Abstract
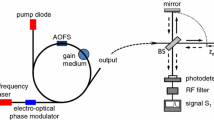
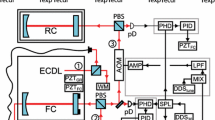
We report on an improved scheme of quasi-common-path microchip laser feedback interferometry, which demonstrates a high stability and accuracy. An additional beam splitter is used to divide the external cavity into a measuring feedback cavity and a reference feedback cavity. With this scheme, the optical path lengths of the measuring and reference feedback light can be made nearly the same, thus greatly reducing the long-period phase fluctuation caused by the laser frequency drift. The final system performances are evaluated as followed: the short-term displacement resolution is better than 2 nm, the output fluctuation is less than 10 nm within a 40-min-long stability test, and the maximum error within the 100-μm range is 25 nm when calibrated with the Agilent 5529A dual-frequency laser interferometer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guofan Jin and Jinzhen Li, Laser Surveying (Science Publishing House, Beijing, 1998).
W. M. Wang, K. T. V. Gratten, A. W. Palmer, and W. J. O. Boyle, “Self-Mixing Interference Inside a Single-Mode Diode Laser for Optical Sensing Applications,” IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 12, 1577–1587 (1995).
T. Bosch and N. Servagent, “Optical Feedback Interferometry for Sensing Application,” Opt. Eng. 40, 20–27 (2001).
A. Bearden, M. P. Neil, and L. C. Osborne, “Imaging and Vibrational Analysis with Laser-Feedback Interferometry,” Opt. Lett. 18, 238–240 (1993).
Ben Ovryn and J. H. Andrews, “Phase-Shifted Laser Feedback Interferometry,” Opt. Lett. 23, 1078–1080 (1998).
Dongmei Guo, Min Wan, and Suqing Tan, “Self-Mixing Interferometer Based on Sinusoidal Phase Modulating Tachnique,” Opt. Express 13, 1537–1543 (2005).
E. Lacot, R. Day, and F. Stoeckel, “Laser Optical Feedback Tomography,” Opt. Lett. 24, 744–746 (1999).
E. Lacot, R. Day, J. Pinel, and F. Stoeckel, “Laser Relaxation-Oscillation Frequency Imaging,” Opt. Lett. 26, 1483–1485 (2001).
R. Kawai, Y. Asakawa, and K. Otsuka, “Ultrahigh-Sensitivity Self-Mixing Laser Doppler Velocimetry with Laser-Diode-Pumped Microchip LiNdP04 Lasers,” IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 11, 706–708 (1999).
K. Otsuka, K. Abe, J.-Y. Ko, and T-S Lim, “Real-Time Nanometer Vibration Measurement with a Self-Mixing Microchip Solid-State Laser,” Opt. Lett. 27, 1339–1341 (2002).
E. Lacot and O. Hugon, “Phase-Sensitive Laser Detection by Frequency-Shifted Optical Feedback,” Phys. Rev. A 70, 053824-1–053824-8 (2004).
C. Yin, L. Huang, M. Gong, et al., “A Novel Compact Side-Pumped Bonded Slab Microchip Laser,” Laser Phys. Lett. 4, 584–587 (2007).
Y. Wang, L. Huang, M. Cong, et al., “1 MHz Repetition Rate Single-Frequency Gain-Switched Nd:YAG Microchip Laser,” Laser Phys. Lett. 4, 580–583 (2007).
J. Scaronulc, H. Jelinkova, K. Nejezchleb, and V. Scaronkoda, “Nd:YAG/V:YAG Microchip Laser Operating at 1338 nm,” Laser Phys. Lett. 2, 519–524 (2005).
H. Lei, M. Gong, Y. Ping, and L. Qiang, “Repetition Rate Continuously Controllable Passively Q-Switched Nd:YAG Bonded Microchip Laser,” Laser Phys. Lett. 4, 572–575(2007).
Xinjun Wan, Duo Li, and Shulian Zhang, “Quasi-Common-Path Laser Feedback Interferometry Based on Frequency Shifting and Multiplexing”, Opt. Lett. 32, 367–369 (2007).
M. Sargent III, M. O. Scully, and W. E. Lamb, Jr., Laser Physics (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1974).
J. J. Zayhowski, “Microchip Lasers,” Opt. Mater. 11, 255–267 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Text © Astro, Ltd., 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Z., Li, D., Wan, X. et al. Quasi-common-path microchip laser feedback interferometry with a high stability and accuracy. Laser Phys. 18, 939–946 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X08080021
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054660X08080021