-Doped Fiber,” J. Light-wave Technol. 16, 200 (1998).
G.-S. Kim, Y.-G. Han, R. M. Sova, et al., “Optical Fiber Modal Birefringence Measurement Based on Lyot-Sagnac Interferometer,” IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 15, 269 (2003).
Y. Liu, B. Liu, X. Feng, et al., “High-Birefringence Fiber Loop Mirrors and Their Applications as Sensors,” Appl. Opt. 44, 2382 (2005).
Z.-Y. Liu, Y.-G. Liu, J.-B. Du, et al., “Channel-Spacing and Wavelength Switchable Multiwavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser Using Sampled Hi-Bi Fiber Grating and Photonic Crystal Fiber Loop Mirror,” Laser Phys. Lett. 5, 122 (2008).
X. M. Liu, X. Q. Zhou, X. F. Tang, et al., “Switchable and Tunable Multiwavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser with Fiber Bragg Gratings and Photonic Crystal Fiber,” IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 17, 1626 (2005); X. Liu, X. Yang, F. Lu, et al., “Stable and Uniform Dual-Wavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser Based on Fiber Bragg Gratings and Photonic Crystal Fiber,” Opt. Express 13, 142 (2005).
F. Heismann and M. S. Whalen, “Broadband Reset-Free Automatic Polarization Controller,” Electron. Lett. 27, 377 (1991).
J. Hashimoto, K. Koyama, T. Katsuyama, et al., “1.3 μm Traveling-Wave GaInNAs Semiconductor Optical Amplifier,” Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, 3419 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Text © Astro, Ltd., 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, G., Chung, Y. & Moon, D.S. L-band tunable multiwavelength fiber laser using an unpumped polarization maintaining an erbium-ytterbium double-clad fiber-loop mirror. Laser Phys. 18, 1196–1199 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X08100150
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X08100150